File
... Look at the picture carefully. Serotonin is a neurotransmitter. The nerve pathways in your brain that it is found in are related to feeling good. Why might Prozac work to reduce depression? ...
... Look at the picture carefully. Serotonin is a neurotransmitter. The nerve pathways in your brain that it is found in are related to feeling good. Why might Prozac work to reduce depression? ...
Nervous System
... Between the axon ending and the dendrite of the next neuron is a very tiny gap called the synapse (or synaptic gap, or synaptic cleft), which we will discuss in a little bit. For every neuron, there are between 1000 and 10,000 synapses. ...
... Between the axon ending and the dendrite of the next neuron is a very tiny gap called the synapse (or synaptic gap, or synaptic cleft), which we will discuss in a little bit. For every neuron, there are between 1000 and 10,000 synapses. ...
Q1 (from chapter 1)
... A. Lobotomy causes drastic changes in personality and comportment B. Major motor and sensory pathways cross sides C. Bilateral hippocampectomy causes global aphasia D. In most people the left hemisphere is dominant for language abilities E. Orbitofrontal cortex is responsible for social behavior Q2 ...
... A. Lobotomy causes drastic changes in personality and comportment B. Major motor and sensory pathways cross sides C. Bilateral hippocampectomy causes global aphasia D. In most people the left hemisphere is dominant for language abilities E. Orbitofrontal cortex is responsible for social behavior Q2 ...
File
... But new dendrites can grow Provides room for more connections to other neurons New connections are basis for learning ...
... But new dendrites can grow Provides room for more connections to other neurons New connections are basis for learning ...
The Brain and Behavior
... CNS. • Motoneurons or Multipolar neurons carry signals from the CNS muscles and glands. • Interneurons or Pseudopolare (Spelling) cells form all the neural wiring within the CNS. These have two axons (instead of an axon and a dendrite). One axon communicates with the spinal cord; one with either the ...
... CNS. • Motoneurons or Multipolar neurons carry signals from the CNS muscles and glands. • Interneurons or Pseudopolare (Spelling) cells form all the neural wiring within the CNS. These have two axons (instead of an axon and a dendrite). One axon communicates with the spinal cord; one with either the ...
Review - TheThinkSpot
... nervous system, which registers stimuli and regulates conscious actions, and the autonomic nervous system, which controls ...
... nervous system, which registers stimuli and regulates conscious actions, and the autonomic nervous system, which controls ...
Unit 3A: Neural Processing and the Endocrine System Introduction
... 2. Biological psychologists study the linkage and interplay between the body and the mind. 3. Even more broadly, there is a biopsychosocial component. This concept believes we do the things we do because of (1) our bodies, (2) our minds or thinking, and (3) the culture that we live in. Neurons 1. Ne ...
... 2. Biological psychologists study the linkage and interplay between the body and the mind. 3. Even more broadly, there is a biopsychosocial component. This concept believes we do the things we do because of (1) our bodies, (2) our minds or thinking, and (3) the culture that we live in. Neurons 1. Ne ...
Working Together for a World Free of Chemical Weapons
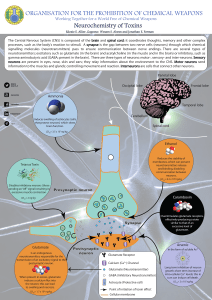
... The Central Nervous System (CNS) is composed of the brain and spinal cord; it coordinates thoughts, memory and other complex processes, such as the body’s reaction to stimuli. A synapse is the gap between two nerve cells (neurons) through which chemical signalling molecules (neurotransmitters) pass ...
... The Central Nervous System (CNS) is composed of the brain and spinal cord; it coordinates thoughts, memory and other complex processes, such as the body’s reaction to stimuli. A synapse is the gap between two nerve cells (neurons) through which chemical signalling molecules (neurotransmitters) pass ...
Nervous Sys Learning targets
... 1. List the basic functions of the nervous system 2. draw a concept map to show the structural and functional divisions of the nervous system 3. List the types of neuroglia and cite their functions ...
... 1. List the basic functions of the nervous system 2. draw a concept map to show the structural and functional divisions of the nervous system 3. List the types of neuroglia and cite their functions ...
1) Which is NOT a characteristic of living organisms
... 13) Both gates of the voltage-gated Na+ channels are open. 14) The voltage-gated Na+ channels activation gates are closed but the inactivation gates are open. 15) The neuron is depolarizing without using voltage-gated channels. 16) K+ is leaving the neuron through voltage-gated channels. 17) Which l ...
... 13) Both gates of the voltage-gated Na+ channels are open. 14) The voltage-gated Na+ channels activation gates are closed but the inactivation gates are open. 15) The neuron is depolarizing without using voltage-gated channels. 16) K+ is leaving the neuron through voltage-gated channels. 17) Which l ...
Synapses - JNCASR Desktop
... • When an action potential reaches a synapse, voltage gated ion channels cell membrane are opened allowing an influx of calcium ions into the pre-synaptic terminal… ie, depolarization of the membrane. • This causes a small 'packet' of a chemical neurotransmitter to be released into a small gap betw ...
... • When an action potential reaches a synapse, voltage gated ion channels cell membrane are opened allowing an influx of calcium ions into the pre-synaptic terminal… ie, depolarization of the membrane. • This causes a small 'packet' of a chemical neurotransmitter to be released into a small gap betw ...
Unit 3A Notes
... 2. Biological psychologists study the linkage and interplay between the body and the mind. 3. Even more broadly, there is a biopsychosocial component. This concept believes we do the things we do because of (1) our bodies, (2) our minds or thinking, and (3) the culture that we live in. 2. Neurons 1. ...
... 2. Biological psychologists study the linkage and interplay between the body and the mind. 3. Even more broadly, there is a biopsychosocial component. This concept believes we do the things we do because of (1) our bodies, (2) our minds or thinking, and (3) the culture that we live in. 2. Neurons 1. ...
Study questions for this lab.
... ascend upward toward the brain? Where is this tract located? Where are third order neuronal cell bodies located in the pain and temperature pathway? Of what use is this knowledge about the routes by which the various sensory modalities pass from the spinal cord to the brain? What is an electromyogra ...
... ascend upward toward the brain? Where is this tract located? Where are third order neuronal cell bodies located in the pain and temperature pathway? Of what use is this knowledge about the routes by which the various sensory modalities pass from the spinal cord to the brain? What is an electromyogra ...
OCR Document - MrsGorukhomework
... to initiate an impulse, that is, depolarizes the cell, which also means strong enough to open the voltage gated channels. Once that starts, the action potential continues. Strong impulses do NOT initiate a stronger response. If threshold is reached its all-or-none. But stronger impulses must be reco ...
... to initiate an impulse, that is, depolarizes the cell, which also means strong enough to open the voltage gated channels. Once that starts, the action potential continues. Strong impulses do NOT initiate a stronger response. If threshold is reached its all-or-none. But stronger impulses must be reco ...
General design of the nervous system
... The incoming signal enters the neuron throught synapses mainly on the neuronal dendrites, but also on the cell body. The output signal travels by way of a single axon, leaving the neuron, but this axon has many separate branches to other parts of the nervous system or peripheral body. ...
... The incoming signal enters the neuron throught synapses mainly on the neuronal dendrites, but also on the cell body. The output signal travels by way of a single axon, leaving the neuron, but this axon has many separate branches to other parts of the nervous system or peripheral body. ...
Neuroscience and Behavior
... problem on both sides of my periphery. So, several more tests were run, and he thought I was either going blind from the Reyes’ Syndrome I had five years prior, I had a tumor somewhere in my brain. It turned out to be the latter. I had a pituitary adenoma. It seemed like a week later, I was rushed i ...
... problem on both sides of my periphery. So, several more tests were run, and he thought I was either going blind from the Reyes’ Syndrome I had five years prior, I had a tumor somewhere in my brain. It turned out to be the latter. I had a pituitary adenoma. It seemed like a week later, I was rushed i ...
Name
... 1. What is homeostasis? Give examples. 2. What are the functions of the nervous system? 3. What is the structure of a neuron and what kinds of neurons are found in the body? 4. How do nerve impulses travel from one neuron to another? 5. What are the structure and functions of the central nervous sys ...
... 1. What is homeostasis? Give examples. 2. What are the functions of the nervous system? 3. What is the structure of a neuron and what kinds of neurons are found in the body? 4. How do nerve impulses travel from one neuron to another? 5. What are the structure and functions of the central nervous sys ...
SChapter 12
... that is usually caused by neurotransmitters. 5) Response of postsynaptic cell can vary depending on the response of the receptor that was stimulated *see fig. 12-7 for an overview of these important processes* ▪Transmembrane Potential- three important concepts regarding the transmembrane potential: ...
... that is usually caused by neurotransmitters. 5) Response of postsynaptic cell can vary depending on the response of the receptor that was stimulated *see fig. 12-7 for an overview of these important processes* ▪Transmembrane Potential- three important concepts regarding the transmembrane potential: ...
Tayler
... Cerebral Hemispheres: Controls muscle functions along with speech, thought, emotions, reading, writing, and learning o Right hemisphere o Left hemisphere ...
... Cerebral Hemispheres: Controls muscle functions along with speech, thought, emotions, reading, writing, and learning o Right hemisphere o Left hemisphere ...