Slide 1
... and allows positively charged ions into the axon. This overwhelming positive charge causes an electrical charge to form (an action potential). At 120 meters per second, the action potential travels to the terminal buttons via the axon. ...
... and allows positively charged ions into the axon. This overwhelming positive charge causes an electrical charge to form (an action potential). At 120 meters per second, the action potential travels to the terminal buttons via the axon. ...
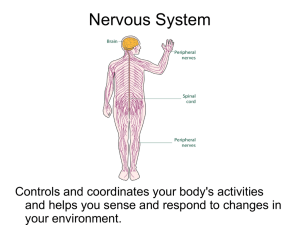
Nervous System
... Figure 11.15a Action potential propagation in unmyelinated and myelinated axons. ...
... Figure 11.15a Action potential propagation in unmyelinated and myelinated axons. ...
Nervous System - Uplift Education
... Generation and propagation of nerve impulse along one neuron= irritability Conductivity is the ability of one neuron to signal another. This occurs in an entirely different fashion at the synapse, or gap, ...
... Generation and propagation of nerve impulse along one neuron= irritability Conductivity is the ability of one neuron to signal another. This occurs in an entirely different fashion at the synapse, or gap, ...
Resting Membrane Potential
... 2. What must happen before sodium can rush into the axon? 3. Why does potassium leave the neuron during ...
... 2. What must happen before sodium can rush into the axon? 3. Why does potassium leave the neuron during ...
neurons
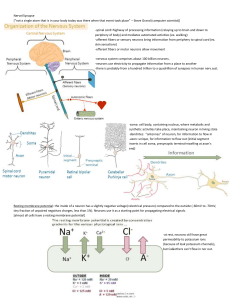
... contains genetic material and other structures that are found in virtually all the cells in the body. Extending out from the cell body are many short, branching fibers, called dendrites. Dendrites receive messages from other neurons or specialized cells. The axon is a single, elongated tube that ext ...
... contains genetic material and other structures that are found in virtually all the cells in the body. Extending out from the cell body are many short, branching fibers, called dendrites. Dendrites receive messages from other neurons or specialized cells. The axon is a single, elongated tube that ext ...
The neuron Label the following terms: Soma Axon terminal Axon
... 1. The presynaptic neuron sends neurotransmitters to postsynaptic neuron. 2. Neurotransmitters bind to receptors on the postsynaptic cell. - This action will either excite or inhibit the postsynaptic cell. - The soma becomes more positive. 3. The positive charge reaches the axon hillock. - Once the ...
... 1. The presynaptic neuron sends neurotransmitters to postsynaptic neuron. 2. Neurotransmitters bind to receptors on the postsynaptic cell. - This action will either excite or inhibit the postsynaptic cell. - The soma becomes more positive. 3. The positive charge reaches the axon hillock. - Once the ...
I. Functions and Divisions of the Nervous System A. The nervous
... b. Anionic proteins balance the cations inside the cell, while chloride ions mostly balance cations outside of the cell. c. Potassium ions (K+) play the most important role in generating a resting membrane potential, since the membrane is roughly 25 times more permeable to K+ than Na+. D. Membrane P ...
... b. Anionic proteins balance the cations inside the cell, while chloride ions mostly balance cations outside of the cell. c. Potassium ions (K+) play the most important role in generating a resting membrane potential, since the membrane is roughly 25 times more permeable to K+ than Na+. D. Membrane P ...
Assignment 2 - Gordon State College
... 1. Communication in the nervous system takes place via _____________ or nerve cells. 2. The human brain is estimated to have (how many) _____________________neurons. 3. Cells that provide nutrition and support for neurons, remove waste products, and enhance the speed of communication are called ____ ...
... 1. Communication in the nervous system takes place via _____________ or nerve cells. 2. The human brain is estimated to have (how many) _____________________neurons. 3. Cells that provide nutrition and support for neurons, remove waste products, and enhance the speed of communication are called ____ ...
The Neuron - Austin Community College
... Their magnitude varies directly with the strength of the stimulus – the stronger the stimulus the more the voltage changes and the farther the current goes Sufficiently strong graded potentials can initiate action potentials if they maintain threshold by the time reach the trigger zone ...
... Their magnitude varies directly with the strength of the stimulus – the stronger the stimulus the more the voltage changes and the farther the current goes Sufficiently strong graded potentials can initiate action potentials if they maintain threshold by the time reach the trigger zone ...
The Nervous System
... These 2 systems are antagonistic. Typically, we balance these 2 to keep ourselves in a state of dynamic balance. We’ll go further into the difference btwn these 2 later! ...
... These 2 systems are antagonistic. Typically, we balance these 2 to keep ourselves in a state of dynamic balance. We’ll go further into the difference btwn these 2 later! ...
Impulse Conduction Practice Questions
... a. Which area of the graph indicates the diffusion of Na+ ions into the neurons? Explain your answer. (2 marks) ...
... a. Which area of the graph indicates the diffusion of Na+ ions into the neurons? Explain your answer. (2 marks) ...
Chapter 2: Introduction to Physiology of Perception
... neurons. • Recording electrode is inside the nerve fiber. • Reference electrode is outside the fiber. ...
... neurons. • Recording electrode is inside the nerve fiber. • Reference electrode is outside the fiber. ...
Psychology`s biological roots: neurons and neural communication
... Neural comm. ii After passing through the empty synaptic cleft the neurotransmitters attach or bind to receptors on the postsynaptic neuron These neurotransmitters can then make the receiving neuron either more or less likely to fire It is in this infinitesimally small space that irregularities ca ...
... Neural comm. ii After passing through the empty synaptic cleft the neurotransmitters attach or bind to receptors on the postsynaptic neuron These neurotransmitters can then make the receiving neuron either more or less likely to fire It is in this infinitesimally small space that irregularities ca ...
How is the Nervous System Organized? a Class Objectives a What
... from one neuron to the next. - It is associated with _________________________________ ...
... from one neuron to the next. - It is associated with _________________________________ ...
Name: Date: Period: ______ Unit 7, Part 2 Notes: The Nervous
... 19. Initially, scientists measured the resting potential of a nerve cell using a microelectrode placed inside the cell, a reference microelectrode placed outside the cell, and a voltmeter (voltage meter). ...
... 19. Initially, scientists measured the resting potential of a nerve cell using a microelectrode placed inside the cell, a reference microelectrode placed outside the cell, and a voltmeter (voltage meter). ...
W10 Brain Development
... ▫ Organizing thoughts, planning for the future ▫ Undergoes significant changes during adolescence Not fully developed until mid-20’s. ...
... ▫ Organizing thoughts, planning for the future ▫ Undergoes significant changes during adolescence Not fully developed until mid-20’s. ...
irons.conroeisd.net
... A biochemical reaction that both humans and animals experience during intense stress or fear. The nervous system releases hormones causing changes to occur throughout the body. ...
... A biochemical reaction that both humans and animals experience during intense stress or fear. The nervous system releases hormones causing changes to occur throughout the body. ...
doc Nerve and synapses
... -Many types of neurotransmitters interact mainly or entirely with metabotropic receptors. These substances, such as dopamine, serotonin and norepinephrine, as well as neuropeptides like substance Y and endorphins, are often referred to as neuromodulators. They are not directly involved in the fast f ...
... -Many types of neurotransmitters interact mainly or entirely with metabotropic receptors. These substances, such as dopamine, serotonin and norepinephrine, as well as neuropeptides like substance Y and endorphins, are often referred to as neuromodulators. They are not directly involved in the fast f ...
NAME: AP Biology/ Ms. Gaynor (Unit #10: Animal Physiology
... 1. Draw and label the parts of a neuron including: cell body, dendrites, nucleus, axon, myelin sheath, Schwann cells, and Nodes of Ranvier. Then add arrows to your drawing to show the direction of impulse. ...
... 1. Draw and label the parts of a neuron including: cell body, dendrites, nucleus, axon, myelin sheath, Schwann cells, and Nodes of Ranvier. Then add arrows to your drawing to show the direction of impulse. ...
Document
... receive input from other neurons are called: A. dendrites B. axons C. vesicles D. myelins ...
... receive input from other neurons are called: A. dendrites B. axons C. vesicles D. myelins ...
The Nervous System
... Key Concepts and Important Terms • Nervous systems function in sensory input, integration, and motor output. • The nervous system is composed of neurons and supporting cells. • Membrane potentials arise from differences in ion concentrations between a cell’s contents and the extracellular fluid. • ...
... Key Concepts and Important Terms • Nervous systems function in sensory input, integration, and motor output. • The nervous system is composed of neurons and supporting cells. • Membrane potentials arise from differences in ion concentrations between a cell’s contents and the extracellular fluid. • ...
Module 3
... that is already inside the axon (thus Neurons at rest have a slightly negative charge). • The mixing of + and – ions causes an electrical charge that opens up the next portal (letting in more K) while closing the original portal. • Process continues down axon to the axon terminal. • Terminal buttons ...
... that is already inside the axon (thus Neurons at rest have a slightly negative charge). • The mixing of + and – ions causes an electrical charge that opens up the next portal (letting in more K) while closing the original portal. • Process continues down axon to the axon terminal. • Terminal buttons ...
Nueron - AP Psychology Community
... that is already inside the axon (thus Neurons at rest have a slightly negative charge). • The mixing of + and – ions causes an electrical charge that opens up the next portal (letting in more K) while closing the original portal. • Process continues down axon to the axon terminal. • Terminal buttons ...
... that is already inside the axon (thus Neurons at rest have a slightly negative charge). • The mixing of + and – ions causes an electrical charge that opens up the next portal (letting in more K) while closing the original portal. • Process continues down axon to the axon terminal. • Terminal buttons ...
THE NERVOUS SYSTEM - Fox Valley Lutheran High School
... Nerve cells have an electrical potential of 70 mV. Due to the difference of + & - charged ions on each side of the cell mem. Na+-K+ pumps move Na+ ions out of cell and actively pump K+ ions into the cell. This Active transport causes the cytoplasm to have more K+ ions and fewer Na+ ions than the sur ...
... Nerve cells have an electrical potential of 70 mV. Due to the difference of + & - charged ions on each side of the cell mem. Na+-K+ pumps move Na+ ions out of cell and actively pump K+ ions into the cell. This Active transport causes the cytoplasm to have more K+ ions and fewer Na+ ions than the sur ...