LECTURE FIVE
... central problem with all the different notions of holism as the idea that the determining factor in semantic evaluation is the notion of an "epistemic bond". Briefly, P is an epistemic bond of Q if the meaning of P is considered by someone to be relevant for the determination of the meaning of Q. Me ...
... central problem with all the different notions of holism as the idea that the determining factor in semantic evaluation is the notion of an "epistemic bond". Briefly, P is an epistemic bond of Q if the meaning of P is considered by someone to be relevant for the determination of the meaning of Q. Me ...
The human brain is a 3 pound mass of fatty tissue that controls all
... Action potentials: Nerve impulses involve the opening and closing of ion channels, water-filled molecular tunnels that pass through the cell membrane and allow ions— electrically charged atoms—or small molecules to enter or leave the cell. The flow of these ions creates an electrical current that pr ...
... Action potentials: Nerve impulses involve the opening and closing of ion channels, water-filled molecular tunnels that pass through the cell membrane and allow ions— electrically charged atoms—or small molecules to enter or leave the cell. The flow of these ions creates an electrical current that pr ...
Nervous System ppt
... Pumps Na+ (sodium) outside & Pumps K+ (potassium) inside Membrane leaks and some K+ goes back out Resting Potential= -70mV because overall postive charge outside and negative charge inside ...
... Pumps Na+ (sodium) outside & Pumps K+ (potassium) inside Membrane leaks and some K+ goes back out Resting Potential= -70mV because overall postive charge outside and negative charge inside ...
What is real? How do you define real?
... neural encoding by showing how reverse-correlation methods are used to construct estimates of firing rates in response to time-varying stimuli. These methods have been applied extensively to neural responses in the retina, lateral geniculate nucleus (LGN) of the thalamus, and primary visual cortex, ...
... neural encoding by showing how reverse-correlation methods are used to construct estimates of firing rates in response to time-varying stimuli. These methods have been applied extensively to neural responses in the retina, lateral geniculate nucleus (LGN) of the thalamus, and primary visual cortex, ...
Module I. Introduction to biophysical models of individual cells and... plane analysis important to capture phenomenology and sometimes – biophysical mechanisms
... Module I. Introduction to biophysical models of individual cells and phase plane analysis Models of different detailedness are needed at different times. Sometimes it is important to capture phenomenology and sometimes – biophysical mechanisms 1. Neuron, ions, firing, bursting, spiking, tonic and ph ...
... Module I. Introduction to biophysical models of individual cells and phase plane analysis Models of different detailedness are needed at different times. Sometimes it is important to capture phenomenology and sometimes – biophysical mechanisms 1. Neuron, ions, firing, bursting, spiking, tonic and ph ...
Text 4-Nervous system: Organization and Physiology
... Remember the synapse … when the action potential arrives at the axon terminals … The synapse is the point of communication between two neurons. Chemical synapses have a synaptic cleft (about 10 – 20 nm wide) and neurotransmitter diffuses across the cleft to bind to receptors on the postsynaptic neu ...
... Remember the synapse … when the action potential arrives at the axon terminals … The synapse is the point of communication between two neurons. Chemical synapses have a synaptic cleft (about 10 – 20 nm wide) and neurotransmitter diffuses across the cleft to bind to receptors on the postsynaptic neu ...
D. Vertebrate Nervous Systems
... Proteins, amino acids, sulfate, and phosphate are the principal intracellular anions. Cl– is the principal extracellular anion. Ungated ion channels allow ions to diffuse across the plasma membrane. These channels are always open. This diffusion does not achieve an equilibrium since the so ...
... Proteins, amino acids, sulfate, and phosphate are the principal intracellular anions. Cl– is the principal extracellular anion. Ungated ion channels allow ions to diffuse across the plasma membrane. These channels are always open. This diffusion does not achieve an equilibrium since the so ...
Describe how action potentials are generated
... Threshold and Action Potentials • Threshold – membrane is depolarized by 15 to 20 mV • Established by the total amount of current flowing through the membrane • Weak (subthreshold) stimuli are not relayed into action potentials • Strong (threshold) stimuli are relayed into action potentials • All-o ...
... Threshold and Action Potentials • Threshold – membrane is depolarized by 15 to 20 mV • Established by the total amount of current flowing through the membrane • Weak (subthreshold) stimuli are not relayed into action potentials • Strong (threshold) stimuli are relayed into action potentials • All-o ...
Describe how action potentials are generated and
... Threshold and Action Potentials • Threshold – membrane is depolarized by 15 to 20 mV • Established by the total amount of current flowing through the membrane • Weak (subthreshold) stimuli are not relayed into action potentials • Strong (threshold) stimuli are relayed into action potentials • All-o ...
... Threshold and Action Potentials • Threshold – membrane is depolarized by 15 to 20 mV • Established by the total amount of current flowing through the membrane • Weak (subthreshold) stimuli are not relayed into action potentials • Strong (threshold) stimuli are relayed into action potentials • All-o ...
Slide ()
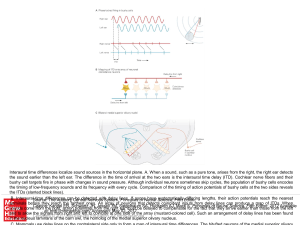
... the sound earlier than the left ear. The difference in the time of arrival at the two ears is the interaural time delay (ITD). Cochlear nerve fibers and their bushy cell targets fire in phase with changes in sound pressure. Although individual neurons sometimes skip cycles, the population of bushy c ...
... the sound earlier than the left ear. The difference in the time of arrival at the two ears is the interaural time delay (ITD). Cochlear nerve fibers and their bushy cell targets fire in phase with changes in sound pressure. Although individual neurons sometimes skip cycles, the population of bushy c ...
File
... Activity 34.2 The Human Cerebrum 1. What part of the brain controls muscle activity and maintaining balance. 2. What is the job of the frontal lobe? 3. What is the job of the parietal lobe? Activity 34.3 Structures of the Human Brain Practice the structures of the human brain. Interactive Tutorial 3 ...
... Activity 34.2 The Human Cerebrum 1. What part of the brain controls muscle activity and maintaining balance. 2. What is the job of the frontal lobe? 3. What is the job of the parietal lobe? Activity 34.3 Structures of the Human Brain Practice the structures of the human brain. Interactive Tutorial 3 ...
Report
... The background K channels (K2P) TRESK and TREK2 are highly expressed in the dorsal root ganglia (DRG), accounting for the largest fraction of the resting potassium conductance in these neurons. Recent evidence supports the role of TRESK in setting up sensory neuron excitability under pathological co ...
... The background K channels (K2P) TRESK and TREK2 are highly expressed in the dorsal root ganglia (DRG), accounting for the largest fraction of the resting potassium conductance in these neurons. Recent evidence supports the role of TRESK in setting up sensory neuron excitability under pathological co ...
Membrane potential
... channels in the membrane to open • As a result of ion flow through these channels, the inside of neuron briefly ...
... channels in the membrane to open • As a result of ion flow through these channels, the inside of neuron briefly ...
Lectures 26-27 Study Guide
... helpful, but that you don’t need to know, I will write in green. Questions to think about I will write in blue. Lecture 26: Physiology, Membrane Potential Neuron: Nerve cells that transfer information within the body. Neurons are elongated because they have to transmit signals around the brain and b ...
... helpful, but that you don’t need to know, I will write in green. Questions to think about I will write in blue. Lecture 26: Physiology, Membrane Potential Neuron: Nerve cells that transfer information within the body. Neurons are elongated because they have to transmit signals around the brain and b ...
Bradley`s.
... Its unique ability to send and receive specific signals from specific parts of the body using nerve cells, chemicals, and electrical impulses is simply amazing ...
... Its unique ability to send and receive specific signals from specific parts of the body using nerve cells, chemicals, and electrical impulses is simply amazing ...
Nervous Tissue - MrsSconyersAnatomy
... composition Kinetic energy – energy being used for motion or force ...
... composition Kinetic energy – energy being used for motion or force ...
Nervous System - De Anza College
... long distance – electrical signals short distance chemical signals ...
... long distance – electrical signals short distance chemical signals ...
Time Zones
... 2. Name 2 things that can compromise neural communication (especially synaptic transmission): 3. Name the main function of the Myelin Sheath? 4. Name the 3 types of Neurons: 5. One word to describe all of a human’s cell nuclei (in regards to genetics)? 6. These long threads make a chromosome. Genes ...
... 2. Name 2 things that can compromise neural communication (especially synaptic transmission): 3. Name the main function of the Myelin Sheath? 4. Name the 3 types of Neurons: 5. One word to describe all of a human’s cell nuclei (in regards to genetics)? 6. These long threads make a chromosome. Genes ...
Chapter 2 quiz level - easy topic: neurons
... A) bundles of nerves. B) cells in the brain that are believed to help clean and feed brain cells. C) chemical transmitters found in the hypothalamus. D) cells that send and receive information. ...
... A) bundles of nerves. B) cells in the brain that are believed to help clean and feed brain cells. C) chemical transmitters found in the hypothalamus. D) cells that send and receive information. ...
Assignment 1 - Gordon State College
... 1. Communication in the nervous system takes place via _____________ or nerve cells. 2. The human brain is estimated to have (how many) _____________________neurons. 3. Cells that provide nutrition and support for neurons, remove waste products, and enhance the speed of communication are called ____ ...
... 1. Communication in the nervous system takes place via _____________ or nerve cells. 2. The human brain is estimated to have (how many) _____________________neurons. 3. Cells that provide nutrition and support for neurons, remove waste products, and enhance the speed of communication are called ____ ...