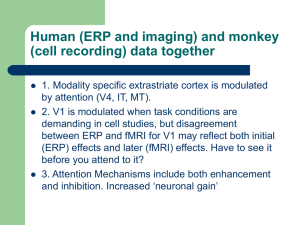
Final - Center for Neural Science
... a) Patient A has difficulty recognizing objects and is unaware of his deficit. Patient B has difficulty with spatial orientation and localization and is aware of his deficit. b) Patient A has difficulty with spatial orientation and localization and is unaware of his deficit. Patient B has difficulty ...
... a) Patient A has difficulty recognizing objects and is unaware of his deficit. Patient B has difficulty with spatial orientation and localization and is aware of his deficit. b) Patient A has difficulty with spatial orientation and localization and is unaware of his deficit. Patient B has difficulty ...
nitz - UCSD Cognitive Science
... – neurons of the medial entorhinal cortex exhibit multiple firing fields in any given environment – such fields are arranged according to the nodes of a set of ‘tesselated’ triangles – grids, like head-direction tuning and place cells firing fields rotate with the boundaries of the environment ...
... – neurons of the medial entorhinal cortex exhibit multiple firing fields in any given environment – such fields are arranged according to the nodes of a set of ‘tesselated’ triangles – grids, like head-direction tuning and place cells firing fields rotate with the boundaries of the environment ...
Perception - U
... Scotomas and Blindsight • Individuals with damage to primary visual cortex have scotomas or areas of blindness in corresponding areas of the visual field • Amazingly, when forced to guess, some brain-damaged patients can respond to stimuli in their scotomas (e.g., can grab a moving object or guess ...
... Scotomas and Blindsight • Individuals with damage to primary visual cortex have scotomas or areas of blindness in corresponding areas of the visual field • Amazingly, when forced to guess, some brain-damaged patients can respond to stimuli in their scotomas (e.g., can grab a moving object or guess ...
Nervous System - Lemon Bay High School
... coordination of muscle activity. • Pons: relays sensory info from the cerebellum to the cerebral cortex. • Medulla oblongata: the “primitive” brain; controls heart rate, respirations, ...
... coordination of muscle activity. • Pons: relays sensory info from the cerebellum to the cerebral cortex. • Medulla oblongata: the “primitive” brain; controls heart rate, respirations, ...
HONORS BIOLOGY Chapter 28 Nervous Systems
... But not the strength of action potentials 28.6 Neurons communicate at synapses Synapses are junctions where signals are transmitted between Two neurons or between neurons and effector cells ...
... But not the strength of action potentials 28.6 Neurons communicate at synapses Synapses are junctions where signals are transmitted between Two neurons or between neurons and effector cells ...
Chapter 7 part two
... representational resources, and only one or a small number of stimuli can be represented at one time. As the neural representations of visual stimuli are highly distributed, competitive processing occurs in many of the brain areas sensitive to visual input. Second, the competition is integrated acro ...
... representational resources, and only one or a small number of stimuli can be represented at one time. As the neural representations of visual stimuli are highly distributed, competitive processing occurs in many of the brain areas sensitive to visual input. Second, the competition is integrated acro ...
The Neural Control of Behavior
... chord •PERIPHERAL NERVOUS SYSTEM: the entire set of cranial and spinal nerves that connect the central nervous system (brain and spinal chord) to the body’s sensory organs, muscles, and glands. •NERVE: a large bundle containing the axons of many neurons. Located in the PNS, nerves connect the CNS wi ...
... chord •PERIPHERAL NERVOUS SYSTEM: the entire set of cranial and spinal nerves that connect the central nervous system (brain and spinal chord) to the body’s sensory organs, muscles, and glands. •NERVE: a large bundle containing the axons of many neurons. Located in the PNS, nerves connect the CNS wi ...
Chapter 12-13 Summary
... II. Schwann cells myelinated neuron processes in the PNS. III. Make a Table of neuroglia with function and location. (See Table 12.2) B. Neurons (Review Figure 12.2 & 12.22) i. ...
... II. Schwann cells myelinated neuron processes in the PNS. III. Make a Table of neuroglia with function and location. (See Table 12.2) B. Neurons (Review Figure 12.2 & 12.22) i. ...
Nervous Tissue
... The part of the neuron which immediately surrounds the nucleus Usually used synonymously with neuron or soma ...
... The part of the neuron which immediately surrounds the nucleus Usually used synonymously with neuron or soma ...
Slide ()
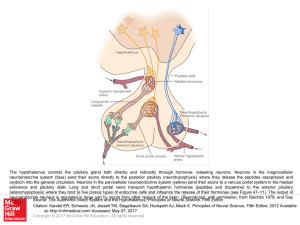
... neuroendocrine system (blue) send their axons directly to the posterior pituitary (neurohypophysis) where they release the peptides vasopressin and oxytocin into the general circulation. Neurons in the parvicellular neuroendocrine system (yellow) send their axons to a venous portal system in the med ...
... neuroendocrine system (blue) send their axons directly to the posterior pituitary (neurohypophysis) where they release the peptides vasopressin and oxytocin into the general circulation. Neurons in the parvicellular neuroendocrine system (yellow) send their axons to a venous portal system in the med ...
File
... Overview of the Nervous System • STRUCTURES: brain, spinal cord, & peripheral nerves • FUNCTION: Recognizes and coordinates the body’s response to changes in its internal and external environments ...
... Overview of the Nervous System • STRUCTURES: brain, spinal cord, & peripheral nerves • FUNCTION: Recognizes and coordinates the body’s response to changes in its internal and external environments ...
PowerPoint Slides Chapter 6
... At the ganglion cell level, the system responds in an opponentprocess fashion Ganglion level has red-green & blue-yellow (opponent-process); receptive field illuminated with the color shown, the cell rate of firing increases E.g. red-green ganglion cells excited by red and inhibited by green ...
... At the ganglion cell level, the system responds in an opponentprocess fashion Ganglion level has red-green & blue-yellow (opponent-process); receptive field illuminated with the color shown, the cell rate of firing increases E.g. red-green ganglion cells excited by red and inhibited by green ...
Chapter 22 Thalamus
... Orderly arrangement of receptors exists along skin, basilar membrane, and retina Differences in peripheral innervation density are tightly correlated w/ spatial acuity Receptors; sites of convergence and divergence A single ganglion cell receives input from several receptors and in many cases ...
... Orderly arrangement of receptors exists along skin, basilar membrane, and retina Differences in peripheral innervation density are tightly correlated w/ spatial acuity Receptors; sites of convergence and divergence A single ganglion cell receives input from several receptors and in many cases ...
Abstract View OPTICAL RECORDING OF THE TRITONIA SWIMMING CENTRAL PATTERN GENERATOR. ;
... during fictive swimming. Candidate central pattern generator (CPG) interneurons were identified by their bursting patterns and positions in the brain. Previously identifed populations of interneurons were imaged, including the dorsal swim interneurons (DSI), C2, and ventral swim interneurons (VSI). ...
... during fictive swimming. Candidate central pattern generator (CPG) interneurons were identified by their bursting patterns and positions in the brain. Previously identifed populations of interneurons were imaged, including the dorsal swim interneurons (DSI), C2, and ventral swim interneurons (VSI). ...
Module 3 Brain`s Building Blocks
... are arranged like rungs on a twisted ladder There are about 30,000 genes that contain chemical instructions that equal about 300,000 pages of written instructions Genes program the development of individual parts into a complex body & brain ...
... are arranged like rungs on a twisted ladder There are about 30,000 genes that contain chemical instructions that equal about 300,000 pages of written instructions Genes program the development of individual parts into a complex body & brain ...
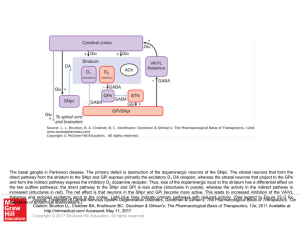
BASAL GANGLIA
... projections from the cortex to terminal sites in the striatum and the labeled stratopallidal output cells are organizeds as sets of patches in the striatum. B The input clusters and output clusters overlap extensively (cross-hatching in B). Experiments using multiple-electrode recording suggest that ...
... projections from the cortex to terminal sites in the striatum and the labeled stratopallidal output cells are organizeds as sets of patches in the striatum. B The input clusters and output clusters overlap extensively (cross-hatching in B). Experiments using multiple-electrode recording suggest that ...
July 1
... spectral power law. Using a PCA based method on sub dural electrocorticographic recordings in humans, we were able to decouple this power law behavior from the classic alpha and beta rhythms, revealing its presence at low frequencies. The projection of the dynamic spectrum to this power law, is able ...
... spectral power law. Using a PCA based method on sub dural electrocorticographic recordings in humans, we were able to decouple this power law behavior from the classic alpha and beta rhythms, revealing its presence at low frequencies. The projection of the dynamic spectrum to this power law, is able ...
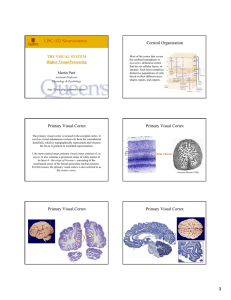
LISC-322 Neuroscience Cortical Organization Primary Visual Cortex
... receives visual information exclusively from the contralateral hemifield, which is topographically represented and wherein the fovea is granted an extended representation. Like most cortical areas, primary visual cortex consists of six layers. It also contains a prominent stripe of white matter in i ...
... receives visual information exclusively from the contralateral hemifield, which is topographically represented and wherein the fovea is granted an extended representation. Like most cortical areas, primary visual cortex consists of six layers. It also contains a prominent stripe of white matter in i ...
Slide () - AccessAnesthesiology
... direct pathway from the striatum to the SNpr and GPi express primarily the excitatory D1 DA receptor, whereas the striatal neurons that project to the GPe and form the indirect pathway express the inhibitory D2 dopamine receptor. Thus, loss of the dopaminergic input to the striatum has a differentia ...
... direct pathway from the striatum to the SNpr and GPi express primarily the excitatory D1 DA receptor, whereas the striatal neurons that project to the GPe and form the indirect pathway express the inhibitory D2 dopamine receptor. Thus, loss of the dopaminergic input to the striatum has a differentia ...
SM 11.04.12 - Premio principe asturias
... for their significant neurobiological research into so-called «mirror neurons,» nerve cells found in the ventral premotor cortex of the brain which are activated not only when an individual performs a particular action, such as a hand movement, but also when the individual observes the same action b ...
... for their significant neurobiological research into so-called «mirror neurons,» nerve cells found in the ventral premotor cortex of the brain which are activated not only when an individual performs a particular action, such as a hand movement, but also when the individual observes the same action b ...
What happens in hereditary color deficiency? Red or green cone
... Receptors show adaptation ◦ most sensitive to changes rather than constant stimulation ◦ why is this important? ...
... Receptors show adaptation ◦ most sensitive to changes rather than constant stimulation ◦ why is this important? ...
Stimulus – Response: Reaction Time - Science
... Axons carry messages away from the cell body. Any message carried by a neuron is called an IMPULSE. There are three types of neurons — SENSORY NEURONS, MOTOR NEURONS, and INTERNEURONS—that transport impulses. ...
... Axons carry messages away from the cell body. Any message carried by a neuron is called an IMPULSE. There are three types of neurons — SENSORY NEURONS, MOTOR NEURONS, and INTERNEURONS—that transport impulses. ...
Chapter 2 - The Brain (Part II)
... auditory areas, each receiving information primarily from the opposite ear An area at the rear of the frontal lobes that controls voluntary movements. Area at the front of the parietal lobes that registers and processes body touch and movement sensations. Areas of the cerebral cortex that are not in ...
... auditory areas, each receiving information primarily from the opposite ear An area at the rear of the frontal lobes that controls voluntary movements. Area at the front of the parietal lobes that registers and processes body touch and movement sensations. Areas of the cerebral cortex that are not in ...
Audition and Equilibrium
... stimulated…which set of sensory axons have action potentials • Intensity coded by degree of displacement of stereocilia of hair cells and ultimately the frequency of action potentials in those axons that are active ...
... stimulated…which set of sensory axons have action potentials • Intensity coded by degree of displacement of stereocilia of hair cells and ultimately the frequency of action potentials in those axons that are active ...