Nerve tissue for stu..
... C. Myelinated axons in the central nervous system (CNS) – myelin sheath is formed by processes of oligodendrocytes. One inetrnodal segment is formed by one process of oligodendrocyte. One oligodendrocyte can form more internodal segments by its processes. D. Non-myelinated axons in the CNS – axons a ...
... C. Myelinated axons in the central nervous system (CNS) – myelin sheath is formed by processes of oligodendrocytes. One inetrnodal segment is formed by one process of oligodendrocyte. One oligodendrocyte can form more internodal segments by its processes. D. Non-myelinated axons in the CNS – axons a ...
Option A.3 Pt 1 - Peoria Public Schools
... retina. Rods work well in dim light and give us black and white vision. Cones work well in bright light and give us color vision. • List the three types of cones. a. Red, blue, green ...
... retina. Rods work well in dim light and give us black and white vision. Cones work well in bright light and give us color vision. • List the three types of cones. a. Red, blue, green ...
sensory overload - Saint Michael`s College
... like running a car engine with an almost empty fuel tank and no oil at full speed. The engine will eventually stop working; so do neurons. The only difference is that we can fix car engines, but usually not the central nervous system.” What we don’t see, but experience in the form of various brain d ...
... like running a car engine with an almost empty fuel tank and no oil at full speed. The engine will eventually stop working; so do neurons. The only difference is that we can fix car engines, but usually not the central nervous system.” What we don’t see, but experience in the form of various brain d ...
Brain Parts Matching Review - District 196 e
... govern the endocrine system via the pituitary gland. _______ 17. the portion of the cerebral cortex lying at the top of the head and toward the rear; receives sensory input for touch and body positions. _______ 18. an area at the rear of the frontal lobes that controls voluntary movements. _______ 1 ...
... govern the endocrine system via the pituitary gland. _______ 17. the portion of the cerebral cortex lying at the top of the head and toward the rear; receives sensory input for touch and body positions. _______ 18. an area at the rear of the frontal lobes that controls voluntary movements. _______ 1 ...
In Pursuit of Ecstasy - Heartland Community College
... Neural Control and the Senses Chapter 25 ...
... Neural Control and the Senses Chapter 25 ...
Information Processing SG
... The nervous system is like an information highway. It is responsible for controlling and coordinating all the functions and movements in the body and allows you to respond to changes in your environment The nervous system is made up of _____________ that are strings of long thin cells called _______ ...
... The nervous system is like an information highway. It is responsible for controlling and coordinating all the functions and movements in the body and allows you to respond to changes in your environment The nervous system is made up of _____________ that are strings of long thin cells called _______ ...
Chapter 2
... specific stimulus by firing of specifically tuned neurons specialized to just respond to a specific stimulus ...
... specific stimulus by firing of specifically tuned neurons specialized to just respond to a specific stimulus ...
Note: This hypothesis is mainly concerned with peripheral neurons
... In vitro assays have shown that NTs enhance both axonal and dendritic growth In vivo, the situation is more difficult to study Why? In standard knockouts, it is difficult to separate the survival effects of NTs from their effects on the morphology of neurons. This problem has begun to be addressed ...
... In vitro assays have shown that NTs enhance both axonal and dendritic growth In vivo, the situation is more difficult to study Why? In standard knockouts, it is difficult to separate the survival effects of NTs from their effects on the morphology of neurons. This problem has begun to be addressed ...
Attending to Contrast
... study. Stimuli consisted of patches of sinusoidal gratings (rows of alternating bright and dark bars), which were presented at various levels of contrast. With this experimental design, the authors could compare the firing rates of neurons across a range of contrasts, and thus compute the neuron’s c ...
... study. Stimuli consisted of patches of sinusoidal gratings (rows of alternating bright and dark bars), which were presented at various levels of contrast. With this experimental design, the authors could compare the firing rates of neurons across a range of contrasts, and thus compute the neuron’s c ...
Neurotransmitters: Acetylcholine (Ach) transmitter plays a role in
... Excitatory – excite the next cell into firing. Inhibitory – inhibit the next cell from firing. If excitatory signals exceed inhibitory signals the combined signals trigger an action potential. Threshold – the level of stimulation required to trigger a neural impulse. *Increasing the level of sti ...
... Excitatory – excite the next cell into firing. Inhibitory – inhibit the next cell from firing. If excitatory signals exceed inhibitory signals the combined signals trigger an action potential. Threshold – the level of stimulation required to trigger a neural impulse. *Increasing the level of sti ...
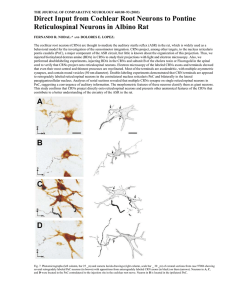
THE JOURNAL OF COMPARATIVE NEUROLOGY 460:80–93 (2003)
... THE JOURNAL OF COMPARATIVE NEUROLOGY 460:80–93 (2003) ...
... THE JOURNAL OF COMPARATIVE NEUROLOGY 460:80–93 (2003) ...
cnidarians
... o Stimulated – release coiled, hollow thread o Sticky or long and coil around prey or barbs/spines 2. Prey then pushed into mouth 3. Lastly, gastrovascular cavity for digestion o Body motion helps circulate contents ...
... o Stimulated – release coiled, hollow thread o Sticky or long and coil around prey or barbs/spines 2. Prey then pushed into mouth 3. Lastly, gastrovascular cavity for digestion o Body motion helps circulate contents ...
3/26
... Nerves allow us to perceive the environment while the brain integrates the incoming signals to determine an appropriate response. CB 48.3 ...
... Nerves allow us to perceive the environment while the brain integrates the incoming signals to determine an appropriate response. CB 48.3 ...
Introduction to Neural Networks
... • Connectionism refers to a computer modeling approach to computation that is loosely based upon the architecture of the brain. • Many different models: – Multiple, individual “nodes” or “units” that operate at the same time (in parallel) – A network that connects the nodes together – Information is ...
... • Connectionism refers to a computer modeling approach to computation that is loosely based upon the architecture of the brain. • Many different models: – Multiple, individual “nodes” or “units” that operate at the same time (in parallel) – A network that connects the nodes together – Information is ...
The language of the brain
... When it comes to laying down memories, the relative timing of spikes seems to be as important as the rate of firing. In particular, the synchronized firing of spikes in the cortex is important for increasing the strengths of synapses—an important process in forming long-term memories. A synapse is s ...
... When it comes to laying down memories, the relative timing of spikes seems to be as important as the rate of firing. In particular, the synchronized firing of spikes in the cortex is important for increasing the strengths of synapses—an important process in forming long-term memories. A synapse is s ...
The Nervous System
... • Sensory neurons send messages about your body or environment to the spinal cord up to the brain for interpretation. ...
... • Sensory neurons send messages about your body or environment to the spinal cord up to the brain for interpretation. ...
No Slide Title
... 1. carries messages to & from Brain Sensory Neurons Sensory info to CNS Motor Neurons from CNS to muscles and glands ...
... 1. carries messages to & from Brain Sensory Neurons Sensory info to CNS Motor Neurons from CNS to muscles and glands ...