Neurons - Jordan High School
... Passive channels always open Chemically gated channels need specific chemicals Voltage-gated channels respond to changes in transmembrane potential ...
... Passive channels always open Chemically gated channels need specific chemicals Voltage-gated channels respond to changes in transmembrane potential ...
Nerve Chips
... Nanotechnology – design of new “impossible” materials Electrode coatings that contain brain molecules, “trick” cells into acting like electrode is part of brain Polymer chains that can enter the cell Conductive polymer chains that place your electrode inside a ...
... Nanotechnology – design of new “impossible” materials Electrode coatings that contain brain molecules, “trick” cells into acting like electrode is part of brain Polymer chains that can enter the cell Conductive polymer chains that place your electrode inside a ...
We have seen how the Nervous System plays an important role in
... neurons that respond to and send messages. These “messages” are actually electrical. We can use our knowledge of physics to understand how they are transmitted! Different types of neurons respond to different stimuli. A stimulus is anything that generates a nerve response. For example, light is a st ...
... neurons that respond to and send messages. These “messages” are actually electrical. We can use our knowledge of physics to understand how they are transmitted! Different types of neurons respond to different stimuli. A stimulus is anything that generates a nerve response. For example, light is a st ...
Ch.10
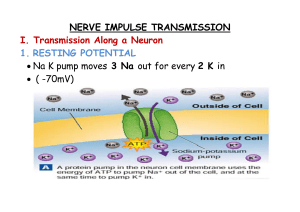
... inside the cell. • There is a higher concentration of Na+ outside the membrane and higher K+ concentration inside. The Na+/ K+ pumps, three sodium ions out for every two potassium ions it pumps in. • When voltage-gated channels open and close the concentration of ions change, causing a change in mem ...
... inside the cell. • There is a higher concentration of Na+ outside the membrane and higher K+ concentration inside. The Na+/ K+ pumps, three sodium ions out for every two potassium ions it pumps in. • When voltage-gated channels open and close the concentration of ions change, causing a change in mem ...
PPTX - Bonham Chemistry
... gland into the bloodstream and transported therein to reach its target cell. The distinction between a neurotransmitter and a hormone is physiological, not chemical. It depends on whether the molecule acts over a short distance (across a synapse) or over a long distance (from the secretory organ, th ...
... gland into the bloodstream and transported therein to reach its target cell. The distinction between a neurotransmitter and a hormone is physiological, not chemical. It depends on whether the molecule acts over a short distance (across a synapse) or over a long distance (from the secretory organ, th ...
Structure of a Neuron Transmission of “Information” Nerve Impulse
... – Across narrow gaps between cells ...
... – Across narrow gaps between cells ...
Neurones & the Action Potential
... Neurones & the Action Potential Objective: To understand how neurones conduct impulses from one part of the body to another. ...
... Neurones & the Action Potential Objective: To understand how neurones conduct impulses from one part of the body to another. ...
PowerPoint for 9/29
... (with each other): The action potential travels down the axon from the cell body to the ...
... (with each other): The action potential travels down the axon from the cell body to the ...
For electrical signaling
... kT: The thermal energy of an ion K: Boltzmann constant q: the charge of a single proton VT: 24 ~27 mV Membrane potentials: about -3 to +2 times VT ...
... kT: The thermal energy of an ion K: Boltzmann constant q: the charge of a single proton VT: 24 ~27 mV Membrane potentials: about -3 to +2 times VT ...
Neurons - World of Teaching
... causing them to “leak” out. This causes outside of membrane to have an abundance of + charges compared to inside. The inside of the membrane is negative compared to the outside. This is helped by the (-) proteins etc. The “sodium-potassium” pump pulls 2 K+ ions in for 3 Na+ ions sent out. This furth ...
... causing them to “leak” out. This causes outside of membrane to have an abundance of + charges compared to inside. The inside of the membrane is negative compared to the outside. This is helped by the (-) proteins etc. The “sodium-potassium” pump pulls 2 K+ ions in for 3 Na+ ions sent out. This furth ...
Biology 3201 - s3.amazonaws.com
... causing them to “leak” out. This causes outside of membrane to have an abundance of + charges compared to inside. The inside of the membrane is negative compared to the outside. This is helped by the (-) proteins etc. The “sodium-potassium” pump pulls 2 K+ ions in for 3 Na+ ions sent out. This furth ...
... causing them to “leak” out. This causes outside of membrane to have an abundance of + charges compared to inside. The inside of the membrane is negative compared to the outside. This is helped by the (-) proteins etc. The “sodium-potassium” pump pulls 2 K+ ions in for 3 Na+ ions sent out. This furth ...
Developer Notes
... messages. These “messages” are actually electrical. We can use our knowledge of physics to understand how they are transmitted! Different types of neurons respond to different stimuli. A stimulus is anything that generates a nerve response. For example, light is a stimulus that generates a response ...
... messages. These “messages” are actually electrical. We can use our knowledge of physics to understand how they are transmitted! Different types of neurons respond to different stimuli. A stimulus is anything that generates a nerve response. For example, light is a stimulus that generates a response ...
Neurons and Functional Neuroanatomy
... The action potential moves down the length of the axon in one direction The action potential moves in one direction because the membrane is refractory (unable to respond) once the action potential has been initiated at any particular place on the membrane ...
... The action potential moves down the length of the axon in one direction The action potential moves in one direction because the membrane is refractory (unable to respond) once the action potential has been initiated at any particular place on the membrane ...
Bio 3411 Problem Set 9 Name: (Due Monday, November 28th 2011
... 5. You are studying the neuromuscular junction (NMJ) and make the follow recordings of action potentials in the presynaptic and postsynaptic terminals in response to electrical stimulation of the motor neuron under control conditions. Sketch what you predict your recordings will look like under the ...
... 5. You are studying the neuromuscular junction (NMJ) and make the follow recordings of action potentials in the presynaptic and postsynaptic terminals in response to electrical stimulation of the motor neuron under control conditions. Sketch what you predict your recordings will look like under the ...
Babylon university Medical physics exam
... depolarization of the nerve and muscles of both atria, causing atria to contract and pump blood into ventricles. The electrical signals then passes through aterioventricle AV anode, which initiates depolarization of right and left ventricles causing them to contract and force blood to pulmonary and ...
... depolarization of the nerve and muscles of both atria, causing atria to contract and pump blood into ventricles. The electrical signals then passes through aterioventricle AV anode, which initiates depolarization of right and left ventricles causing them to contract and force blood to pulmonary and ...
Nerve Cell Impulses
... Histology of the Nervous System A review of Cell types 2) Neuroglia (glial cells, continue) d) oligodendrocyte – produce myelin sheath in the CNS, which insulates and protects axons e) Schwann cells – produce myelin sheath in PNS, insulates axons, maintains their micro-environment, enables regenera ...
... Histology of the Nervous System A review of Cell types 2) Neuroglia (glial cells, continue) d) oligodendrocyte – produce myelin sheath in the CNS, which insulates and protects axons e) Schwann cells – produce myelin sheath in PNS, insulates axons, maintains their micro-environment, enables regenera ...
steps in nerve impulse transmission
... 1. Neurotransmitters (NT) are chemicals released from one neuron at the presynaptic nerve terminal. 2. NT then cross the synapse where they may be accepted by the next neuron at a specialized site called a receptor 3. The action that follows activation of a receptor site may be either depolarizati ...
... 1. Neurotransmitters (NT) are chemicals released from one neuron at the presynaptic nerve terminal. 2. NT then cross the synapse where they may be accepted by the next neuron at a specialized site called a receptor 3. The action that follows activation of a receptor site may be either depolarizati ...
Nervous System - Wando High School
... receptive or input regions that provide enormous surface area for receiving signals from receptor organs/glands ...
... receptive or input regions that provide enormous surface area for receiving signals from receptor organs/glands ...
Name: Date: A.P. Psychology Unit 3-A F.R.Q.: Biological Bases of
... a. Resting Potential b. Action Potential c. Refractory Period d. “All-Or-None” Response e. Threshold f. Synapse g. Dendrites h. Neurotransmitters i. ...
... a. Resting Potential b. Action Potential c. Refractory Period d. “All-Or-None” Response e. Threshold f. Synapse g. Dendrites h. Neurotransmitters i. ...
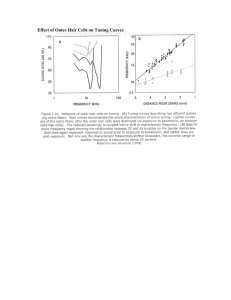
Effect of Outer Hair Cells on Tuning Curves
... and "a." In this example, the input wave is filtered into four frequency bands (the band with the highest center frequency is shown at the top, the lowest is at bottom). Next, the speech envelope is derived for each channel. With this information the signal processor constructs a train of biphasic p ...
... and "a." In this example, the input wave is filtered into four frequency bands (the band with the highest center frequency is shown at the top, the lowest is at bottom). Next, the speech envelope is derived for each channel. With this information the signal processor constructs a train of biphasic p ...
Sending Signals Notes
... • When an impulse reaches the Axon Terminal, dozen of vesicles fuse with the cell membrane and discharge the Neurotransmitter into the Synaptic Cleft (GAP). • The molecules of the neurotransmitter diffuse across the gap and attach themselves to SPECIAL RECEPTORS on the membrane of the neuron recei ...
... • When an impulse reaches the Axon Terminal, dozen of vesicles fuse with the cell membrane and discharge the Neurotransmitter into the Synaptic Cleft (GAP). • The molecules of the neurotransmitter diffuse across the gap and attach themselves to SPECIAL RECEPTORS on the membrane of the neuron recei ...