Plasticity, Hippocampal Place Cells, and Cognitive Maps
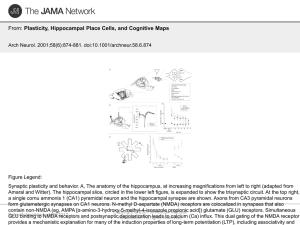
... Synaptic plasticity and behavior. A, The anatomy of the hippocampus, at increasing magnifications from left to right (adapted from Amaral and Witter). The hippocampal slice, circled in the lower left figure, is expanded to show the trisynaptic circuit. At the top right, a single cornu ammonis 1 (CA1 ...
... Synaptic plasticity and behavior. A, The anatomy of the hippocampus, at increasing magnifications from left to right (adapted from Amaral and Witter). The hippocampal slice, circled in the lower left figure, is expanded to show the trisynaptic circuit. At the top right, a single cornu ammonis 1 (CA1 ...
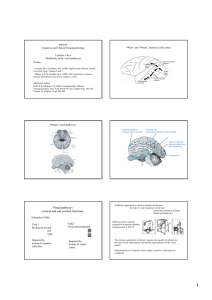
Visual pathways cortical and sub
... Specialised cells and brain areas for recognition of specific category of objects (as reviewed in Lectures 1&2) e.g. face cells in the ventral stream ...
... Specialised cells and brain areas for recognition of specific category of objects (as reviewed in Lectures 1&2) e.g. face cells in the ventral stream ...
What and Where Pathways
... Figure 4.8 (a) Response of a complex cell recorded from the visual cortex of a cat. The stimulus bar is moved back and forth across the receptive field. The cell fires best when the bar is positioned with a specific orientation and is moved in a specific direction (*). (From Hubel and Wiesel, 1959. ...
... Figure 4.8 (a) Response of a complex cell recorded from the visual cortex of a cat. The stimulus bar is moved back and forth across the receptive field. The cell fires best when the bar is positioned with a specific orientation and is moved in a specific direction (*). (From Hubel and Wiesel, 1959. ...
neurobiological-basis-of-behavior
... ependymal cells, radial glial, satellite cells and schwann cells. It is estimated that there are 10 to 50 times more glial cells than there are neurons in the brain. Nerves – bundles of axons - Often located in the peripheral nervous system - Transmit information to various parts of the body Types ...
... ependymal cells, radial glial, satellite cells and schwann cells. It is estimated that there are 10 to 50 times more glial cells than there are neurons in the brain. Nerves – bundles of axons - Often located in the peripheral nervous system - Transmit information to various parts of the body Types ...
The virtue of simplicity
... the visual system9,10. The model was individually adjusted for each cell—necessary for explaining neuronal variability—using a clever reverse-correlation method. Although it seems complex, the actual number of free parameters adjusted was relatively modest. Once developed, the model was tested again ...
... the visual system9,10. The model was individually adjusted for each cell—necessary for explaining neuronal variability—using a clever reverse-correlation method. Although it seems complex, the actual number of free parameters adjusted was relatively modest. Once developed, the model was tested again ...
The Central Nervous System CNS
... • The parts of a neuron include the dendrite which receives the impulse (from another nerve cell or from a sensory organ), the cell body (numbers of which sideby-side form gray matter) where the nucleus is found, and the axon which carries the impulse away from the cell. ...
... • The parts of a neuron include the dendrite which receives the impulse (from another nerve cell or from a sensory organ), the cell body (numbers of which sideby-side form gray matter) where the nucleus is found, and the axon which carries the impulse away from the cell. ...
Basic Architecture of the Visual Cortex
... • Standard wisdom: “smart animals have dumb retinas and dumb animals have smart retinas.” • This is questioned by M. Meister (handout). He argues that human/monkey retinas are more complex than current models suggest. That current models of retinal neurons are based on experimental findings using si ...
... • Standard wisdom: “smart animals have dumb retinas and dumb animals have smart retinas.” • This is questioned by M. Meister (handout). He argues that human/monkey retinas are more complex than current models suggest. That current models of retinal neurons are based on experimental findings using si ...
Document
... How might drug use affect neurons and their ability to communicate with each other? ...
... How might drug use affect neurons and their ability to communicate with each other? ...
Organization of the Nervous System
... A neuron is at rest when it is not sending a signal and is in a negatively charged state. Even at rest, the neuron allows K to pass. Neuron pumps 3 Na ions out for every 2 K ions it pumps in. At rest, there are more Na ions outside and more K ions inside Resting & Action Potential ...
... A neuron is at rest when it is not sending a signal and is in a negatively charged state. Even at rest, the neuron allows K to pass. Neuron pumps 3 Na ions out for every 2 K ions it pumps in. At rest, there are more Na ions outside and more K ions inside Resting & Action Potential ...
Organization of the Nervous System
... A neuron is at rest when it is not sending a signal and is in a negatively charged state. Even at rest, the neuron allows K to pass. Neuron pumps 3 Na ions out for every 2 K ions it pumps in. At rest, there are more Na ions outside and more K ions inside Resting & Action Potential ...
... A neuron is at rest when it is not sending a signal and is in a negatively charged state. Even at rest, the neuron allows K to pass. Neuron pumps 3 Na ions out for every 2 K ions it pumps in. At rest, there are more Na ions outside and more K ions inside Resting & Action Potential ...
Design a Neuron
... Axon terminals – release the electrical impulse as a chemical called a neurotransmitter into the synapse to the next neuron or organ. ...
... Axon terminals – release the electrical impulse as a chemical called a neurotransmitter into the synapse to the next neuron or organ. ...
Ch03
... • Adapt to that characteristic by extended exposure • Re-measure the sensitivity to range of the stimulus characteristic ...
... • Adapt to that characteristic by extended exposure • Re-measure the sensitivity to range of the stimulus characteristic ...
AP Psych Vision Module 13 - Pleasantville High School
... break down visual stimuli into small components and have receptive fields with center-surround organization. ...
... break down visual stimuli into small components and have receptive fields with center-surround organization. ...
Module 6 The Cerebral Cortex and Our Divided Brain
... glial cells. They support, nourish, and protect neurons, and play a role in learning and thinking. For example, glial cell death has been linked to clinical depression. They also guide neural connections, and mop up excess ions. The more complex the brain, the more glial cells. ...
... glial cells. They support, nourish, and protect neurons, and play a role in learning and thinking. For example, glial cell death has been linked to clinical depression. They also guide neural connections, and mop up excess ions. The more complex the brain, the more glial cells. ...
Nervous System - APBio
... • 3. When threshold is met, membrane is in rising phase • 4. The Na+ channels close and K+ channels open- falling phase • 5. Because more K+ are open than usual, the membrane potential is more neg – undershoot • 6. More K+ close returning the potential to normal ...
... • 3. When threshold is met, membrane is in rising phase • 4. The Na+ channels close and K+ channels open- falling phase • 5. Because more K+ are open than usual, the membrane potential is more neg – undershoot • 6. More K+ close returning the potential to normal ...
Lecture 2 (Neurons)
... Neuron – A specialized cell of the body that can communicate information quickly by using ionic currents and chemical signals called neurotransmitters. Nerve - Many neurons that are bundled together and covered by a connective tissue sheath. Nervous System – The entire network of interconnecting neu ...
... Neuron – A specialized cell of the body that can communicate information quickly by using ionic currents and chemical signals called neurotransmitters. Nerve - Many neurons that are bundled together and covered by a connective tissue sheath. Nervous System – The entire network of interconnecting neu ...
Key - Cornell
... 4. Which characteristics of real neurons can you think of that leaky integrate-and-fire neurons do not model? Non-linearities in summation, refractory period 5. If one does not want to explicitly model action potential generation using Na+ and K+ channels, what is a good alternative? How is a refrac ...
... 4. Which characteristics of real neurons can you think of that leaky integrate-and-fire neurons do not model? Non-linearities in summation, refractory period 5. If one does not want to explicitly model action potential generation using Na+ and K+ channels, what is a good alternative? How is a refrac ...
Nervous System Nervous System
... Broad Concept: There is a relationship between the organization of cells into tissues, and tissues into organs. The structure and function of organs determine their relationships within body systems of an organism. Homeostasis allows the body to perform its normal functions. ...
... Broad Concept: There is a relationship between the organization of cells into tissues, and tissues into organs. The structure and function of organs determine their relationships within body systems of an organism. Homeostasis allows the body to perform its normal functions. ...
primary visual cortex
... 1. What is the structure of the eye and where are the receptors for light? (continued) 2. How is information about light relayed to the brain? 3. What are the major areas of the brain that are associated with the perception of light? ...
... 1. What is the structure of the eye and where are the receptors for light? (continued) 2. How is information about light relayed to the brain? 3. What are the major areas of the brain that are associated with the perception of light? ...