Unit Test Neuro: Core ( Topic 6.5) and Options E ( Topics 1,2,4) HL
... E.1.3 Draw and label a diagram of a reflex arc for a pain withdraw reflex including the spinal cord and its spinal nerves, the receptor cell, sensory neuron, relay neuron, motor neuron and effector. (1) ...
... E.1.3 Draw and label a diagram of a reflex arc for a pain withdraw reflex including the spinal cord and its spinal nerves, the receptor cell, sensory neuron, relay neuron, motor neuron and effector. (1) ...
Motor Neuron
... – Found in neural pathways in the central nervous system – Connect sensory and motor neurons ...
... – Found in neural pathways in the central nervous system – Connect sensory and motor neurons ...
Chapter 14
... 8. Electrical synapses permit direct physical contact between presynaptic and postsynaptic cells. They are connected by a gap junction, which allows ion flow between the cells. In a chemical synapse, the most common type in humans, a neurotransmitter passes between the presynaptic and postsynaptic c ...
... 8. Electrical synapses permit direct physical contact between presynaptic and postsynaptic cells. They are connected by a gap junction, which allows ion flow between the cells. In a chemical synapse, the most common type in humans, a neurotransmitter passes between the presynaptic and postsynaptic c ...
Sensation and Perception
... Retinal cells send initial information through thalamus to visual cortex Feature detectors respond to specific characteristics - lines, movements, angles Supercell clusters of neurons interpret more complex patterns - faces, complete objects Some ...
... Retinal cells send initial information through thalamus to visual cortex Feature detectors respond to specific characteristics - lines, movements, angles Supercell clusters of neurons interpret more complex patterns - faces, complete objects Some ...
1-The cell body
... called synapses. 3-The axon (Gr. axon, axis), which is a single long process ending at synapses specialized to generate and conduct nerve impulses to other cells (nerve, muscle, and gland cells). Axons may also receive information from other neurons, information that mainly modifies the transmission ...
... called synapses. 3-The axon (Gr. axon, axis), which is a single long process ending at synapses specialized to generate and conduct nerve impulses to other cells (nerve, muscle, and gland cells). Axons may also receive information from other neurons, information that mainly modifies the transmission ...
2.2 Electrical Communication Study Guide by Hisrich
... 2.2.d How are electrical impulses created in the human body? Na+/K+ pump keeps outside of membrane + and inside – by pumping positive ions out of the membrane, priming the membrane to carry charges ...
... 2.2.d How are electrical impulses created in the human body? Na+/K+ pump keeps outside of membrane + and inside – by pumping positive ions out of the membrane, priming the membrane to carry charges ...
Nervous System - Creston High School
... and skilled skeletal muscle, functions in intellectual and emotional processing. Shows lateralization of function – Most people the left hemisphere is dominant and is specialized for language and mathematical skills – The right hemisphere is more concerned with visualspatial skills and creative en ...
... and skilled skeletal muscle, functions in intellectual and emotional processing. Shows lateralization of function – Most people the left hemisphere is dominant and is specialized for language and mathematical skills – The right hemisphere is more concerned with visualspatial skills and creative en ...
Mirror Neurons & You
... progressive sophistication of input & output information to certain signal behaviors Examples: tool use, communication-pretty much all aspects of what we ...
... progressive sophistication of input & output information to certain signal behaviors Examples: tool use, communication-pretty much all aspects of what we ...
Histology of Nerve the Nervous System
... system,consisting of the brain and the spinal cord, and the peripheral nervous system,composed of nerve fibers and small aggregates of nerve cells called nerve ganglia Structurally,nerve tissue consists of two cell types:nerve cells,or neurons, Usually show numerous long processes, and several types ...
... system,consisting of the brain and the spinal cord, and the peripheral nervous system,composed of nerve fibers and small aggregates of nerve cells called nerve ganglia Structurally,nerve tissue consists of two cell types:nerve cells,or neurons, Usually show numerous long processes, and several types ...
Slide ()
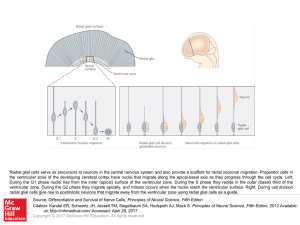
... Radial glial cells serve as precursors to neurons in the central nervous system and also provide a scaffold for radial neuronal migration. Progenitor cells in the ventricular zone of the developing cerebral cortex have nuclei that migrate along the apical-basal axis as they progress through the cell ...
... Radial glial cells serve as precursors to neurons in the central nervous system and also provide a scaffold for radial neuronal migration. Progenitor cells in the ventricular zone of the developing cerebral cortex have nuclei that migrate along the apical-basal axis as they progress through the cell ...
The Nervous Systeminofnotes
... • Receives information • Responds to information • Maintains homeostasis ...
... • Receives information • Responds to information • Maintains homeostasis ...
Medial Temporal Lobe Switches Memory Encoding in Neocortex
... artificial visuo-auditory memory traces can be established in the rat auditory cortex and that their encoding depends on the entorhinal cortex of the medial temporal lobe in the rat. We trained rats to associate a visual stimulus with electrical stimulation of the auditory cortex using a classical c ...
... artificial visuo-auditory memory traces can be established in the rat auditory cortex and that their encoding depends on the entorhinal cortex of the medial temporal lobe in the rat. We trained rats to associate a visual stimulus with electrical stimulation of the auditory cortex using a classical c ...
EQ2.3 - nerve cells communicate-
... How do nerve cells communicate? #3: Ema If it weren’t for nerve cells we wouldn’t be able to understand our thoughts, motor and emotional responses, learning and memory skills. Nerve cells or neurons constantly gather information from the inside of our organism and its external environment. Thus eva ...
... How do nerve cells communicate? #3: Ema If it weren’t for nerve cells we wouldn’t be able to understand our thoughts, motor and emotional responses, learning and memory skills. Nerve cells or neurons constantly gather information from the inside of our organism and its external environment. Thus eva ...
Slide ()
... The olfactory epithelium. A. The olfactory epithelium contains sensory neurons interspersed with supporting cells as well as a basal layer of stem cells. Cilia extend from the dendrite of each neuron into the mucus lining the nasal cavity. An axon extends from the basal end of each neuron to the olf ...
... The olfactory epithelium. A. The olfactory epithelium contains sensory neurons interspersed with supporting cells as well as a basal layer of stem cells. Cilia extend from the dendrite of each neuron into the mucus lining the nasal cavity. An axon extends from the basal end of each neuron to the olf ...
Slide 1
... circuit consists of a population of excitatory neurons (E) that recurrently excite one another, and a population of inhibitory neurons (I) that recurrently inhibit one another (red/pink synapses are excitatory, black/grey synapses are inhibitory). The excitatory cells excite the inhibitory neurons, ...
... circuit consists of a population of excitatory neurons (E) that recurrently excite one another, and a population of inhibitory neurons (I) that recurrently inhibit one another (red/pink synapses are excitatory, black/grey synapses are inhibitory). The excitatory cells excite the inhibitory neurons, ...
CS 256: Neural Computation Lecture Notes
... • Two types of electric potentials – Synaptic/receptor potentials are graded, sustained and local. They are usually stimulated by neurotransmitters. (The stronger the stimulus, the larger the potential.) They add in an quasilinear manner. – Action potentials, a transient spike that can propagate alo ...
... • Two types of electric potentials – Synaptic/receptor potentials are graded, sustained and local. They are usually stimulated by neurotransmitters. (The stronger the stimulus, the larger the potential.) They add in an quasilinear manner. – Action potentials, a transient spike that can propagate alo ...
Study Guide Solutions - Elsevier: Baars and Gage
... The brain constantly generates expectations about the world it encounters. Walking downstairs in the dark, we have expectations about every step we take. In dealing with ambiguities like the figures shown here, we constantly make predictions about which of two perceptual interpretations is the best ...
... The brain constantly generates expectations about the world it encounters. Walking downstairs in the dark, we have expectations about every step we take. In dealing with ambiguities like the figures shown here, we constantly make predictions about which of two perceptual interpretations is the best ...
Reuptake, or re-uptake, is the reabsorption of a neurotransmitter by
... (1) What is the name for the neural reaction whereby, following repeated presentations, an organism learns to ignore a stimulus. Page 333. Habituation. (2) Name four areas of the brain which exhibit long-term potentiation. Page 337. Thalamus, motor cortex, cerebellum and amygdala. (3) If a drug is u ...
... (1) What is the name for the neural reaction whereby, following repeated presentations, an organism learns to ignore a stimulus. Page 333. Habituation. (2) Name four areas of the brain which exhibit long-term potentiation. Page 337. Thalamus, motor cortex, cerebellum and amygdala. (3) If a drug is u ...
Nervous_System_Neurons
... So how is the nerve message continued along the axon/dendrite route??? ...
... So how is the nerve message continued along the axon/dendrite route??? ...
Data Structures CSCI 262, Spring 2002 Lecture 2 Classes
... visual cortex by recording electrical signals from the cell while showing the animal a visual stimulus (e.g. a bar of light). The cell will respond by increasing or decreasing the rate of action potentials when the light is in the cell's receptive field. Show Movie! ...
... visual cortex by recording electrical signals from the cell while showing the animal a visual stimulus (e.g. a bar of light). The cell will respond by increasing or decreasing the rate of action potentials when the light is in the cell's receptive field. Show Movie! ...
The nervous system
... the cells to one another, to centers throughout the body or to other neurons. These neurons operate on excitation or inhibition and although nerve cells can vary in size and location their communication with one another determines their function. These nerves conduct impulses from sensory receptors ...
... the cells to one another, to centers throughout the body or to other neurons. These neurons operate on excitation or inhibition and although nerve cells can vary in size and location their communication with one another determines their function. These nerves conduct impulses from sensory receptors ...
The brain is the body`s most complex organ. Neurons communicate
... Sensorycircuits (sight, touch, hearing, smell, taste) bring information to the nervous system, whereas motor circuits send information to muscles and glands. ...
... Sensorycircuits (sight, touch, hearing, smell, taste) bring information to the nervous system, whereas motor circuits send information to muscles and glands. ...
Neurophysiology
... • Post-Stimulus Time Histogram-- Shows firing rate changes over time • Period or Interval Histograms-- Show phase-locking of neural firing ...
... • Post-Stimulus Time Histogram-- Shows firing rate changes over time • Period or Interval Histograms-- Show phase-locking of neural firing ...