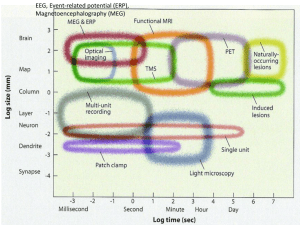
Chapter 12
... 33. Go through the sequence of events that allow an action potential on an axon to be transmitted into a graded potential on a postsynaptic membrane. Excitatory and Inhibitory Postsynaptic Potentials 34. Indicate the voltage changes associated with EPSPs and IPSPs, and how these potentials are relat ...
... 33. Go through the sequence of events that allow an action potential on an axon to be transmitted into a graded potential on a postsynaptic membrane. Excitatory and Inhibitory Postsynaptic Potentials 34. Indicate the voltage changes associated with EPSPs and IPSPs, and how these potentials are relat ...
Nervous System
... It begins in the dendrites, moves rapidly towards the neurons cells body, and then down the axon until it reaches the axon tips. It travels along the neuron in the form of electricity. ...
... It begins in the dendrites, moves rapidly towards the neurons cells body, and then down the axon until it reaches the axon tips. It travels along the neuron in the form of electricity. ...
Nervous System
... It is like the rubber coating around a wire If you want insulation the myelin sheath is who you should hire Ions and action potential, is that ever confusing But listen to this, and then you’ll be cruising It’s the change in electrical potential of an impulse of a muscle cell or nerve cell See? not ...
... It is like the rubber coating around a wire If you want insulation the myelin sheath is who you should hire Ions and action potential, is that ever confusing But listen to this, and then you’ll be cruising It’s the change in electrical potential of an impulse of a muscle cell or nerve cell See? not ...
Nervous System PPT
... – left = right side of body – right = left side of body • The right side of your brain perceives and controls the left side of your body • Left side of brain perceives and controls right side of your ...
... – left = right side of body – right = left side of body • The right side of your brain perceives and controls the left side of your body • Left side of brain perceives and controls right side of your ...
BOX 29.4 MOTOR NEUROPROSTHETICS The fact that a subject`s
... The fact that a subject’s movements can be decoded from populations of neurons, combined with the recently developed ability to implant devices in the brain that record populations of neurons simultaneously, has led to the development of brain-computer interfaces (BCIs) and brain machine interfaces ...
... The fact that a subject’s movements can be decoded from populations of neurons, combined with the recently developed ability to implant devices in the brain that record populations of neurons simultaneously, has led to the development of brain-computer interfaces (BCIs) and brain machine interfaces ...
Studying the concepts pg 344 1-7 Motor neurons are located in the
... while a motor neuron takes information away from the CNS. An interneuron conveys information between neurons in the CNS. ...
... while a motor neuron takes information away from the CNS. An interneuron conveys information between neurons in the CNS. ...
Nerve Cells and Nerve Impulses
... Figure 2.11 (a) Shapes of some glia cells. Oligodendrocytes produce myelin sheaths that insulate certain vertebrate axons in the central nervous system; Schwann cells have a similar function in the periphery. The oligodendrocyte is shown here forming a segment of myelin sheath for two axons; in fac ...
... Figure 2.11 (a) Shapes of some glia cells. Oligodendrocytes produce myelin sheaths that insulate certain vertebrate axons in the central nervous system; Schwann cells have a similar function in the periphery. The oligodendrocyte is shown here forming a segment of myelin sheath for two axons; in fac ...
The Nervous System
... 1. A nerve impulse begins with a stimulus- usually this is a neurotransmitter released by other neurons, pain receptors, light excites receptors in the eye, etc. 2. Once the neuron is stimulated the “sodium gates” of the neuron open and sodium ions begin flowing across the cell membrane. This is cal ...
... 1. A nerve impulse begins with a stimulus- usually this is a neurotransmitter released by other neurons, pain receptors, light excites receptors in the eye, etc. 2. Once the neuron is stimulated the “sodium gates” of the neuron open and sodium ions begin flowing across the cell membrane. This is cal ...
The brain is the body`s most complex organ. Neurons communicate
... Synapses are chemical or electrical junctions that allow electrical signals to pass from neurons to other cells. ...
... Synapses are chemical or electrical junctions that allow electrical signals to pass from neurons to other cells. ...
Neurology - wsscience
... Transient hyperpolarization of the postsynaptic membrane Repolarization produced by the addition of multiple stimul Reflection of the activation of an opposing transmembrane potential ...
... Transient hyperpolarization of the postsynaptic membrane Repolarization produced by the addition of multiple stimul Reflection of the activation of an opposing transmembrane potential ...
Cell types: Muscle cell Adipocyte Liver cell Pancreatic cell Example
... 1. Description of the cell type: basic functions, tissue/organ where it can be found Neurons: The main cell type of the nervous system. Neurons perceive outside information, integrate them and innervate muscles, induce hormone, enzyme secretion, DNA transcription. They receive inputs via their synap ...
... 1. Description of the cell type: basic functions, tissue/organ where it can be found Neurons: The main cell type of the nervous system. Neurons perceive outside information, integrate them and innervate muscles, induce hormone, enzyme secretion, DNA transcription. They receive inputs via their synap ...
Lecture 6C
... glucose was absorbed and metabolized by active neurons to a much greater extent than by other neurons. After the experiment, the animals were sacrificed and the cortical radioactivity pattern was analyzed. This method provides high resolution radioactive labeling of active neurons. The physical patt ...
... glucose was absorbed and metabolized by active neurons to a much greater extent than by other neurons. After the experiment, the animals were sacrificed and the cortical radioactivity pattern was analyzed. This method provides high resolution radioactive labeling of active neurons. The physical patt ...
Pipecleaner Neuron Guide - spectrUM Discovery Area
... neurotransmitter) to the dendrite of another neuron. Neurotransmitters work like key and lock with the lock being on the receiving neuron that opens the door allowing sodium ions/electrical charge to flow into the neuron. ...
... neurotransmitter) to the dendrite of another neuron. Neurotransmitters work like key and lock with the lock being on the receiving neuron that opens the door allowing sodium ions/electrical charge to flow into the neuron. ...
Psychology 210
... Information processing and communicating nerve cells Glia Addressed later What do you know about neurons coming into this class? How does a neuron communicate with another neuron? What type of signal is processed in a neuron? What are the parts of a neuron? Parts of a Neuron 3 main parts ___________ ...
... Information processing and communicating nerve cells Glia Addressed later What do you know about neurons coming into this class? How does a neuron communicate with another neuron? What type of signal is processed in a neuron? What are the parts of a neuron? Parts of a Neuron 3 main parts ___________ ...
Ch 49 Pract Test Nervous System
... Which statement about the resting potential of a neuron is true? a. Sodium ions are in balance inside and outside the neuron’s membrane. b. There are many times more sodium ions outside the neuron’s membrane than inside. c. There are fewer potassium ions inside the neuron’s membrane than outside. d ...
... Which statement about the resting potential of a neuron is true? a. Sodium ions are in balance inside and outside the neuron’s membrane. b. There are many times more sodium ions outside the neuron’s membrane than inside. c. There are fewer potassium ions inside the neuron’s membrane than outside. d ...
Nervous System Neuron: nerve cell, functional unit of nervous
... -bundles 1000000 neurons grouped into different tracts -associate with different brain and body parts 100-1000 neurons can transfer one signal. ...
... -bundles 1000000 neurons grouped into different tracts -associate with different brain and body parts 100-1000 neurons can transfer one signal. ...
Neurotransmitters
... neurotransmitters are released into the synapse and passed along to the dendrites of the next neuron. • If enough neurotransmitters have been sent, the next neuron will fire. If not, the message ends. This is called the all-or-nothing ...
... neurotransmitters are released into the synapse and passed along to the dendrites of the next neuron. • If enough neurotransmitters have been sent, the next neuron will fire. If not, the message ends. This is called the all-or-nothing ...
File
... This is the term for eliminating “weaker” groups of people who possess undesirable genes; it is being raised as an ethical issue in the conversation about mapping genes. ...
... This is the term for eliminating “weaker” groups of people who possess undesirable genes; it is being raised as an ethical issue in the conversation about mapping genes. ...
Name: Date: Grade / Section: _____ Neurons Questions Notes 1
... Ferries are boats that carry cars and people across a river. If the river represents the synapse… 1. What could the ferry represent? 2. What could the cars / people represent? 3. What could the road leading the ferry represent? ...
... Ferries are boats that carry cars and people across a river. If the river represents the synapse… 1. What could the ferry represent? 2. What could the cars / people represent? 3. What could the road leading the ferry represent? ...
How is the Nervous System Organized? Class Objectives:
... layer of cells containing fat, encases and insulates most axons. ...
... layer of cells containing fat, encases and insulates most axons. ...
here - York University
... The Basics The neuron is the fundamental unit for the nervous system. It contains 3 main structures: the cell body, the dendrite for input electrical signals, and the axon for output electrical signals. The segment connecting the axon and cell body is called the axonal intial segment (a.k.a. axonal ...
... The Basics The neuron is the fundamental unit for the nervous system. It contains 3 main structures: the cell body, the dendrite for input electrical signals, and the axon for output electrical signals. The segment connecting the axon and cell body is called the axonal intial segment (a.k.a. axonal ...
The Brain
... Axon - the elongated fiber that extends from the cell body to the terminal endings and transmits the neural signal. The larger the axon, the faster it transmits information Myelin Sheath - fatty substance called myelin that acts as an insulator. These myelinated axons transmit information much faste ...
... Axon - the elongated fiber that extends from the cell body to the terminal endings and transmits the neural signal. The larger the axon, the faster it transmits information Myelin Sheath - fatty substance called myelin that acts as an insulator. These myelinated axons transmit information much faste ...