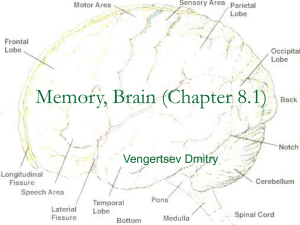
lesson 6
... changes in the membrane potential that last a few ten thousandths of a second. • Action potentials can be divided into three phases: the resting or polarized state, depolarization, and repolarization • The amplitude of an action potential is nearly constant and is not related to the size of the stim ...
... changes in the membrane potential that last a few ten thousandths of a second. • Action potentials can be divided into three phases: the resting or polarized state, depolarization, and repolarization • The amplitude of an action potential is nearly constant and is not related to the size of the stim ...
PNS Study Guide
... 11. Which part of the neuron RECEIVES information and which part of the neuron SENDS information away from the cell body? 12. What is the space called in between neurons where chemicals are exchanged? What are these special chemicals called? 13. *** Describe the 3 functional classifications and the ...
... 11. Which part of the neuron RECEIVES information and which part of the neuron SENDS information away from the cell body? 12. What is the space called in between neurons where chemicals are exchanged? What are these special chemicals called? 13. *** Describe the 3 functional classifications and the ...
Chapter 11: Fundamentals of the Nervous System and Nervous Tissue
... ______1. Nervous system subdivision that is composed of the brain and spinal cord. ______2. Subdivision of the PNS that controls voluntary activities such as activation of skeletal muscles. ______3. Nervous system subdivision that is composed of the cranial and spinal nerves. ______4. Subdivision of ...
... ______1. Nervous system subdivision that is composed of the brain and spinal cord. ______2. Subdivision of the PNS that controls voluntary activities such as activation of skeletal muscles. ______3. Nervous system subdivision that is composed of the cranial and spinal nerves. ______4. Subdivision of ...
Chapter 9 Nervous
... Describe the neuron, the nerve impulse, and the synapse, and explain the components of a reflex arc Neuron - specialized cell that lies within the nervous system; conducts electrochemical signals along their length body - major portion of neuron axon - transmits signals to other structures (groups a ...
... Describe the neuron, the nerve impulse, and the synapse, and explain the components of a reflex arc Neuron - specialized cell that lies within the nervous system; conducts electrochemical signals along their length body - major portion of neuron axon - transmits signals to other structures (groups a ...
SNARE molecules at the trans-Golgi network and endosome and their roles in neuronal growth and axonal transport.
... Polarized membrane traffic to different domains of the neuron is well documented, and is required for both establishment and maintenance of neuronal polarity. Some soluble N-ethylmaleimide sensitive factor attachment protein receptor (SNARE) proteins, which are key components of the eukaryotic membr ...
... Polarized membrane traffic to different domains of the neuron is well documented, and is required for both establishment and maintenance of neuronal polarity. Some soluble N-ethylmaleimide sensitive factor attachment protein receptor (SNARE) proteins, which are key components of the eukaryotic membr ...
Chapter 2
... But new dendrites can grow Provides room for more connections to other neurons New connections are basis for learning ...
... But new dendrites can grow Provides room for more connections to other neurons New connections are basis for learning ...
Nervous System Part 1
... System that receives info about internal and external environment, integrates, and directs activities to respond. Divided into the CNS and the PNS. ...
... System that receives info about internal and external environment, integrates, and directs activities to respond. Divided into the CNS and the PNS. ...
are you ready - Plain Local Schools
... I founded the first school of thought, structuralism, thus making Psychology a separate social science ...
... I founded the first school of thought, structuralism, thus making Psychology a separate social science ...
Leaving Certificate Biology Photosynthesis Quiz
... Nervous System 1 iQuiz FIRST In PowerPoint 2007 if you see a Security Warning click HERE on Options… and then click on Enable this content ...
... Nervous System 1 iQuiz FIRST In PowerPoint 2007 if you see a Security Warning click HERE on Options… and then click on Enable this content ...
Types of neurons
... But new dendrites can grow Provides room for more connections to other neurons New connections are basis for learning ...
... But new dendrites can grow Provides room for more connections to other neurons New connections are basis for learning ...
Types of neurons
... But new dendrites can grow Provides room for more connections to other neurons New connections are basis for learning ...
... But new dendrites can grow Provides room for more connections to other neurons New connections are basis for learning ...
Types of neurons
... But new dendrites can grow Provides room for more connections to other neurons New connections are basis for learning ...
... But new dendrites can grow Provides room for more connections to other neurons New connections are basis for learning ...
The skin performs all of the following except
... Students will know… Explain what an action potential is? K+ ions are entering the neuron Negatively charged proteins are leaving the neuron Na+ ions are entering the neuron The myelin coat has broken down and ions are ...
... Students will know… Explain what an action potential is? K+ ions are entering the neuron Negatively charged proteins are leaving the neuron Na+ ions are entering the neuron The myelin coat has broken down and ions are ...
The Nervous System
... Nervous System Injuries Concussions • Bruise-like injury of brain • Occurs when soft tissue collides against skull • Can cause headache, dizziness, confusion, memory loss, brain damage ...
... Nervous System Injuries Concussions • Bruise-like injury of brain • Occurs when soft tissue collides against skull • Can cause headache, dizziness, confusion, memory loss, brain damage ...
SBI 4U Homeostasis 2
... • A system that uses ATP in order to keep the electrical potential difference across the membrane. • For every three sodium ions transported out of the cell, two potassium ions are transported into the cell. • An overall positive charge is going to accumulate on the outside of the cell membrane and ...
... • A system that uses ATP in order to keep the electrical potential difference across the membrane. • For every three sodium ions transported out of the cell, two potassium ions are transported into the cell. • An overall positive charge is going to accumulate on the outside of the cell membrane and ...
Structure of a Neuron
... membrane which selectively allows things in and out of the cell. – Large negatively charged molecules found in the ICF such as proteins and phosphates are confined to the inside of the cell. The membrane is impermeable to these molecules which contributes to the ICF maintaining RMP of -70mV ...
... membrane which selectively allows things in and out of the cell. – Large negatively charged molecules found in the ICF such as proteins and phosphates are confined to the inside of the cell. The membrane is impermeable to these molecules which contributes to the ICF maintaining RMP of -70mV ...
Vocabulary: Chapter 1 Body Control Systems Neuron
... information from the senses. Cerebellum- the part of the brain that coordinates movements and helps maintain balance. Brain stem- part of the brain that controls involuntary actions, such as breathing: connects the brain to the spinal cord. Hypothalamus- part of the brain that controls body temperat ...
... information from the senses. Cerebellum- the part of the brain that coordinates movements and helps maintain balance. Brain stem- part of the brain that controls involuntary actions, such as breathing: connects the brain to the spinal cord. Hypothalamus- part of the brain that controls body temperat ...
notes - Other Places you want to go
... Neurons – composed of dendrites, axons, and cell bodies Synapse – gap between the axon of a neuron and the receiving cell Neuroglia – support neurons by preforming various tasks so neurons can do their job **Know Figure 16.3 for test** (see Neuron handout) Parts of the Neuron: Dendrites – conduct ...
... Neurons – composed of dendrites, axons, and cell bodies Synapse – gap between the axon of a neuron and the receiving cell Neuroglia – support neurons by preforming various tasks so neurons can do their job **Know Figure 16.3 for test** (see Neuron handout) Parts of the Neuron: Dendrites – conduct ...
Nervous System
... Nervous System • Helps you observe and react to the world around you • Neuron= cells of the nervous system ...
... Nervous System • Helps you observe and react to the world around you • Neuron= cells of the nervous system ...
Neurons
... the neural impulse over synapse PSP – postsynaptic potential – change in membrane potential: ...
... the neural impulse over synapse PSP – postsynaptic potential – change in membrane potential: ...
PSY 301 – Summer 2004
... A branch of psychology that concerns itself with the links between biology and behavior. Other terms: Behavioral neuroscientist, neuropsychologist, physiological/biopsychologist, behavioral endocrinologist etc. ...
... A branch of psychology that concerns itself with the links between biology and behavior. Other terms: Behavioral neuroscientist, neuropsychologist, physiological/biopsychologist, behavioral endocrinologist etc. ...
Human Body Systems - Whitehall District Schools
... • The body’s ability to physiologically maintain a stable, internal condition within narrow limits ...
... • The body’s ability to physiologically maintain a stable, internal condition within narrow limits ...
Candy Neurons Activity
... Pull apart twizzlers (These can be used to make dendrites, axons, and myelin sheaths, and terminal buttons) York Peppermint Patties (These can be used to make the cell body) Pixie sticks (These make great neurotransmitters ...
... Pull apart twizzlers (These can be used to make dendrites, axons, and myelin sheaths, and terminal buttons) York Peppermint Patties (These can be used to make the cell body) Pixie sticks (These make great neurotransmitters ...