Physiological Plasticity of Single Neurons in Auditory Cortex of the
... at the beginning of a session to produce a brief (2-5 s) pupillary dilation. The US was delivered to the subcutaneous tissue of the forepaw contralateral to the recording site via a pair of fine wire electrodes. Pupillary size was monitored by an infrared pupillometer (Cassady, Farley, Weinberger, & ...
... at the beginning of a session to produce a brief (2-5 s) pupillary dilation. The US was delivered to the subcutaneous tissue of the forepaw contralateral to the recording site via a pair of fine wire electrodes. Pupillary size was monitored by an infrared pupillometer (Cassady, Farley, Weinberger, & ...
During Arm-Reaching and Isometric-Force Tasks
... In contrast, area 5 neuron discharge is highly modulated by the direction of movement and by the posture of the arm in reaching tasks (Battaglia-Mayer et al. 2001, 2003; Buneo et al. 2002; Ferraina et al. 2001; Kalaska et al. 1983, 1990; Lacquaniti et al. 1995; Mascaro et al. 2003; Scott et al. 1997 ...
... In contrast, area 5 neuron discharge is highly modulated by the direction of movement and by the posture of the arm in reaching tasks (Battaglia-Mayer et al. 2001, 2003; Buneo et al. 2002; Ferraina et al. 2001; Kalaska et al. 1983, 1990; Lacquaniti et al. 1995; Mascaro et al. 2003; Scott et al. 1997 ...
Neural coding of basic reward terms of animal
... the presence rather than the absence of the conditioned stimulus (contingency). Analysis of the conditions of learning reveals that rewards that are fully predicted do not contribute to learning [5]. Rather, the acquisition of associative strength of a conditioned stimulus depends on the discrepancy ...
... the presence rather than the absence of the conditioned stimulus (contingency). Analysis of the conditions of learning reveals that rewards that are fully predicted do not contribute to learning [5]. Rather, the acquisition of associative strength of a conditioned stimulus depends on the discrepancy ...
Inhibitory Gating of Basolateral Amygdala Inputs to the Prefrontal
... GABAergic interneurons. The PFC also possesses a variety of GABAergic interneurons, which have distinct morphological and physiological properties, including parvalbumin (PV) and somatostatin (SOM) expressing interneurons (Kawaguchi and Kubota, 1997, 1998; Marlin and Carter, 2014). In principle, BLA ...
... GABAergic interneurons. The PFC also possesses a variety of GABAergic interneurons, which have distinct morphological and physiological properties, including parvalbumin (PV) and somatostatin (SOM) expressing interneurons (Kawaguchi and Kubota, 1997, 1998; Marlin and Carter, 2014). In principle, BLA ...
Neuronal activity (c-Fos) delineating interactions of the cerebral
... The cerebral cortex and basal ganglia (BG) form a neural circuit that is disrupted in disorders such as Parkinson’s disease. We found that neuronal activity (c-Fos) in the BG followed cortical activity, i.e., high in arousal state and low in sleep state. To determine if cortical activity is necessar ...
... The cerebral cortex and basal ganglia (BG) form a neural circuit that is disrupted in disorders such as Parkinson’s disease. We found that neuronal activity (c-Fos) in the BG followed cortical activity, i.e., high in arousal state and low in sleep state. To determine if cortical activity is necessar ...
166 - UCSF Physiology - University of California, San Francisco
... use of a null allele of 1 integrin gene (Stephens et al., 1995) and generated heterozygous animals with one null allele and one Figure 1. emx1–cre induces recombination in excitatory but not inhibitory neurons in the hippocampus. a– c, Confocal conditional allele. This ensures the effi- micrographs ...
... use of a null allele of 1 integrin gene (Stephens et al., 1995) and generated heterozygous animals with one null allele and one Figure 1. emx1–cre induces recombination in excitatory but not inhibitory neurons in the hippocampus. a– c, Confocal conditional allele. This ensures the effi- micrographs ...
Sensorimotor cortical influences on cuneate nucleus
... undoubted functional importance, since if the neocortex imposes its rhythmic patterns of activity on the subcortical structures receiving direct corticofugal input, then the cortex may coherently induce oscillatory activity on these structures, thus deafferenting itself during the states of sleep an ...
... undoubted functional importance, since if the neocortex imposes its rhythmic patterns of activity on the subcortical structures receiving direct corticofugal input, then the cortex may coherently induce oscillatory activity on these structures, thus deafferenting itself during the states of sleep an ...
The neurophysiological correlates of motor tics following focal
... The cortico-basal ganglia pathway is involved in normal motor control and implicated in multiple movement disorders. Brief repetitive muscle contractions known as motor tics are a common symptom in several basal ganglia related motor disorders. We used focal micro-injections of the GABA-A antagonist ...
... The cortico-basal ganglia pathway is involved in normal motor control and implicated in multiple movement disorders. Brief repetitive muscle contractions known as motor tics are a common symptom in several basal ganglia related motor disorders. We used focal micro-injections of the GABA-A antagonist ...
A Computational Model of the Amygdala Nuclei`s Role in - laral
... the amygdala system. It receives afferent connections from various sensory and associative areas of cortex, from thalamus, and from deeper regions within the brain-stem, and it sends efferent connections both to BLA and to CeA. The model has an input layer (INP) of four leaky neurons (inp) activated ...
... the amygdala system. It receives afferent connections from various sensory and associative areas of cortex, from thalamus, and from deeper regions within the brain-stem, and it sends efferent connections both to BLA and to CeA. The model has an input layer (INP) of four leaky neurons (inp) activated ...
Title
... account for this attribution of Mr. Crane’s and Mr. Tees’s mental states? According to ST, we put ourselves in Mr. Crane’s and Mr. Tees’s shoes, so to speak, and imagine how upset we would be in each of their situations. According to TT, we deploy a theory, with some folk-psychological laws about wh ...
... account for this attribution of Mr. Crane’s and Mr. Tees’s mental states? According to ST, we put ourselves in Mr. Crane’s and Mr. Tees’s shoes, so to speak, and imagine how upset we would be in each of their situations. According to TT, we deploy a theory, with some folk-psychological laws about wh ...
Hypergravity hinders axonal development of motor neurons
... Earth and its stable gravitational conditions. Altering gravity can have profound impacts on the human body. This is especially relevant with the possibility of long-term space travel and habitation and the associated changes in gravity in different space environments. Although some of the effects o ...
... Earth and its stable gravitational conditions. Altering gravity can have profound impacts on the human body. This is especially relevant with the possibility of long-term space travel and habitation and the associated changes in gravity in different space environments. Although some of the effects o ...
Expression of ml-m4 Muscarinic Acetylcholine Receptor Proteins in
... The m l-m4 receptor immunoreactivities were differentially distributed in the rat hippocampus (Figs. I-4). In general, receptor immunoreactivities were localized in neurons, neuritic processes, and diffusely in the neuropil, although each antibody resulted in a distinct pattern of staining. Neuronal ...
... The m l-m4 receptor immunoreactivities were differentially distributed in the rat hippocampus (Figs. I-4). In general, receptor immunoreactivities were localized in neurons, neuritic processes, and diffusely in the neuropil, although each antibody resulted in a distinct pattern of staining. Neuronal ...
paper - Gatsby Computational Neuroscience Unit
... the variables z1 , . . . ,zl representing a motor plan or motor commands to muscles. Recent publications show that human reasoning and learning can also be cast into the form of probabilistic inference problems [27–29]. In these models learning of concepts, ranging from concrete to more abstract one ...
... the variables z1 , . . . ,zl representing a motor plan or motor commands to muscles. Recent publications show that human reasoning and learning can also be cast into the form of probabilistic inference problems [27–29]. In these models learning of concepts, ranging from concrete to more abstract one ...
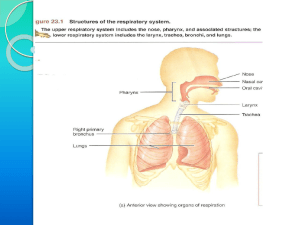
Respiratory System (Power Point Document)
... bronchioles, Terminal bronchioles, respiratory bronchioles, albeolar ducts and finally alveoli. Situated from the superior border of the 5th thorasic vertebra divided in to a right primary bronchus which goes in to the right lungs and a left primary bronchus which goes in to the left lungs. BLOOD AN ...
... bronchioles, Terminal bronchioles, respiratory bronchioles, albeolar ducts and finally alveoli. Situated from the superior border of the 5th thorasic vertebra divided in to a right primary bronchus which goes in to the right lungs and a left primary bronchus which goes in to the left lungs. BLOOD AN ...
Zinc Alters Excitatory Amino Acid Neurotoxicity on Cortical Neurons
... Department of Neurology, Stanford University Medical Center, Stanford, California 94305 ...
... Department of Neurology, Stanford University Medical Center, Stanford, California 94305 ...
Non-reward neural mechanisms in the orbitofrontal cortex
... Rolls, & Kischka, 2004), and even antisocial and psychopathic behaviour (Rolls, 2014). For these reasons, understanding the mechanisms that underlie non-reward is important not only for understanding normal human behaviour and how it changes when rewards are not received, but also for understanding ...
... Rolls, & Kischka, 2004), and even antisocial and psychopathic behaviour (Rolls, 2014). For these reasons, understanding the mechanisms that underlie non-reward is important not only for understanding normal human behaviour and how it changes when rewards are not received, but also for understanding ...
Molecules and mechanisms of dendrite development in Drosophila
... once the severing event has occurred. Importantly, however, caspase activity is very likely to be local, as activated caspases and cleaved caspase substrates are detected selectively in pruning dendritic arbors (Kuo et al., 2006; Williams et al., 2006). How this dendritic specificity is achieved is ...
... once the severing event has occurred. Importantly, however, caspase activity is very likely to be local, as activated caspases and cleaved caspase substrates are detected selectively in pruning dendritic arbors (Kuo et al., 2006; Williams et al., 2006). How this dendritic specificity is achieved is ...
Anticipated synchronization in neuronal circuits
... we investigate the existence of AS in neuronal circuits when the delayed feedback is replaced by an inhibitory loop mediated by chemical synapses. At the neuronal level, we show the existence of AS in 3-neuron or 3-neuron-populations microcircuits, where the self-feedback is provided either by an in ...
... we investigate the existence of AS in neuronal circuits when the delayed feedback is replaced by an inhibitory loop mediated by chemical synapses. At the neuronal level, we show the existence of AS in 3-neuron or 3-neuron-populations microcircuits, where the self-feedback is provided either by an in ...
Computing with Spiking Neuron Networks
... the soma, the cell body of the neuron. This brief electric pulse (1 or 2ms duration) then travels along the neuron’s axon, that in turn is linked up to the receiving end of other neurons, the dendrites (see Figure 1, left view). At the end of the axon, synapses connect one neuron to another, and at ...
... the soma, the cell body of the neuron. This brief electric pulse (1 or 2ms duration) then travels along the neuron’s axon, that in turn is linked up to the receiving end of other neurons, the dendrites (see Figure 1, left view). At the end of the axon, synapses connect one neuron to another, and at ...
Pre-Bötzinger complex

The pre-Bötzinger complex (preBötC) is a cluster of interneurons in the ventrolateral medulla of the brainstem. This complex has been proven to be essential for the generation of respiratory rhythm in mammals. The exact mechanism of the rhythm generation and transmission to motor nuclei remains controversial and the topic of much present research.Several synthetic compounds have been shown to act on neurons specific to the preBötC, most being selective agonists or antagonists to receptor subtypes on neurons in the vicinity. Since many of these neurons express GABA, glutamate, serotonin and adenosine receptors, chemicals custom tailored to bind at these sites are most effective at altering respiratory rhythm.Adenosine modulates the preBötC output via activation of the A1 and A2A receptor subtypes. An adenosine A1 receptor agonist has been shown to depress preBötC rhythmogenesis independent of the neurotransmitters GABA and glycine in ""in vitro"" preparations from 0-7 day old mice. Another synthetic drug specific to the adenosine A2A receptor subtype is CGS-21680 that has been shown to cause apneas in 14-21 day old rat pups in vivo. For this reason, it has been used as a model to study pathological conditions such as apnea of prematurity and SIDS in neonatal infants.