Chapter 14 - The Nervous System: Organization
... Excitatory and inhibitory postsynaptic potentials • A synaptic potential can be excitatory (they depolarize) or inhibitory (they polarize). Some neurotransmitters depolarize and others polarize. • There are more than 50 different neurotransmitters. • In the brain and spinal cord, hundreds of excita ...
... Excitatory and inhibitory postsynaptic potentials • A synaptic potential can be excitatory (they depolarize) or inhibitory (they polarize). Some neurotransmitters depolarize and others polarize. • There are more than 50 different neurotransmitters. • In the brain and spinal cord, hundreds of excita ...
Chp3 Weiten - Napa Valley College
... Mirror neurons appear to provide a new model for understanding complex social cognition at a neural level. New findings suggest mirror neurons may play a fundamental role in the acquisition of new motor skills ...
... Mirror neurons appear to provide a new model for understanding complex social cognition at a neural level. New findings suggest mirror neurons may play a fundamental role in the acquisition of new motor skills ...
ActionPotentialWebquestCompleteGarrettIan
... 4. After sodium ions have flooded into the cell and the sodium gates close, what happens to the potassium ions? 5. How does an action potential conduct along an axon? 6. Describe and draw an action potential. Part 3 – Ions Control Membrane Potential Go to http://www.bristol.ac.uk/synaptic/basics/bas ...
... 4. After sodium ions have flooded into the cell and the sodium gates close, what happens to the potassium ions? 5. How does an action potential conduct along an axon? 6. Describe and draw an action potential. Part 3 – Ions Control Membrane Potential Go to http://www.bristol.ac.uk/synaptic/basics/bas ...
Action potentials travel along the axons of neurons.
... A nerve is usually composed of a bundle of neurons with Glial cells and blood vessel to supply needed materials. Neurons are not connected directly to one another – there are gaps (synapses) between the neurons. Action potentials travel along the axons of neurons. ...
... A nerve is usually composed of a bundle of neurons with Glial cells and blood vessel to supply needed materials. Neurons are not connected directly to one another – there are gaps (synapses) between the neurons. Action potentials travel along the axons of neurons. ...
An accident caused a tamping iron to go through his head
... movement of potassium ions out). Polarity is reversed to +40mV called the action potential. ...
... movement of potassium ions out). Polarity is reversed to +40mV called the action potential. ...
Document
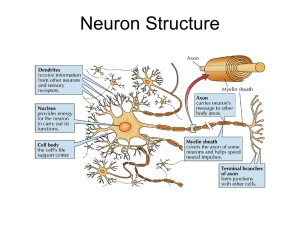
... – triggers impulses that are conducted away from the cell body along an axon Neurons are supported structurally and functionally by supporting cells (neuroglia). – Schwann cells – oligodendrocytes produce myelin sheath interrupted by nodes of Ranvier ...
... – triggers impulses that are conducted away from the cell body along an axon Neurons are supported structurally and functionally by supporting cells (neuroglia). – Schwann cells – oligodendrocytes produce myelin sheath interrupted by nodes of Ranvier ...
File - Biology with Radjewski
... to receptors proteins and open the ion channels of the new neuron cell. • If enough ion channels are opened, the action potential will continue through the new neuron. If not, the nervous signal will be terminated. • After the neurotransmitters have opened the ion channels, they will be cleared out ...
... to receptors proteins and open the ion channels of the new neuron cell. • If enough ion channels are opened, the action potential will continue through the new neuron. If not, the nervous signal will be terminated. • After the neurotransmitters have opened the ion channels, they will be cleared out ...
Chapter 2
... emotional control, speech, working memory • Parietal: Body sensations • Occipital: Vision • Temporal: Hearing, language comprehension ...
... emotional control, speech, working memory • Parietal: Body sensations • Occipital: Vision • Temporal: Hearing, language comprehension ...
Neuron Physiology Notes
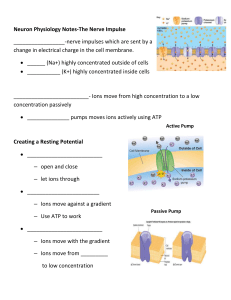
... Neuron Physiology Notes-The Nerve Impulse _________________-nerve impulses which are sent by a change in electrical charge in the cell membrane. ______ (Na+) highly concentrated outside of cells ___________ (K+) highly concentrated inside cells ...
... Neuron Physiology Notes-The Nerve Impulse _________________-nerve impulses which are sent by a change in electrical charge in the cell membrane. ______ (Na+) highly concentrated outside of cells ___________ (K+) highly concentrated inside cells ...
The Brain and Its Disorders
... How To Study the Brain Psychopathologies Amnesias, Language Disorders, and Prosopagnosia ...
... How To Study the Brain Psychopathologies Amnesias, Language Disorders, and Prosopagnosia ...
Lecture_31_2014_noquiz
... • The idea is to remove this part of the brain with removing as little as possible from other adjoining areas. Doctors still do this today. • Based on electrical stimulation of conscious patients, we know that different parts of the brain do different things. ...
... • The idea is to remove this part of the brain with removing as little as possible from other adjoining areas. Doctors still do this today. • Based on electrical stimulation of conscious patients, we know that different parts of the brain do different things. ...
Nervous System - Cloudfront.net
... 1. Electrical current travels down the axon 2. Vesicles with chemicals move toward the membrane what is that called? 3. Chemicals are released and diffuse toward the next cell’s plasma membrane 4. The chemicals open up the transport proteins and allow the signal to pass to the next cell - what type ...
... 1. Electrical current travels down the axon 2. Vesicles with chemicals move toward the membrane what is that called? 3. Chemicals are released and diffuse toward the next cell’s plasma membrane 4. The chemicals open up the transport proteins and allow the signal to pass to the next cell - what type ...
PowerPoint
... • When an impulse reaches the Axon Terminal, dozen of vesicles fuse with the cell membrane and discharge the Neurotransmitter into the Synaptic Cleft (GAP). • The molecules of the neurotransmitter diffuse across the gap and attach themselves to SPECIAL RECEPTORS on the membrane of the neuron receiv ...
... • When an impulse reaches the Axon Terminal, dozen of vesicles fuse with the cell membrane and discharge the Neurotransmitter into the Synaptic Cleft (GAP). • The molecules of the neurotransmitter diffuse across the gap and attach themselves to SPECIAL RECEPTORS on the membrane of the neuron receiv ...
Chapter 10
... • understanding how neurotransmitters fit receptors can help explain the actions of certain drugs • drugs have different mechanisms of action • several questions remain about the biological effects of addiction, such as why some individuals become addicted and others do not ...
... • understanding how neurotransmitters fit receptors can help explain the actions of certain drugs • drugs have different mechanisms of action • several questions remain about the biological effects of addiction, such as why some individuals become addicted and others do not ...
Types of neurons - Brigham Young University
... You photoreceptors can detect down to 1 photon -70 mV across 3nm is equivalent to 200,000V across 1cm ...
... You photoreceptors can detect down to 1 photon -70 mV across 3nm is equivalent to 200,000V across 1cm ...
Sample Questions for Evaluation #1 – General
... c) observable relationship between specific independent and dependent variables. d) set of principles that organizes observations and explains newly discovered facts. 9. In a written report of their research, psychologists specify exactly how anxiety is assessed, thus providing their readers with a( ...
... c) observable relationship between specific independent and dependent variables. d) set of principles that organizes observations and explains newly discovered facts. 9. In a written report of their research, psychologists specify exactly how anxiety is assessed, thus providing their readers with a( ...
1. 2. a) Explain the compositions of white matter and gray matter
... 2. a) Explain the compositions of white matter and gray matter. White matter consists of glial cells and myelinated axons. It does not contain the cell bodies of neurons and acts as a signal pathway for the gray matter regions of the central nervous system. Gray matter consists of glial cells and un ...
... 2. a) Explain the compositions of white matter and gray matter. White matter consists of glial cells and myelinated axons. It does not contain the cell bodies of neurons and acts as a signal pathway for the gray matter regions of the central nervous system. Gray matter consists of glial cells and un ...
Ch 48 Nervous System
... the unexcited nerve. – A change in voltage MAY result in an electrical impulse. ...
... the unexcited nerve. – A change in voltage MAY result in an electrical impulse. ...
9.3 Synaptic Transmission
... When the nerve impulse reaches the end of the axon of the presynaptic neuron it causes synaptic vesicles to move to the presynaptic ...
... When the nerve impulse reaches the end of the axon of the presynaptic neuron it causes synaptic vesicles to move to the presynaptic ...
Nervous System Notes
... • Space between axon terminal of one neuron and dendrites of another. • Neurotransmitters in vesicles released in cleft either cause the cell to fire (excitatory) or not fire (inhibitory). ...
... • Space between axon terminal of one neuron and dendrites of another. • Neurotransmitters in vesicles released in cleft either cause the cell to fire (excitatory) or not fire (inhibitory). ...
Psych 9A. Lec. 05 PP Slides: Brain and Nervous System
... Afferent (towards the central nervous system: CNS) Efferent (away from or out of the CNS) Many simple reflexes rely on circuits within the spine: no need for brain involvement. ...
... Afferent (towards the central nervous system: CNS) Efferent (away from or out of the CNS) Many simple reflexes rely on circuits within the spine: no need for brain involvement. ...