The Nervous System
... Gray Matter: Darker CNS tissues made up of neurons’ cell bodies & dendrites White Matter: Paler CNS tissues comprised of myelin-sheathed nerve fibers ...
... Gray Matter: Darker CNS tissues made up of neurons’ cell bodies & dendrites White Matter: Paler CNS tissues comprised of myelin-sheathed nerve fibers ...
The Nervous System - Volunteer State Community College
... Signal transmission along a neuron depends on voltages created by ionic fluxes across neuron plasma membranes. Membrane potentials arise from differences in ion concentrations between a cell’s contents and the extracellular fluid. All cells have an electrical potential or voltage across their plasma ...
... Signal transmission along a neuron depends on voltages created by ionic fluxes across neuron plasma membranes. Membrane potentials arise from differences in ion concentrations between a cell’s contents and the extracellular fluid. All cells have an electrical potential or voltage across their plasma ...
46 Chapter Review: Fill-in-the
... deficiency of it is associated with Parkinson's disease, and anoversensitivity to it is associated with some cases of schizophrenia. 10. The control voluntary body mo;'ements, speech production, and such functions as thinking, motivation, planning for the future, impulse control, and emotional respo ...
... deficiency of it is associated with Parkinson's disease, and anoversensitivity to it is associated with some cases of schizophrenia. 10. The control voluntary body mo;'ements, speech production, and such functions as thinking, motivation, planning for the future, impulse control, and emotional respo ...
CHAPTER 12 AND 13 OUTLINE
... • • Causes the membrane to become more permeable to potassium and chloride ions • • Leaves the charge on the inner surface negative • • Reduces the postsynaptic neuron’s ability to produce an action potential Summation • • A single EPSP cannot induce an action potential • • EPSPs must summate tempo ...
... • • Causes the membrane to become more permeable to potassium and chloride ions • • Leaves the charge on the inner surface negative • • Reduces the postsynaptic neuron’s ability to produce an action potential Summation • • A single EPSP cannot induce an action potential • • EPSPs must summate tempo ...
Chapter 48: The Nervous System
... Depolarization: Na+ channels open & Na+ flows into neuron reversing polarity Re-polarization: K+ ions allowed into neuron as Na+ is blocked Refractory: brief period of time when cell can not be stimulated to carry an impulse ...
... Depolarization: Na+ channels open & Na+ flows into neuron reversing polarity Re-polarization: K+ ions allowed into neuron as Na+ is blocked Refractory: brief period of time when cell can not be stimulated to carry an impulse ...
The Brain
... ions- Positively charged sodium and potassium atoms flow back and forth across the cell membrane but they do not cross at the same rate- there is a slightly higher concentration of negatively charged ions inside the cell 2. -70 millivolts- charge ...
... ions- Positively charged sodium and potassium atoms flow back and forth across the cell membrane but they do not cross at the same rate- there is a slightly higher concentration of negatively charged ions inside the cell 2. -70 millivolts- charge ...
Inside the brain
... The parietal lobe processes information from the body and senses, and integrates it to help orient the body and carry out movement in space. The occipital lobe is the part of the brain that manages vision, containing dozens of areas that are specialised for processing inputs from the eyes. The tempo ...
... The parietal lobe processes information from the body and senses, and integrates it to help orient the body and carry out movement in space. The occipital lobe is the part of the brain that manages vision, containing dozens of areas that are specialised for processing inputs from the eyes. The tempo ...
Document
... • Oligodendricytes and Schwann cells – Provide insulation around axons of CNS and PNS neurons ...
... • Oligodendricytes and Schwann cells – Provide insulation around axons of CNS and PNS neurons ...
PD233-Lecture6
... Potential difference leads to flow of current flow when two points with different electric potential are connected with conducting media. ...
... Potential difference leads to flow of current flow when two points with different electric potential are connected with conducting media. ...
The Nervous System
... Responds and adapts to changes that occur both inside and outside the body (Ex: pain, temperature, pregnancy) ...
... Responds and adapts to changes that occur both inside and outside the body (Ex: pain, temperature, pregnancy) ...
neuron
... through the cell membrane • If resting potential rises above threshold, an action potential starts to travel from the cell body down the axon – Threshold - Each neuron receives excitatory and inhibitory signals from many neurons. When the excitatory signals minus the inhibitory signals exceed a mini ...
... through the cell membrane • If resting potential rises above threshold, an action potential starts to travel from the cell body down the axon – Threshold - Each neuron receives excitatory and inhibitory signals from many neurons. When the excitatory signals minus the inhibitory signals exceed a mini ...
Cells of the Nervous System
... • Form myelin which helps the speed of the action potential. In Multiple Sclerosis, the myelin is broken down and axons become less efficient. ...
... • Form myelin which helps the speed of the action potential. In Multiple Sclerosis, the myelin is broken down and axons become less efficient. ...
Resting Potential
... cells; form inner lining of brain & s.c.; provide a layer for diffusion to occur ...
... cells; form inner lining of brain & s.c.; provide a layer for diffusion to occur ...
Chapter 8 Study Guide: The Nervous System
... – Neurons and glial cells – Neurons conduct impulses, whereas glial cells are for support ...
... – Neurons and glial cells – Neurons conduct impulses, whereas glial cells are for support ...
Circulatory System Directs blood from the heart to the rest of the
... •Small branches called dendrites receive chemical or electrical input from the body. Neurons have many dendrites •Large branches are called axons, or nerve fibers, which carry information away from the cell in the form of a nerve impulse. Neurons commonly have only 1 axon •Nerves are simply bundles ...
... •Small branches called dendrites receive chemical or electrical input from the body. Neurons have many dendrites •Large branches are called axons, or nerve fibers, which carry information away from the cell in the form of a nerve impulse. Neurons commonly have only 1 axon •Nerves are simply bundles ...
36.1 The Nervous System Neurons: Basic units of
... The cerebrum controls conscious activities – language, intelligence, memory, movement, senses The cerebellum controls balance, posture, and coordination The medulla oblongata controls involuntary activities The sympathetic nervous system control functions in times of stress and the parasympathetic c ...
... The cerebrum controls conscious activities – language, intelligence, memory, movement, senses The cerebellum controls balance, posture, and coordination The medulla oblongata controls involuntary activities The sympathetic nervous system control functions in times of stress and the parasympathetic c ...
neuron
... • 5. Myelin Sheath: a layer of fatty cells segmentally encasing the fibers of many axons which allows faster transmission speeds in neurons ...
... • 5. Myelin Sheath: a layer of fatty cells segmentally encasing the fibers of many axons which allows faster transmission speeds in neurons ...
Handout - Science in the News
... Channelrhodopsin: A protein that can be artificially introduced into neurons to give them the ability to convert light into electrical impulses. Dendrite: Wire-like appendages that neurons use to receive impulses from other neurons (axons make synapses onto dendrites). DNA: Genetic material of cells ...
... Channelrhodopsin: A protein that can be artificially introduced into neurons to give them the ability to convert light into electrical impulses. Dendrite: Wire-like appendages that neurons use to receive impulses from other neurons (axons make synapses onto dendrites). DNA: Genetic material of cells ...
Nerves Powerpoint
... – In peripheral nervous system, Schwann cells provide the myelin and can also regrow the axon if it is damaged ...
... – In peripheral nervous system, Schwann cells provide the myelin and can also regrow the axon if it is damaged ...
UNIT 3A: Biological Bases of Behavior – Neural Processing and the
... 3 million times slower than that of electricity through a wire Brain activity is measured in milliseconds (thousandths of a second) v. computer activity in nanoseconds (billionths of a second) ...
... 3 million times slower than that of electricity through a wire Brain activity is measured in milliseconds (thousandths of a second) v. computer activity in nanoseconds (billionths of a second) ...
Chapter 4
... IPSPs – If membrane is depolarized sufficiently it will generate a sudden change in the electrical state of the cell • Action Potential ...
... IPSPs – If membrane is depolarized sufficiently it will generate a sudden change in the electrical state of the cell • Action Potential ...
Homeostasis Test%28CNS%29-Tawsif Hossain
... a) Single main dendrite and axon b) Is found in the brain and spinal cord c) Has several dendrites and a single axon d) Has a single process that extends from the cell body e) Found in the peripheral nervous system. 3) Which of the option is true? Serotonin: a) Is used by the brain and autonomic neu ...
... a) Single main dendrite and axon b) Is found in the brain and spinal cord c) Has several dendrites and a single axon d) Has a single process that extends from the cell body e) Found in the peripheral nervous system. 3) Which of the option is true? Serotonin: a) Is used by the brain and autonomic neu ...
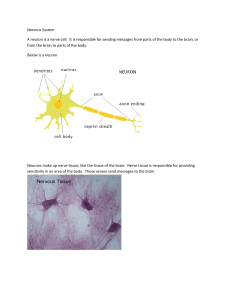
Nervous System A neuron is a nerve cell. It is responsible for
... Below you will find a plastic model of the brain. The brain is responsible for sending and receiving all the signals that make the organs of our bodies function properly. The brain is why we blink, breathe and our hearts beat without thinking about it or being able to really stop it for very long. ...
... Below you will find a plastic model of the brain. The brain is responsible for sending and receiving all the signals that make the organs of our bodies function properly. The brain is why we blink, breathe and our hearts beat without thinking about it or being able to really stop it for very long. ...