ch. 48 Nervous System notes
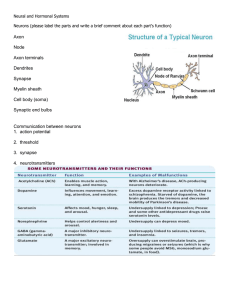
... Interneurons: integrate sensory input and motor output (carry stimuli in the brain and spinal cord) Motor Neurons: convey impulses from CNS to effector cells in muscles or glands Glial cells: support, protect, and nourish neurons ...
... Interneurons: integrate sensory input and motor output (carry stimuli in the brain and spinal cord) Motor Neurons: convey impulses from CNS to effector cells in muscles or glands Glial cells: support, protect, and nourish neurons ...
Neurons
... This transmission of an electrochemical impulse is called “firing.” They can either fire, or not. This is called the “all-or-none principle.” A neuron always fires with the same intensity regardless of the stimulation from the dendrites. ...
... This transmission of an electrochemical impulse is called “firing.” They can either fire, or not. This is called the “all-or-none principle.” A neuron always fires with the same intensity regardless of the stimulation from the dendrites. ...
Biology and Behaviour
... Seems to me that if we are to truly understand behaviour and that if we accept that the brain controls it, we must understand the brain The nervous system is built out of neurons or nerve cells, and glial cells, which are sort of the glue Glial cells do other support functions too ...
... Seems to me that if we are to truly understand behaviour and that if we accept that the brain controls it, we must understand the brain The nervous system is built out of neurons or nerve cells, and glial cells, which are sort of the glue Glial cells do other support functions too ...
Chapter 7: The Nervous System
... 1. Irritability- neurons have the ability to respond to a stimulus 2. Conductivity- the ability to transmit an impulse 3. The plasma membrane at rest is polarized, this is called the Resting potential (-70 mV); this means fewer positive ions are inside the cell (K+) than outside (Na+). As long as th ...
... 1. Irritability- neurons have the ability to respond to a stimulus 2. Conductivity- the ability to transmit an impulse 3. The plasma membrane at rest is polarized, this is called the Resting potential (-70 mV); this means fewer positive ions are inside the cell (K+) than outside (Na+). As long as th ...
Nervous System Student Notes
... Small branches called ___________ receive chemical or electrical input from the body. Neurons have _________ dendrites Large branches are called _____________________, which carry information away from the cell in the form of a nerve impulse. Neurons commonly have only ____________ ____________ are ...
... Small branches called ___________ receive chemical or electrical input from the body. Neurons have _________ dendrites Large branches are called _____________________, which carry information away from the cell in the form of a nerve impulse. Neurons commonly have only ____________ ____________ are ...
Lecture 9
... Computational neuroscience studies the nervous system from the point of view of its functionality and relies both on experimental data and on theoretical models of individual neurons and networks • Single neuron descriptions/models • Signal processing through synapses • Small circuits • Large neura ...
... Computational neuroscience studies the nervous system from the point of view of its functionality and relies both on experimental data and on theoretical models of individual neurons and networks • Single neuron descriptions/models • Signal processing through synapses • Small circuits • Large neura ...
Earthworm Action Potentials
... development of myelination allowed conduction velocities of similar magnitude in nerves of much smaller size.) A major experimental advantage of the earthworm nervous system is that these giant fibers can be stimulated by electrodes placed on the body of the animal and their responses can be recorde ...
... development of myelination allowed conduction velocities of similar magnitude in nerves of much smaller size.) A major experimental advantage of the earthworm nervous system is that these giant fibers can be stimulated by electrodes placed on the body of the animal and their responses can be recorde ...
Resting Potential
... What is the membrane potential if the ratio of sodium permeability to potassium is .02, chloride is not permeable, and the concentrations of the ions are as in the earlier table in the notes? What happens if, suddenly, the permeability to sodium becomes very high relative to potassium? 2. Passive pr ...
... What is the membrane potential if the ratio of sodium permeability to potassium is .02, chloride is not permeable, and the concentrations of the ions are as in the earlier table in the notes? What happens if, suddenly, the permeability to sodium becomes very high relative to potassium? 2. Passive pr ...
Neural and Hormonal Systems Neurons (please label the parts and
... The corpus callosum is a large ban of neural fibers that connects the two hemispheres of the brain. In some surgeries, the fibers are severed which cuts off communication between the two hemispheres of the brains. This is used as a form of treatment for epileptic seizures. ...
... The corpus callosum is a large ban of neural fibers that connects the two hemispheres of the brain. In some surgeries, the fibers are severed which cuts off communication between the two hemispheres of the brains. This is used as a form of treatment for epileptic seizures. ...
The Nervous System
... Talking Cells • The “signal” sent through a neuron is actually an electrical signal • Electricity is generated anytime an ion moves. By using the dam metaphor, the cells create ion movement cascades called action potentials – The movement of the ions cause changes in the + and – charges inside the ...
... Talking Cells • The “signal” sent through a neuron is actually an electrical signal • Electricity is generated anytime an ion moves. By using the dam metaphor, the cells create ion movement cascades called action potentials – The movement of the ions cause changes in the + and – charges inside the ...
31.1 The Neuron
... your senses. In your notes write out the path it would take from outside the body and through the aspects of the nervous system. ...
... your senses. In your notes write out the path it would take from outside the body and through the aspects of the nervous system. ...
nervous system 2 notes - Hicksville Public Schools
... I will drop a dollar bill between your open fingers. If you are able to catch the dollar, it is yours. ...
... I will drop a dollar bill between your open fingers. If you are able to catch the dollar, it is yours. ...
File
... System • STRUCTURES: brain, spinal cord, & peripheral nerves • FUNCTION: Recognizes and coordinates the body’s response to changes in its internal and external environments ...
... System • STRUCTURES: brain, spinal cord, & peripheral nerves • FUNCTION: Recognizes and coordinates the body’s response to changes in its internal and external environments ...
Neurons are the cells that carry messages between parts of the body
... The endocrine system uses chemicals released into the blood (hormones) to communicate between parts of the body. An organ that releases hormones is called a gland. The gland releases the hormones into the blood stream so they can then reach the target cells. Target cells have receptors on their cell ...
... The endocrine system uses chemicals released into the blood (hormones) to communicate between parts of the body. An organ that releases hormones is called a gland. The gland releases the hormones into the blood stream so they can then reach the target cells. Target cells have receptors on their cell ...
biology - TeacherWeb
... problem-solving, movement (___________ cortex), and some aspects of speech (____________ area); also considered the area where the seat of ______________ lies b. temporal lobe = part of the cerebrum in charge of _____________, speech reception, and some parts of the ________________ (hippocampus) c. ...
... problem-solving, movement (___________ cortex), and some aspects of speech (____________ area); also considered the area where the seat of ______________ lies b. temporal lobe = part of the cerebrum in charge of _____________, speech reception, and some parts of the ________________ (hippocampus) c. ...
Chapter 32 The Nervous System, Cells of the Nervous System
... form in stages, with shortterm memories including experiences of the preceding few minutes and long-term memories including experience from many years before D Hippocampus 海馬體plays a role in long-term memories D Amygdala杏仁核gives emotions. ...
... form in stages, with shortterm memories including experiences of the preceding few minutes and long-term memories including experience from many years before D Hippocampus 海馬體plays a role in long-term memories D Amygdala杏仁核gives emotions. ...
The Neuron: Building Block of the Nervous System
... the electrical charge across the cell membrane of the axon. When the neuron fires, this charge travels down the axon and causes neurotransmitters to be released by the terminal buttons. Sets off a chain reaction like a set of falling dominos. ...
... the electrical charge across the cell membrane of the axon. When the neuron fires, this charge travels down the axon and causes neurotransmitters to be released by the terminal buttons. Sets off a chain reaction like a set of falling dominos. ...
overview of neural f..
... Effect of E.P.S.P is to INCREASE probability that the receiving neuron will 'fire' (i.e. produce an action potential). ...
... Effect of E.P.S.P is to INCREASE probability that the receiving neuron will 'fire' (i.e. produce an action potential). ...
Chapter 2: Brain Development
... • Most embryonic cells are pluripotent stem cells • A variety of chemicals signal cells to turn into specialized cells • Ectodermal cells are inhibited by molecules, signalling a development into neural cells and not skin cells • After neural cell determination: ...
... • Most embryonic cells are pluripotent stem cells • A variety of chemicals signal cells to turn into specialized cells • Ectodermal cells are inhibited by molecules, signalling a development into neural cells and not skin cells • After neural cell determination: ...
Quiz Chapter 3 Brain Neural Communication Dr Myer How do
... What are the four lobes in the cortex? What is the frontal lobe responsible for? The parietal lobe? The temporal lobe? The occipital lobe? What is an experience-dependent brain? What is plasticity? What is an experience-expectant brain? What are two types of brain injury? Can your brain ...
... What are the four lobes in the cortex? What is the frontal lobe responsible for? The parietal lobe? The temporal lobe? The occipital lobe? What is an experience-dependent brain? What is plasticity? What is an experience-expectant brain? What are two types of brain injury? Can your brain ...
nervous system
... Neuron cell bodies are clustered together in the PNS= ganglia Satellite cells- surround neuron cell bodies, regulate environment Schwann cells- form a sheath around every axon, can myelinate axons ...
... Neuron cell bodies are clustered together in the PNS= ganglia Satellite cells- surround neuron cell bodies, regulate environment Schwann cells- form a sheath around every axon, can myelinate axons ...
Chapter 3: The Biological Bases of Behavior
... Communication in the Nervous System • Glia – structural support and insulation • Neurons – communication – Soma – cell body – Dendrites – receive – Axon – transmit away – Myelin sheath – speeds up transmission – Terminal Button – end of axon; secretes neurotransmitters – Neurotransmitters – chemica ...
... Communication in the Nervous System • Glia – structural support and insulation • Neurons – communication – Soma – cell body – Dendrites – receive – Axon – transmit away – Myelin sheath – speeds up transmission – Terminal Button – end of axon; secretes neurotransmitters – Neurotransmitters – chemica ...
Document
... •The study of processes and functions, incidental to, and characteristic of, life. •Physiology is an integrative science; examining body operation at all levels of organization, from cells to organs. •Homeostasis, flexibility, cell-to-cell communication, ...
... •The study of processes and functions, incidental to, and characteristic of, life. •Physiology is an integrative science; examining body operation at all levels of organization, from cells to organs. •Homeostasis, flexibility, cell-to-cell communication, ...