Chapter 3 Biological Aspects of Psychology
... the key parts of a neuron, including specialized receptor areas (dendrites), the cell body (soma), the fiber along which impulses are transmitted (axon), and the junctions across which chemical messengers carry signals to other neurons (synapses). Neurons vary considerably in size and shape and are ...
... the key parts of a neuron, including specialized receptor areas (dendrites), the cell body (soma), the fiber along which impulses are transmitted (axon), and the junctions across which chemical messengers carry signals to other neurons (synapses). Neurons vary considerably in size and shape and are ...
INC-IEM Neuroengineering Seminar - 13-11-04
... Abstract: To date, brain-machine interfaces (BMIs) have sought to interface the brain with the external world using intrinsic neuronal signals as input commands for controlling external devices, or device-generated electrical signals to mimic sensory inputs to the nervous system. A new generation of ...
... Abstract: To date, brain-machine interfaces (BMIs) have sought to interface the brain with the external world using intrinsic neuronal signals as input commands for controlling external devices, or device-generated electrical signals to mimic sensory inputs to the nervous system. A new generation of ...
Synapses - Franklin College
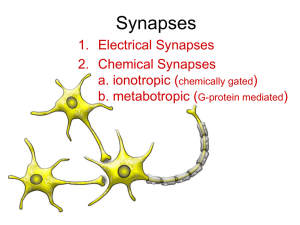
... Two neurons releasing neurotransmitters that act on a third neuron. The first two neurons could be in the Central Nervous System, and the third might be a motor neuron leading out to a muscle or gland. Schwann Cells form a myelin sheath Around the axon of motor neurons Neurons ...
... Two neurons releasing neurotransmitters that act on a third neuron. The first two neurons could be in the Central Nervous System, and the third might be a motor neuron leading out to a muscle or gland. Schwann Cells form a myelin sheath Around the axon of motor neurons Neurons ...
Unit 6 Day 5 Anatomy
... • Resting Potential is the electrochemical condition of the neuron that is not firing. ...
... • Resting Potential is the electrochemical condition of the neuron that is not firing. ...
Introduction to electrophysiological recordings
... surface layers, the electrode see positive charges 'leaving' and thus record a negative potential, whereas ...
... surface layers, the electrode see positive charges 'leaving' and thus record a negative potential, whereas ...
Slide 1
... Rapid depolarization in one spot causes membrane just ahead to depolarize too. Speed of conduction depends on the size of the axon and the number of ion channels. Myelin permits the action potential to travel rapidly from node to node by blocking the membrane ...
... Rapid depolarization in one spot causes membrane just ahead to depolarize too. Speed of conduction depends on the size of the axon and the number of ion channels. Myelin permits the action potential to travel rapidly from node to node by blocking the membrane ...
Neuron Notes Neuron- Cells that carry messages throughout the
... 3types: 1. sensory neurons- carry impulses from sense organs to brain; 2. motor neurons- carry impulses from brain to muscles/glands. 3. Interneuron: carry impulses between sensory and motor neurons (connects them) Parts of the Neuron: 1. cell body: largest part, contains nucleus and most of cytopla ...
... 3types: 1. sensory neurons- carry impulses from sense organs to brain; 2. motor neurons- carry impulses from brain to muscles/glands. 3. Interneuron: carry impulses between sensory and motor neurons (connects them) Parts of the Neuron: 1. cell body: largest part, contains nucleus and most of cytopla ...
Nervous_System_Neurons
... SENSORY NEURONS (AFFERENT) – emerge from the skin or sense organs, carry impulses to spinal cord and brain ...
... SENSORY NEURONS (AFFERENT) – emerge from the skin or sense organs, carry impulses to spinal cord and brain ...
Week 2 Lecture Notes
... The patch clamp consists of an electrode inside a glass pipette. The pipette, which contains a salt solution resembling the fluid normally found within the cell, is lowered to the cell membrane where a tight seal is formed. When a little suction is applied to the pipette, the "patch" of membrane wi ...
... The patch clamp consists of an electrode inside a glass pipette. The pipette, which contains a salt solution resembling the fluid normally found within the cell, is lowered to the cell membrane where a tight seal is formed. When a little suction is applied to the pipette, the "patch" of membrane wi ...
electrochemical impulse
... 2. What causes neuron excitation? • When a sensory neuron detects a change in the environment known as a stimulus, it has to be strong enough to trigger the depolarization of the membrane. • The intensity of the stimulus must reach a set level called the threshold level before the signal will be se ...
... 2. What causes neuron excitation? • When a sensory neuron detects a change in the environment known as a stimulus, it has to be strong enough to trigger the depolarization of the membrane. • The intensity of the stimulus must reach a set level called the threshold level before the signal will be se ...
Nervous System webquest……
... 1. How many Na+ ions are being pumped out? 2. How many K+ ions are being pumped in? 3. Since the numbers are different, could this cause imbalance of charge on either side of the membrane? 4. What molecule is providing the energy for this ion transport? 5. What is the process called when particles a ...
... 1. How many Na+ ions are being pumped out? 2. How many K+ ions are being pumped in? 3. Since the numbers are different, could this cause imbalance of charge on either side of the membrane? 4. What molecule is providing the energy for this ion transport? 5. What is the process called when particles a ...
To allow an immediate response to stimuli in the
... -Often, axons will be wrapped in a “Myelin sheath” (fat) -Gaps in this sheath are known as “nodes of Ranvier” B. Neuroglia -“supporting” cells; support, insulate and protect neurons -“Schwann cells” = neuroglia which produce the myelin sheath ...
... -Often, axons will be wrapped in a “Myelin sheath” (fat) -Gaps in this sheath are known as “nodes of Ranvier” B. Neuroglia -“supporting” cells; support, insulate and protect neurons -“Schwann cells” = neuroglia which produce the myelin sheath ...
Peripheral nervous system
... • long-term memory - involves structural changes in neural connections ...
... • long-term memory - involves structural changes in neural connections ...
The Nervous System
... 16. Within a neuron, what is the function of the axon? 17. What would happen to the resting potential of a neuron if it ran out of ATP? 18. When a neuron receives an excitatory stimulus, what causes the membrane to depolarize? 19. All stimuli cause neurons to depolarize. True or False 20. When thres ...
... 16. Within a neuron, what is the function of the axon? 17. What would happen to the resting potential of a neuron if it ran out of ATP? 18. When a neuron receives an excitatory stimulus, what causes the membrane to depolarize? 19. All stimuli cause neurons to depolarize. True or False 20. When thres ...
Chapter 2: Biopsychology
... Sections along each chromosome are known as genes. Genes control the chemical reactions that direct an individuals development. ...
... Sections along each chromosome are known as genes. Genes control the chemical reactions that direct an individuals development. ...
Lecture 2_101_blanks
... Is it one working whole? Is it a bunch of different parts that work separately? Phrenology Created by Franz Joseph Gall Different parts of the brain do __________________________________ A Phrenology Guide How correct was Phrenology? Phrenology was ________________________: The traits that were thou ...
... Is it one working whole? Is it a bunch of different parts that work separately? Phrenology Created by Franz Joseph Gall Different parts of the brain do __________________________________ A Phrenology Guide How correct was Phrenology? Phrenology was ________________________: The traits that were thou ...
Nervous System
... Bilateral symmetry usually demonstrate cephalization, nervous system concentration in the head and centralization, presence of CNS and PNS Platyhelminthes with nerve cords to control animal movements is simplest Subsequent phyla see an increase in neuron number and segmentation ...
... Bilateral symmetry usually demonstrate cephalization, nervous system concentration in the head and centralization, presence of CNS and PNS Platyhelminthes with nerve cords to control animal movements is simplest Subsequent phyla see an increase in neuron number and segmentation ...
Chapter 12 - Marion ISD
... Transfer nutrients from blood to neurons Make up blood brain barrier ...
... Transfer nutrients from blood to neurons Make up blood brain barrier ...
here
... The Structure and Function of Neurons Neurons are cells that are specialised to carry neural information throughout the body. Dendrites receive signals from other neurons or sensory receptors. They are connected to the cell body (the control centre). The impulse travels from the cell body along the ...
... The Structure and Function of Neurons Neurons are cells that are specialised to carry neural information throughout the body. Dendrites receive signals from other neurons or sensory receptors. They are connected to the cell body (the control centre). The impulse travels from the cell body along the ...
vocabulary worksheet
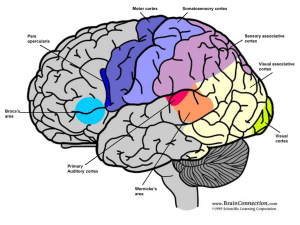
... 27. The _______________ is the outermost covering of the brain consisting of densely packed neurons, responsible for higher thought processes and interpretation of sensory input. 28. The thick band of neurons that connects the right and left cerebral hemispheres is called the _________________ _____ ...
... 27. The _______________ is the outermost covering of the brain consisting of densely packed neurons, responsible for higher thought processes and interpretation of sensory input. 28. The thick band of neurons that connects the right and left cerebral hemispheres is called the _________________ _____ ...
Part1
... CVt = -gCa m(V) (V-ECa) - gKn(V-EK) - gL(V-EL) + Iapp nt = (n(V) - n) / n(V) m(V) = .5(1+tanh((v-v1)/v2) n(V) = .5(1+tanh((v-v3)/v4) n(V) = 1/cosh((v-v3)/2v4) We will write this system as: V’ = f(V,n) + Iapp n’ = g(V,n) ...
... CVt = -gCa m(V) (V-ECa) - gKn(V-EK) - gL(V-EL) + Iapp nt = (n(V) - n) / n(V) m(V) = .5(1+tanh((v-v1)/v2) n(V) = .5(1+tanh((v-v3)/v4) n(V) = 1/cosh((v-v3)/2v4) We will write this system as: V’ = f(V,n) + Iapp n’ = g(V,n) ...
File
... Axon: Long single extension of a neuron, covered with myelin [MY-uh-lin] sheath to insulate and speed up messages through neurons. Terminal Branches of axon: Branched endings of an axon that transmit messages to other neurons. ...
... Axon: Long single extension of a neuron, covered with myelin [MY-uh-lin] sheath to insulate and speed up messages through neurons. Terminal Branches of axon: Branched endings of an axon that transmit messages to other neurons. ...