CONTROL OF FUNCTIONAL ELECTRICAL STIMULATION FOR
... of behavior that must be used? If the later, would it be possible to understand the constraints imposed to reproduce the same motor behavior whenever the motor task needs to be executed? A human can capture a spectrum of functional movements during the life. Most of the movements are mastered in ear ...
... of behavior that must be used? If the later, would it be possible to understand the constraints imposed to reproduce the same motor behavior whenever the motor task needs to be executed? A human can capture a spectrum of functional movements during the life. Most of the movements are mastered in ear ...
Uncomfortable images produce non-sparse responses in a model of
... models of populations of neurons with properties similar to those found in the visual cortex have been shown to produce sparse responses to natural image inputs [4]. Equally, learning algorithms that seek to generate sparse responses to natural image samples produce units with receptive fields that ...
... models of populations of neurons with properties similar to those found in the visual cortex have been shown to produce sparse responses to natural image inputs [4]. Equally, learning algorithms that seek to generate sparse responses to natural image samples produce units with receptive fields that ...
BIO 218 F 2012 Ch 14 Martini Lecture Outline
... Sensory nerves (afferent nerves): transmit impulses toward the spinal cord Motor nerves (efferent nerves): transmit impulses away from the spinal cord ...
... Sensory nerves (afferent nerves): transmit impulses toward the spinal cord Motor nerves (efferent nerves): transmit impulses away from the spinal cord ...
BIO 218 F 2012 Ch 14 Martini Lecture Outline
... Sensory nerves (afferent nerves): transmit impulses toward the spinal cord Motor nerves (efferent nerves): transmit impulses away from the spinal cord ...
... Sensory nerves (afferent nerves): transmit impulses toward the spinal cord Motor nerves (efferent nerves): transmit impulses away from the spinal cord ...
ch14_lecture - Napa Valley College
... See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. ...
... See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. ...
Chapter 14 Lecture Outline
... See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. ...
... See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. ...
Lab Activity 14 - Portland Community College
... • Lower motor neurons go from the spinal cord to a muscle. • The cell body of a lower motor neuron is in the spinal cord and its termination is in a skeletal muscle. • The loss of lower motor neurons leads to weakness, twitching of muscle (fasciculation), and loss of muscle mass (muscle atrophy). “F ...
... • Lower motor neurons go from the spinal cord to a muscle. • The cell body of a lower motor neuron is in the spinal cord and its termination is in a skeletal muscle. • The loss of lower motor neurons leads to weakness, twitching of muscle (fasciculation), and loss of muscle mass (muscle atrophy). “F ...
Computational themes of peripheral processing
... Adaptation processes play an important role in achieving an intensity-invariant representation of the amplitude modulation of the perceived signal and to increase the signalto-noise ratio. Next, the representation of the amplitude modulation of a signal by the auditory receptor neurons (Machens et a ...
... Adaptation processes play an important role in achieving an intensity-invariant representation of the amplitude modulation of the perceived signal and to increase the signalto-noise ratio. Next, the representation of the amplitude modulation of a signal by the auditory receptor neurons (Machens et a ...
Human Nervous System
... * If the nerve is covered with myelin it is referred to as the white matter. * If the nerve is NOT covered with protective myelin sheath is called gray matter which makes up the gray matter of the Brain and spinal cord. ...
... * If the nerve is covered with myelin it is referred to as the white matter. * If the nerve is NOT covered with protective myelin sheath is called gray matter which makes up the gray matter of the Brain and spinal cord. ...
The Superior Olivary Nucleus and Its Influence on Nucleus
... was measured between 280 and 290 mOsm. The junction potential for this intracellular pipette solution was 7 mV with reference to the grounded bath medium. All data are presented with correction for the junction potential. Whole-cell voltage signals were recorded under current clamp using an Axoclamp ...
... was measured between 280 and 290 mOsm. The junction potential for this intracellular pipette solution was 7 mV with reference to the grounded bath medium. All data are presented with correction for the junction potential. Whole-cell voltage signals were recorded under current clamp using an Axoclamp ...
Disorders of the Spinal Cord
... the segmental level: • lower motor neuron cell bodies are located in the anterior horns (grey matter), for each segment, their axons form an anterior spinal root, and project to groups of muscles (the myotome) • sensory neurons in a dorsal root enter the spinal cord (the territory of skin innervated ...
... the segmental level: • lower motor neuron cell bodies are located in the anterior horns (grey matter), for each segment, their axons form an anterior spinal root, and project to groups of muscles (the myotome) • sensory neurons in a dorsal root enter the spinal cord (the territory of skin innervated ...
Normalization in human somatosensory cortex
... MRI acquisition. MRI data were acquired with a 3-T, head-only MRI scanner (Allegra; Siemens, Erlangen, Germany) using a head coil (NM-011; NOVA Medical, Wakefield, MA) for transmitting and an eight-channel phased array surface coil (NMSC-071; NOVA Medical) for receiving. Functional scans were acquir ...
... MRI acquisition. MRI data were acquired with a 3-T, head-only MRI scanner (Allegra; Siemens, Erlangen, Germany) using a head coil (NM-011; NOVA Medical, Wakefield, MA) for transmitting and an eight-channel phased array surface coil (NMSC-071; NOVA Medical) for receiving. Functional scans were acquir ...
make motor neuron posters now
... A. Myelinated axons send messages more quickly than nonmyelinated ones. B. Axons with greater diameter send impulses more quickly. ...
... A. Myelinated axons send messages more quickly than nonmyelinated ones. B. Axons with greater diameter send impulses more quickly. ...
(lateral spinothalamic tract).
... Visceral pain fibers from thoracic & abdominal viscera travel in the reverse direction thru splanchnics (sympathetics) to the spinal cord. Their cell bodies are in the dorsal root ganglia. Their central processes synapse in the dorsal horn. While some visceral pain will travel with the lateral spino ...
... Visceral pain fibers from thoracic & abdominal viscera travel in the reverse direction thru splanchnics (sympathetics) to the spinal cord. Their cell bodies are in the dorsal root ganglia. Their central processes synapse in the dorsal horn. While some visceral pain will travel with the lateral spino ...
Functional Disconnectivities in Autistic Spectrum
... children and adults compared to control subjects or those with acquired syndromes. Since learning disabled children exhibit deficient performance on a variety of tests thought to be a measure of perceptual laterality, evidence of weak laterality or failure to develop laterality has been found across ...
... children and adults compared to control subjects or those with acquired syndromes. Since learning disabled children exhibit deficient performance on a variety of tests thought to be a measure of perceptual laterality, evidence of weak laterality or failure to develop laterality has been found across ...
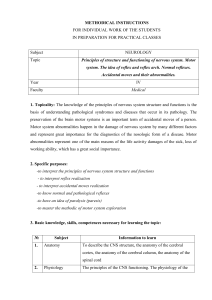
1 Principles of structure and functioning of nervous system
... The list of theoretical questions: 1. Main stages of phylo- and ontogenesis of the nervous system. 2. Structural and functional unit of the nervous system. 3. Main anatomo-topographical sections of the nervous system: cerebral hemisphere, basal ganglia, cerebral column spinal cord, radices, spinal g ...
... The list of theoretical questions: 1. Main stages of phylo- and ontogenesis of the nervous system. 2. Structural and functional unit of the nervous system. 3. Main anatomo-topographical sections of the nervous system: cerebral hemisphere, basal ganglia, cerebral column spinal cord, radices, spinal g ...
Full version (PDF file)
... of the NAc core neurons in which ventral or dorsal DPSP were evoked, so we pooled them (RMPs: F(4,56)=1.4, p>0.05; membrane resistance: F(4,64)=0.8, p>0.05; spike amplitude: F(4,58)=1.6, p>0.05) (Table 1). Muscarine produces a differential dose-dependent decrease in V-DPSP and D-DPSP At RMPs, focal ...
... of the NAc core neurons in which ventral or dorsal DPSP were evoked, so we pooled them (RMPs: F(4,56)=1.4, p>0.05; membrane resistance: F(4,64)=0.8, p>0.05; spike amplitude: F(4,58)=1.6, p>0.05) (Table 1). Muscarine produces a differential dose-dependent decrease in V-DPSP and D-DPSP At RMPs, focal ...
Recruitment properties of intramuscular and nerve
... resolution and reliability approaching that of natural neural control. Unfortunately, electrical stimulation of motor axons tends to result in a recruitment order opposite to that obtained by synaptic inputs [1], [2]. Normally, the smaller motoneurons innervating small numbers of slow, fatigue-resis ...
... resolution and reliability approaching that of natural neural control. Unfortunately, electrical stimulation of motor axons tends to result in a recruitment order opposite to that obtained by synaptic inputs [1], [2]. Normally, the smaller motoneurons innervating small numbers of slow, fatigue-resis ...
Gross Anatomy
... • Roots are short and horizontal in the cervical and thoracic regions while they are longer and more horizontal in the sacral and lumbar • regions. Almost immediately after emerging from its intervertebral foramen, a spinal nerve will divide into a dorsal ramus, a ventral ramus, and a meningeal bran ...
... • Roots are short and horizontal in the cervical and thoracic regions while they are longer and more horizontal in the sacral and lumbar • regions. Almost immediately after emerging from its intervertebral foramen, a spinal nerve will divide into a dorsal ramus, a ventral ramus, and a meningeal bran ...
Ventromedial Thalamic Neurons Convey Nociceptive Signals from
... Figure 2. Single-sweep recordings showing Ad- and C -fiber-evoked responses of a V Ml neuron (black dot in A) after supramaximal percutaneous electrical stimulation (2 msec duration square-wave pulses) of different parts of the body (arrows). Note that the Ad- and C-fiber responses were evoked from ...
... Figure 2. Single-sweep recordings showing Ad- and C -fiber-evoked responses of a V Ml neuron (black dot in A) after supramaximal percutaneous electrical stimulation (2 msec duration square-wave pulses) of different parts of the body (arrows). Note that the Ad- and C-fiber responses were evoked from ...
neuro 04 brainstem student
... Loss of pain and temperature on the contralateral side (spinothalamic tract) Loss of pain and temperature on the same side of the face and nasal and oral cavities (uncrossed spinal trigeminal tract) Difficulty swallowing and a hoarse, weak voice. Due to damage to nucleus ambiguus Loss of gag reflex ...
... Loss of pain and temperature on the contralateral side (spinothalamic tract) Loss of pain and temperature on the same side of the face and nasal and oral cavities (uncrossed spinal trigeminal tract) Difficulty swallowing and a hoarse, weak voice. Due to damage to nucleus ambiguus Loss of gag reflex ...
Chapter 17-Pathways and Integrative Functions
... • Communication of CNS with body structures through pathways • Tracts = groups or bundles of axons that travel together in CNS • Nucleus = collection of neuron cell bodies within CNS • Somatotropy = correspondence between body area of receptors and functional areas in cerebral cortex ...
... • Communication of CNS with body structures through pathways • Tracts = groups or bundles of axons that travel together in CNS • Nucleus = collection of neuron cell bodies within CNS • Somatotropy = correspondence between body area of receptors and functional areas in cerebral cortex ...