CNS Autonomic NS
... These cells can stay depolarized for long periods of time (up to days in some receptors). This is the basis of memory formation and is termed long term potentiation. ...
... These cells can stay depolarized for long periods of time (up to days in some receptors). This is the basis of memory formation and is termed long term potentiation. ...
Organization of Behavior
... changes in activity in brainstem "command" circuits directed by sensory input + or klinotaxis (single receptor compares stimulus over time) tropotaxis (paired receptors--simultaneous comparison) telotaxis (toward a goal--e.g. swim toward shore) not well studied in vertebrates Species-typical behavio ...
... changes in activity in brainstem "command" circuits directed by sensory input + or klinotaxis (single receptor compares stimulus over time) tropotaxis (paired receptors--simultaneous comparison) telotaxis (toward a goal--e.g. swim toward shore) not well studied in vertebrates Species-typical behavio ...
the neuron cheat sheet
... Neurons are nerve cells that transmit nerve signals to and from the brain at up to 200 mph. The neuron consists of a cell body (or soma) with branching dendrites (signal receivers) and a projection called an axon, which conduct the nerve signal. At the other end of the axon, the axon terminals trans ...
... Neurons are nerve cells that transmit nerve signals to and from the brain at up to 200 mph. The neuron consists of a cell body (or soma) with branching dendrites (signal receivers) and a projection called an axon, which conduct the nerve signal. At the other end of the axon, the axon terminals trans ...
NS Outline
... 4. Neuroglia: (nerve glue) support cells in CNS provide support, protection & access to nutrients, & other valuable services for the NS. {nonexcitable} a. Astrocytes: “nurse cells” made up of neuroglia cells that nurish & protect neurons. Star shaped cells in CNS. i. Most abundant neural cells. Form ...
... 4. Neuroglia: (nerve glue) support cells in CNS provide support, protection & access to nutrients, & other valuable services for the NS. {nonexcitable} a. Astrocytes: “nurse cells” made up of neuroglia cells that nurish & protect neurons. Star shaped cells in CNS. i. Most abundant neural cells. Form ...
ppt
... (feedback) Extrastriate visual cortical areas V3 – V5. More complex representation of visual stimulus with feedback from other cortical areas (eg. attention). ...
... (feedback) Extrastriate visual cortical areas V3 – V5. More complex representation of visual stimulus with feedback from other cortical areas (eg. attention). ...
File - Ms Curran`s Leaving Certificate Biology
... Once the threshold is reached the axon changes its permeability to ions At the site of stimulation the inside of the axon becomes +ive & the outside –ive. This change in charge causes the next section of the axon to alter its permeability A chain reaction is set up & a movement of +ive charges ...
... Once the threshold is reached the axon changes its permeability to ions At the site of stimulation the inside of the axon becomes +ive & the outside –ive. This change in charge causes the next section of the axon to alter its permeability A chain reaction is set up & a movement of +ive charges ...
Chapter Summary Chapter 5: Sensation and Perception • Sensation
... Top-down processing is involved in much visual perception. Gestalt theorists have identified several principles by which we recognize stimuli even when visual inputs are limited. We use binocular and monocular cues for depth perception. Perceptual constancies, based on learning from previous experie ...
... Top-down processing is involved in much visual perception. Gestalt theorists have identified several principles by which we recognize stimuli even when visual inputs are limited. We use binocular and monocular cues for depth perception. Perceptual constancies, based on learning from previous experie ...
Document
... __B__9. What is the function of neurotransmitters? a. builds new neurons b. chemically link neurons across the synapse to conduct impulses c. push sodium ions across the plasma membrane d. increases the speed of the impulse along the axon __B__10. The minimum level of a stimulus that is required to ...
... __B__9. What is the function of neurotransmitters? a. builds new neurons b. chemically link neurons across the synapse to conduct impulses c. push sodium ions across the plasma membrane d. increases the speed of the impulse along the axon __B__10. The minimum level of a stimulus that is required to ...
glial cells - Steven-J
... Neurons are nerve cells that transmit nerve signals to and from the brain at up to 200 mph. The neuron consists of a cell body (or soma) with branching dendrites (signal receivers) and a projection called an axon, which conduct the nerve signal. At the other end of the axon, the axon terminals trans ...
... Neurons are nerve cells that transmit nerve signals to and from the brain at up to 200 mph. The neuron consists of a cell body (or soma) with branching dendrites (signal receivers) and a projection called an axon, which conduct the nerve signal. At the other end of the axon, the axon terminals trans ...
Lecture 3.1: Human Vision: Colour.
... a single hue (Young, a British physicist) – By the fact that any colour can be produced by appropriate mixing of the three primary colours. ...
... a single hue (Young, a British physicist) – By the fact that any colour can be produced by appropriate mixing of the three primary colours. ...
Normal Edema
... • Not all cells in the CNS are ‘equal’: while some disease processes affect some groups of cells more than others (‘selective vulnerability’), other disease processes could affect other areas more. • Not all areas in the brain are equal: most areas in the brain have specific functions: a same diseas ...
... • Not all cells in the CNS are ‘equal’: while some disease processes affect some groups of cells more than others (‘selective vulnerability’), other disease processes could affect other areas more. • Not all areas in the brain are equal: most areas in the brain have specific functions: a same diseas ...
Central nervous system
... Conductivity: the property of neurons that give them the ability to transmit nerve impulses Electrical impulses (action potentials) are “all-or-none” responses ...
... Conductivity: the property of neurons that give them the ability to transmit nerve impulses Electrical impulses (action potentials) are “all-or-none” responses ...
Document
... •The study of processes and functions, incidental to, and characteristic of, life. •Physiology is an integrative science; examining body operation at all levels of organization, from cells to organs. •Homeostasis, flexibility, cell-to-cell communication, ...
... •The study of processes and functions, incidental to, and characteristic of, life. •Physiology is an integrative science; examining body operation at all levels of organization, from cells to organs. •Homeostasis, flexibility, cell-to-cell communication, ...
(A): The Neuron
... Neurons transmit messages when stimulated by our senses, or triggered by chemicals of other neurons ...
... Neurons transmit messages when stimulated by our senses, or triggered by chemicals of other neurons ...
PHYLLUM CNIDARIA (11,000 spp, mostly marine) 4 Classes
... Hydrozoa (4,000 spp) Scyphozoa (200 spp) - reduced polyp, developed medusa, no velum Cubozoa (several spp) - cub-shaped jellyfish Anthozoa (6,000 spp) - no medusa, complex polyp Two body forms - POLYP (e.g. sea anemones) - MEDUSA (e.g., jellyfish) Radial symmetry, mouth surrounded by tentacles Blind ...
... Hydrozoa (4,000 spp) Scyphozoa (200 spp) - reduced polyp, developed medusa, no velum Cubozoa (several spp) - cub-shaped jellyfish Anthozoa (6,000 spp) - no medusa, complex polyp Two body forms - POLYP (e.g. sea anemones) - MEDUSA (e.g., jellyfish) Radial symmetry, mouth surrounded by tentacles Blind ...
Nerve Pathways Practice Sheet
... The nervous system is a connection of many different (1) _____________________ (nerve cells). These nerves form pathways that send messages all over the body, in many different directions. (2) ________ neurons detect specific kinds of environmental stimuli, (3) _____________________ connect differen ...
... The nervous system is a connection of many different (1) _____________________ (nerve cells). These nerves form pathways that send messages all over the body, in many different directions. (2) ________ neurons detect specific kinds of environmental stimuli, (3) _____________________ connect differen ...
Receptor Cells
... no rods and cones at this point, so there is a small blind spot in vision (pg. 166) ...
... no rods and cones at this point, so there is a small blind spot in vision (pg. 166) ...
“Definitions” section of your binder Central nervous system
... Somatic Nervous System (SNS): the part of the peripheral nervous system that controls voluntary movement of skeletal muscles Autonomic nervous system (ANS): the part of the peripheral nervous system that controls internal biological functions ...
... Somatic Nervous System (SNS): the part of the peripheral nervous system that controls voluntary movement of skeletal muscles Autonomic nervous system (ANS): the part of the peripheral nervous system that controls internal biological functions ...
Final answers - Center for Neural Science
... extraneous comments are true and even if the correct answer is buried somewhere in there. 1) We will show you an excerpt from Hubel and Wiesel's film of receptive fields. On the accompanying answer sheet, list all of the correct descriptors, but none of the incorrect descriptors (-1 point for each i ...
... extraneous comments are true and even if the correct answer is buried somewhere in there. 1) We will show you an excerpt from Hubel and Wiesel's film of receptive fields. On the accompanying answer sheet, list all of the correct descriptors, but none of the incorrect descriptors (-1 point for each i ...
Slide ()
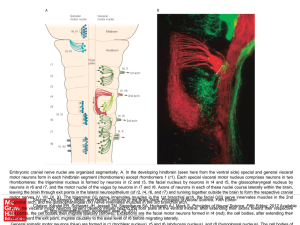
... Embryonic cranial nerve nuclei are organized segmentally. A. In the developing hindbrain (seen here from the ventral side) special and general visceral motor neurons form in each hindbrain segment (rhombomere) except rhombomere 1 (r1). Each special visceral motor nucleus comprises neurons in two rho ...
... Embryonic cranial nerve nuclei are organized segmentally. A. In the developing hindbrain (seen here from the ventral side) special and general visceral motor neurons form in each hindbrain segment (rhombomere) except rhombomere 1 (r1). Each special visceral motor nucleus comprises neurons in two rho ...
Textbook PowerPoint
... Inside the organ of Corti are tiny hair cells that act as sensory receptors for hearing. Stimulation of these receptors produces auditory signals that are transmitted to the brain through the auditory nerve. The brain pools the information from thousands of these cells to create the perception of s ...
... Inside the organ of Corti are tiny hair cells that act as sensory receptors for hearing. Stimulation of these receptors produces auditory signals that are transmitted to the brain through the auditory nerve. The brain pools the information from thousands of these cells to create the perception of s ...
Sensory Cells and Transduction of Stimuli
... Photoreceptors (eye) • Vertebrates have two types of photoreceptors, rod cells and cone cells. In humans, the fovea contains almost exclusively cone cells, which are responsible for color vision but are not very sensitive in dim light. • Color vision is based on the fact that different cone cells c ...
... Photoreceptors (eye) • Vertebrates have two types of photoreceptors, rod cells and cone cells. In humans, the fovea contains almost exclusively cone cells, which are responsible for color vision but are not very sensitive in dim light. • Color vision is based on the fact that different cone cells c ...
AP Psychology - HOMEWORK 9
... During the resting pause following an action potential, called the ___________________ the neuron pumps positively charged ions outside the cell. (1 pt) ...
... During the resting pause following an action potential, called the ___________________ the neuron pumps positively charged ions outside the cell. (1 pt) ...
Final Exam Practice Problems
... 18. What symptoms would expect to see in someone who has a damaged corticospinal tract? What is a neurological test that can be used to test for such damage? Why might babies have a positive result for this test? Difficulty with coordinated limb movements (e.g., they would pick up an object with the ...
... 18. What symptoms would expect to see in someone who has a damaged corticospinal tract? What is a neurological test that can be used to test for such damage? Why might babies have a positive result for this test? Difficulty with coordinated limb movements (e.g., they would pick up an object with the ...