THE VISUAL SYSTEM
... • Optic chiasm: pt at which the optic nerves from the inside half of each eye cross over and then project to the opposite half of the brain • Optic fibers then diverge along 2 paths • Main path projects into thalamus; retinal axons synapse in the Lateral geniculate nucleus (LGN) • Then to the occipi ...
... • Optic chiasm: pt at which the optic nerves from the inside half of each eye cross over and then project to the opposite half of the brain • Optic fibers then diverge along 2 paths • Main path projects into thalamus; retinal axons synapse in the Lateral geniculate nucleus (LGN) • Then to the occipi ...
Introduction To Physiology ~ LECTURE NOTES
... (1871-‐1945) coined the term ‘homeostasis’: it fluctuates within limited range around a set point Homeostasis mechanisms: 1. Receptor-‐ sensitive to environmental change 2. Control centre-‐ receives and processes ...
... (1871-‐1945) coined the term ‘homeostasis’: it fluctuates within limited range around a set point Homeostasis mechanisms: 1. Receptor-‐ sensitive to environmental change 2. Control centre-‐ receives and processes ...
II. ORGANIZATION OF THE HUMAN NERVOUS
... a snail-shaped sensory structure filled with fluid and tiny hairs. These hairs are pushed back & forth, producing electrical impulses. Nerve impulse is transmitted by way of the _auditory nerve_______ to the _brain_____. The semicircular canals are also found in the ear. They play no role in hea ...
... a snail-shaped sensory structure filled with fluid and tiny hairs. These hairs are pushed back & forth, producing electrical impulses. Nerve impulse is transmitted by way of the _auditory nerve_______ to the _brain_____. The semicircular canals are also found in the ear. They play no role in hea ...
PPT2
... The complex cells, which are not sensitive to the polarity of the luminance contrast at edge, would be particularly suitable for representing borders or boundaries of regions. The Hypercomplex cells could serve as derivative operators which act on complex cells’ responses to detect texture boundarie ...
... The complex cells, which are not sensitive to the polarity of the luminance contrast at edge, would be particularly suitable for representing borders or boundaries of regions. The Hypercomplex cells could serve as derivative operators which act on complex cells’ responses to detect texture boundarie ...
Cortex
... David Hubel and Torsten Wiesel (Con’t) 1. Such manipulations are not nearly so effective after this early critical period ends, 1. a finding that led most investigators to conclude that cortical organization becomes fixed in adulthood. 2. Mechanisms 1. the reorganization of sensory maps, as well ...
... David Hubel and Torsten Wiesel (Con’t) 1. Such manipulations are not nearly so effective after this early critical period ends, 1. a finding that led most investigators to conclude that cortical organization becomes fixed in adulthood. 2. Mechanisms 1. the reorganization of sensory maps, as well ...
Chapter 48: Nervous Systems Overview: Command and Control
... Overview: Command and Control Center • The human brain contains an estimated 100 billion nerve cells, or ______________________________ • Each neuron may communicate with thousands of other neurons Nervous systems consist of circuits of neurons and supporting cells • All animals except sponges have ...
... Overview: Command and Control Center • The human brain contains an estimated 100 billion nerve cells, or ______________________________ • Each neuron may communicate with thousands of other neurons Nervous systems consist of circuits of neurons and supporting cells • All animals except sponges have ...
Lecture 7A
... to do. We already know that neurons are much slower than a computer, and in that half second, information entering the brain can traverse only a chain of one hundred neurons. You can come up with the answer with only one hundred steps. A digital computer would take billions of steps to come up with ...
... to do. We already know that neurons are much slower than a computer, and in that half second, information entering the brain can traverse only a chain of one hundred neurons. You can come up with the answer with only one hundred steps. A digital computer would take billions of steps to come up with ...
The Neuron
... motor neurons. (Note that I am using the term "outside world" figuratively in that messages also come "in" from internal organs such as the stomach, and messages often go out to internal organs such as the heart). The large group of neurons which do not form connections with sensory receptors or mus ...
... motor neurons. (Note that I am using the term "outside world" figuratively in that messages also come "in" from internal organs such as the stomach, and messages often go out to internal organs such as the heart). The large group of neurons which do not form connections with sensory receptors or mus ...
The Neural Basis of Visually Guided Behavior
... vVhen the size and contrast are held con stant, behavioral activity increases with increasing angular velocity, reaching maximum at between ...
... vVhen the size and contrast are held con stant, behavioral activity increases with increasing angular velocity, reaching maximum at between ...
Dendritic organization of sensory input to cortical neurons in vivo
... dendritic organization of sensory inputs to neurons of the visual cortex in vivo. • Identified discrete dendritic hotspots as synaptic entry sites for specific sensory features • Afferent sensory inputs with the same orientation preference are widely dispersed over thedendritic tree and do not conve ...
... dendritic organization of sensory inputs to neurons of the visual cortex in vivo. • Identified discrete dendritic hotspots as synaptic entry sites for specific sensory features • Afferent sensory inputs with the same orientation preference are widely dispersed over thedendritic tree and do not conve ...
Myers Module Six
... and play a role in learning and thinking. For example, glial cell death has been linked to clinical depression. They also guide neural connections, and mop up excess ions. ...
... and play a role in learning and thinking. For example, glial cell death has been linked to clinical depression. They also guide neural connections, and mop up excess ions. ...
Nervous System
... • Calcium causes the vesicles to fuse with the membrane and release the neurotransmitter into the next synapse. • The neurotransmitter binds to the receptors on the dendrites gets converted to an electrical signal and on and on ...
... • Calcium causes the vesicles to fuse with the membrane and release the neurotransmitter into the next synapse. • The neurotransmitter binds to the receptors on the dendrites gets converted to an electrical signal and on and on ...
Vestibular senses
... rays to AC circuits; its wavelength is measured in nanometers. - What are the 3 perceived characteristics of light? 1. Hue, corresponding to the spectrum (wavelength) of light. 2. Brightness, corresponding to intensity of wavelength. 3. Saturation, corresponding to the purity of wavelength. - What a ...
... rays to AC circuits; its wavelength is measured in nanometers. - What are the 3 perceived characteristics of light? 1. Hue, corresponding to the spectrum (wavelength) of light. 2. Brightness, corresponding to intensity of wavelength. 3. Saturation, corresponding to the purity of wavelength. - What a ...
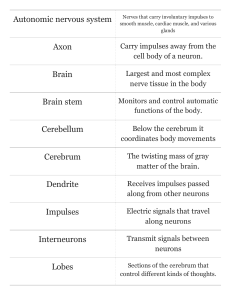
Print › Nervous System | Quizlet
... Nerves that carry involuntary impulses to smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, and various ...
... Nerves that carry involuntary impulses to smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, and various ...
Anatomy of the Basal Ganglia
... eye movements. Types of Neurons in the Striatum Medium spiny neurons—make up 95% of the total. Use GABA as a transmitter. Are the output neurons of the striatum. Large aspiny neurons—interneurons that use ACh as a transmitter. Medium aspiny cells—interneurons that use somatostatin as a neurotransmit ...
... eye movements. Types of Neurons in the Striatum Medium spiny neurons—make up 95% of the total. Use GABA as a transmitter. Are the output neurons of the striatum. Large aspiny neurons—interneurons that use ACh as a transmitter. Medium aspiny cells—interneurons that use somatostatin as a neurotransmit ...
The Nervous System
... Describe how the vertebrate brain integrates information (brings information together) to produce a response. ...
... Describe how the vertebrate brain integrates information (brings information together) to produce a response. ...
Nervous System Cells
... extensions that receive signals • Axon: long extension that transmits impulses away ...
... extensions that receive signals • Axon: long extension that transmits impulses away ...
Review Senses and Nervous System Test
... Review Senses and Nervous System Test *(This is only an outline there is much more you should look over) CH 8 SENSES 1. What are the functions of the parts of eye? 2. What is blind spot, photoreceptors, rods, cones? 3. Read p 258, 262 4. What is colorblindness, cataracts, pink eye, glaucoma 5. What ...
... Review Senses and Nervous System Test *(This is only an outline there is much more you should look over) CH 8 SENSES 1. What are the functions of the parts of eye? 2. What is blind spot, photoreceptors, rods, cones? 3. Read p 258, 262 4. What is colorblindness, cataracts, pink eye, glaucoma 5. What ...
RetinaCircuts
... • Signals from bipolar cells cause effect – Receptors stimulated by dark areas inhibit the response of neighboring cells receiving input from white area – The lateral inhibition causes a reduced response which leads to the perception of ...
... • Signals from bipolar cells cause effect – Receptors stimulated by dark areas inhibit the response of neighboring cells receiving input from white area – The lateral inhibition causes a reduced response which leads to the perception of ...
14.1 Nervous Control notes - Mr Cartlidge`s Saigon Science Blog
... – the central nervous system consisting of brain and spinal cord – the peripheral nervous system – coordination and regulation of body functions The human nervous system is made of two parts-central nervous system (CNS) and peripheral nervous system(PNS); CNS - brain and spinal cord, which have ...
... – the central nervous system consisting of brain and spinal cord – the peripheral nervous system – coordination and regulation of body functions The human nervous system is made of two parts-central nervous system (CNS) and peripheral nervous system(PNS); CNS - brain and spinal cord, which have ...
SOMATOSENSORY SYSTEMS
... gyrus of anesthetized monkeys. All were placed within 1 mm of the plane marked A on the inset drawing, which show the cytoarchitectonic areas. Penetrations perpendicular to the cortical surface and passing down parallel to its radial axis encountered neurons all of the same modality (Powell and Moun ...
... gyrus of anesthetized monkeys. All were placed within 1 mm of the plane marked A on the inset drawing, which show the cytoarchitectonic areas. Penetrations perpendicular to the cortical surface and passing down parallel to its radial axis encountered neurons all of the same modality (Powell and Moun ...
07_Nitz_compiled
... b. The thalamus is the basic structural and functional unit of the brain. c. The neocortex is the basic structural and functional unit of the brain. d. The layers of neo-cortex are the basic structural and functional unit of the brain. e. None of the above. ...
... b. The thalamus is the basic structural and functional unit of the brain. c. The neocortex is the basic structural and functional unit of the brain. d. The layers of neo-cortex are the basic structural and functional unit of the brain. e. None of the above. ...
New Neurons Grow in Adult Brains
... DNA and pass it on to the newly formed cells. At different time points after the injection, ranging from two hours to seven days, the researchers examined the cerebral cortex and found evidence of BrdU containing cells in three different regions. Because BrdU is only incorporated into the DNA of cel ...
... DNA and pass it on to the newly formed cells. At different time points after the injection, ranging from two hours to seven days, the researchers examined the cerebral cortex and found evidence of BrdU containing cells in three different regions. Because BrdU is only incorporated into the DNA of cel ...