Unit VIII: Animal Structure and Function, Part II
... • arranged in circuits of two or more types of neurons + simplest… reflex ...
... • arranged in circuits of two or more types of neurons + simplest… reflex ...
CORTEX I. GENERAL CONSIDERATIONS a. Cerebral cortex = grey
... iii. Layer 4 – many small spiny stellate cells; main input layer for thalamocortical 1) What cells axons; do not project out of cortex (project to other nearby layers) 2) Input *Striate (primary visual cortex) –complicated L4 because inputs are segregated 3) Output iv. Layer 5 – large pyramidal cell ...
... iii. Layer 4 – many small spiny stellate cells; main input layer for thalamocortical 1) What cells axons; do not project out of cortex (project to other nearby layers) 2) Input *Striate (primary visual cortex) –complicated L4 because inputs are segregated 3) Output iv. Layer 5 – large pyramidal cell ...
2. Peripheral Nervous System
... This balance is maintained by the sodium-potassium pump Pumps Na+ (sodium) outside Pumps K+ (potassium) inside Some K+ sneaks back out through channels ...
... This balance is maintained by the sodium-potassium pump Pumps Na+ (sodium) outside Pumps K+ (potassium) inside Some K+ sneaks back out through channels ...
Human Body Systems
... Part II: Relaying the Message (Partners) You will create a flow map of how the nervous system and body interact from the time of seeing a cockroach to your reaction (stepping on it, running, picking it up) Please read the full instructions – you need to use linking words and pictures! ...
... Part II: Relaying the Message (Partners) You will create a flow map of how the nervous system and body interact from the time of seeing a cockroach to your reaction (stepping on it, running, picking it up) Please read the full instructions – you need to use linking words and pictures! ...
A1985AUW1100002
... encountered in the spinal cord. These studies formed the background br subsequent studies of the electrical properties of the hippocampal pyramidal cells, For ejam~te.Alden and I went on to study for the first time the cettular events that underlie seizure.~ Here we encountered two completely differ ...
... encountered in the spinal cord. These studies formed the background br subsequent studies of the electrical properties of the hippocampal pyramidal cells, For ejam~te.Alden and I went on to study for the first time the cettular events that underlie seizure.~ Here we encountered two completely differ ...
Ch on Drugs and Prep for Test
... * Contains the primary auditory cortex * Much of it is used for complex visual tasks in conjunction with the primary visual cortex * These include recognizing faces and perceiving motion * Also crucial to memory * In the left hemisphere, aids language skills ...
... * Contains the primary auditory cortex * Much of it is used for complex visual tasks in conjunction with the primary visual cortex * These include recognizing faces and perceiving motion * Also crucial to memory * In the left hemisphere, aids language skills ...
The role of the nervous system in detecting and
... The role of the nervous system in detecting and responding to stimuli Detecting and responding in animals A complex animal may need to respond immediately to a stimulus. In many situations, it is important that a change is detected instantly and appropriate signals sent quickly to relevant parts of ...
... The role of the nervous system in detecting and responding to stimuli Detecting and responding in animals A complex animal may need to respond immediately to a stimulus. In many situations, it is important that a change is detected instantly and appropriate signals sent quickly to relevant parts of ...
1. 2. a) Explain the compositions of white matter and gray matter
... White matter consists of glial cells and myelinated axons. It does not contain the cell bodies of neurons and acts as a signal pathway for the gray matter regions of the central nervous system. Gray matter consists of glial cells and unmyelinated axons. It contains neuronal cell bodies. b) Explain s ...
... White matter consists of glial cells and myelinated axons. It does not contain the cell bodies of neurons and acts as a signal pathway for the gray matter regions of the central nervous system. Gray matter consists of glial cells and unmyelinated axons. It contains neuronal cell bodies. b) Explain s ...
Human Biology Name: Bio 5 - Spring 2006 Exam 1
... 6. An important mineral, used by erythrocytes in transporting oxygen, is ____________. 7. The "chemical cash" of the cell, at least in terms of providing energy, is the molecule known as __________________. (abbreviation is fine!). 8. The "blueprint" for all the cells, tissues, organs and organ syst ...
... 6. An important mineral, used by erythrocytes in transporting oxygen, is ____________. 7. The "chemical cash" of the cell, at least in terms of providing energy, is the molecule known as __________________. (abbreviation is fine!). 8. The "blueprint" for all the cells, tissues, organs and organ syst ...
Slide ()
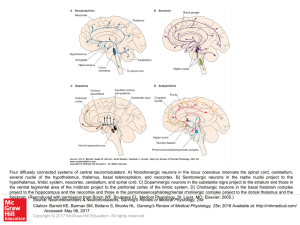
... Four diffusely connected systems of central neuromodulators. A) Noradrenergic neurons in the locus coeruleus innervate the spinal cord, cerebellum, several nuclei of the hypothalamus, thalamus, basal telencephalon, and neocortex. B) Serotonergic neurons in the raphe nuclei project to the hypothalamu ...
... Four diffusely connected systems of central neuromodulators. A) Noradrenergic neurons in the locus coeruleus innervate the spinal cord, cerebellum, several nuclei of the hypothalamus, thalamus, basal telencephalon, and neocortex. B) Serotonergic neurons in the raphe nuclei project to the hypothalamu ...
Nerve activates contraction - Silver Falls School District
... Found in neural pathways in CNS Connect sensory and motor neurons ...
... Found in neural pathways in CNS Connect sensory and motor neurons ...
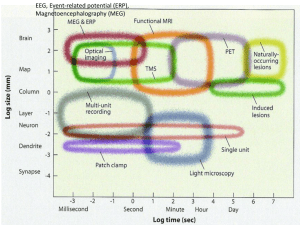
Abstract
... Amazing abilities of our brain, such as sensation, cognition, learning, memory, and even consciousness are thought to be realized through complex interactions of streams of millisecond-order electrical spikes (known as action potentials) generated by billions of neurons. How can one investigate such ...
... Amazing abilities of our brain, such as sensation, cognition, learning, memory, and even consciousness are thought to be realized through complex interactions of streams of millisecond-order electrical spikes (known as action potentials) generated by billions of neurons. How can one investigate such ...
Study Guide 1
... 2. Describe the basic flow of information in most sensory systems starting with an external stimulus and ending in the cerebral cortex. 3. What are the chemical senses? Why are they important? 4. Where are the receptor cells for taste located, and what are they called? 5. How does transduction occur ...
... 2. Describe the basic flow of information in most sensory systems starting with an external stimulus and ending in the cerebral cortex. 3. What are the chemical senses? Why are they important? 4. Where are the receptor cells for taste located, and what are they called? 5. How does transduction occur ...
Neuron highlight
... substantia nigra (SN) are easy to miss. Nestled deep in a bend of the brainstem, these nuclei house the bodies of most of the dopamine neurons that innervate the striatum and prefrontal cortex. Tract tracing studies indicate that while the VTA projects to more ventral regions of the striatum and pre ...
... substantia nigra (SN) are easy to miss. Nestled deep in a bend of the brainstem, these nuclei house the bodies of most of the dopamine neurons that innervate the striatum and prefrontal cortex. Tract tracing studies indicate that while the VTA projects to more ventral regions of the striatum and pre ...
Module 04
... other nearby neurons for much the same reason that people live in cities—it is easier to have brief, quick interactions with other people when they are nearby. Learning occurs as feedback builds and strengthens these neural connections (neurons that fire together wire together). . . . information hi ...
... other nearby neurons for much the same reason that people live in cities—it is easier to have brief, quick interactions with other people when they are nearby. Learning occurs as feedback builds and strengthens these neural connections (neurons that fire together wire together). . . . information hi ...
Central Sensitization
... in the central nervous system (CNS) in the processing of afferent nociceptive signals leading to hypersensitivity. There is increased responsiveness of nociceptive neurons to their normal input and there can also be long term potentiation (LTP) after repeated stimulation from the periphery. This is ...
... in the central nervous system (CNS) in the processing of afferent nociceptive signals leading to hypersensitivity. There is increased responsiveness of nociceptive neurons to their normal input and there can also be long term potentiation (LTP) after repeated stimulation from the periphery. This is ...
BOX 31.2 DIFFERENCES BETWEEN THE VESTIBULAR AND
... Phylogenetically, the vestibular and fastigial (medial) cerebellar nuclei predate the interpositus and dentate. Perhaps as a result, the vestibular and fastigial cerebellar circuits exhibit some distinctive properties compared to their relatively younger neighbors: 1. Unipolar brush cells are presen ...
... Phylogenetically, the vestibular and fastigial (medial) cerebellar nuclei predate the interpositus and dentate. Perhaps as a result, the vestibular and fastigial cerebellar circuits exhibit some distinctive properties compared to their relatively younger neighbors: 1. Unipolar brush cells are presen ...
The Human Organism: Introduction to Human Body - Nicole
... animals to detect a stimulus and coordinate a response. ...
... animals to detect a stimulus and coordinate a response. ...
Somatic Sensory System
... S2 and Parietal Posterior Cortex • S2 is lateral to S1 and is association area • PPC is posterior to S1 and is involved in perception/recognition of sensation • Neurons in S2 and PPC have complex receptive fields which can include sensory information as well as attention and visual and movement pla ...
... S2 and Parietal Posterior Cortex • S2 is lateral to S1 and is association area • PPC is posterior to S1 and is involved in perception/recognition of sensation • Neurons in S2 and PPC have complex receptive fields which can include sensory information as well as attention and visual and movement pla ...
Sensation and Perception
... • Protecting the surface of the eye • Transmitting vibrations received by the eardrum to the hammer, anvil, and stirrup • Transforming vibrations into neural signals • Coordinating impulses from the rods and cones in the retina • Sending messages to the brain about orientation of the head and body ...
... • Protecting the surface of the eye • Transmitting vibrations received by the eardrum to the hammer, anvil, and stirrup • Transforming vibrations into neural signals • Coordinating impulses from the rods and cones in the retina • Sending messages to the brain about orientation of the head and body ...