BIOL 105 S 2011 MTX 2 QA 110512.1
... C) the spinal cord would not be able to process information at that level. D) the brain would not be able to communicate with that level of the spinal cord. E) incoming sensory information would be disrupted. Answer: E 63) The part of the brain that functions to control skeletal muscles is the A) me ...
... C) the spinal cord would not be able to process information at that level. D) the brain would not be able to communicate with that level of the spinal cord. E) incoming sensory information would be disrupted. Answer: E 63) The part of the brain that functions to control skeletal muscles is the A) me ...
29.4 Central and Peripheral Nervous Systems The
... 29.4 Central and Peripheral Nervous Systems The CNS: • The brain has three parts. 1. cerebrum controls thought, movement, emotion 2. cerebellum located in back of skull, balances the actions of muscles so body can move smoothly 3. brain stem Brain stem controls basic life ...
... 29.4 Central and Peripheral Nervous Systems The CNS: • The brain has three parts. 1. cerebrum controls thought, movement, emotion 2. cerebellum located in back of skull, balances the actions of muscles so body can move smoothly 3. brain stem Brain stem controls basic life ...
Voltage-Dependent Switching of Sensorimotor Integration by a
... of 15 stimulations as in C and E (gray box; p ⬍ 0.001; n ⫽ 20). From the last stimulation of the induction series (time 0, T0 in C) until 60 min later (T60 ), one to three additional vpln stimulations per preparation were delivered at ⱖ5 min intervals so as not to permit a decrease in inactivation d ...
... of 15 stimulations as in C and E (gray box; p ⬍ 0.001; n ⫽ 20). From the last stimulation of the induction series (time 0, T0 in C) until 60 min later (T60 ), one to three additional vpln stimulations per preparation were delivered at ⱖ5 min intervals so as not to permit a decrease in inactivation d ...
chapter 9: nervous system
... more likely sites for the development of a tumor. Fully mature neurons, as well as some precursor cells, are not capable of mitosis. 3. Critical Thinking Issue(s) a. Explain what happens when your arm “falls asleep” after awkwardly lying on it for an extended period of time. Answer: The pressure exe ...
... more likely sites for the development of a tumor. Fully mature neurons, as well as some precursor cells, are not capable of mitosis. 3. Critical Thinking Issue(s) a. Explain what happens when your arm “falls asleep” after awkwardly lying on it for an extended period of time. Answer: The pressure exe ...
Optogenetic drive of neocortical pyramidal neurons generates fMRI
... signal is higher for 40 relative to 8 Hz. Quantifying this result (Fig. 2B), firing rate (MUA) was elevated (n=2 animals) for 40 Hz compared to 8 Hz (Wilcoxon rank-sum test, P=5.78e-12), the LFP power ratio (n=3) decreased with increased stimulation frequency (P=0.0134) and the dcLFP (n=3) average v ...
... signal is higher for 40 relative to 8 Hz. Quantifying this result (Fig. 2B), firing rate (MUA) was elevated (n=2 animals) for 40 Hz compared to 8 Hz (Wilcoxon rank-sum test, P=5.78e-12), the LFP power ratio (n=3) decreased with increased stimulation frequency (P=0.0134) and the dcLFP (n=3) average v ...
1285174151_463961
... The Anatomy and Functions of the Brainstem (cont’d.) • Midbrain – Ventral cerebral peduncles: convey impulses from cortex to pons and spinal cord – Dorsal tectum: reflex center – Controls movement of head and eyeball (visual stimuli) – Controls movement of head and trunk (auditory stimuli) ...
... The Anatomy and Functions of the Brainstem (cont’d.) • Midbrain – Ventral cerebral peduncles: convey impulses from cortex to pons and spinal cord – Dorsal tectum: reflex center – Controls movement of head and eyeball (visual stimuli) – Controls movement of head and trunk (auditory stimuli) ...
LESSON PLAN
... Conclusion: ½ anterior part of the spinal cord has a ……… nature ½ posterior part of the spinal cord has a ……………. nature - in the central part there is the …………. canal where ………….. fluid can be found Structure of spinal nerve - the spinal nerve connects the spinal cord with r……….. and e……… Structure ...
... Conclusion: ½ anterior part of the spinal cord has a ……… nature ½ posterior part of the spinal cord has a ……………. nature - in the central part there is the …………. canal where ………….. fluid can be found Structure of spinal nerve - the spinal nerve connects the spinal cord with r……….. and e……… Structure ...
Eagleman Ch 7. The Motor System
... The supplementary motor area and presupplementary motor are part of the medial motor system. Activity in the pre-supplementary motor area begins several seconds before selfinitiated movements. ...
... The supplementary motor area and presupplementary motor are part of the medial motor system. Activity in the pre-supplementary motor area begins several seconds before selfinitiated movements. ...
Trial time warping to discriminate stimulus-related
... sensory stimuli. However, these methods are not designed to test whether the activity of a cell is associated to the sensory, cognitive, or motor aspects of a task, particularly when the task includes many such events in a sequence. Here we describe a novel warping method to discover whether the cel ...
... sensory stimuli. However, these methods are not designed to test whether the activity of a cell is associated to the sensory, cognitive, or motor aspects of a task, particularly when the task includes many such events in a sequence. Here we describe a novel warping method to discover whether the cel ...
Chapter 27 - Fullfrontalanatomy.com
... center for body movements. • The forebrain contains the most sophisticated integrating centers in the brain: – The thalamus, which relays information to the cerebral cortex – The hypothalamus, with many regulatory functions – The cerebrum, the largest and most sophisticated part of the brain © 2010 ...
... center for body movements. • The forebrain contains the most sophisticated integrating centers in the brain: – The thalamus, which relays information to the cerebral cortex – The hypothalamus, with many regulatory functions – The cerebrum, the largest and most sophisticated part of the brain © 2010 ...
Properties of Primary Sensory (Lemniscal) Synapses in the
... sensory inputs to the neocortex. In the primary somatosensory thalamus (ventrobasal thalamus), sensory inputs deliver tactile information through the medial lemniscus tract. The transmission of sensory information through this pathway is affected by behavioral state. For instance, the relay of high- ...
... sensory inputs to the neocortex. In the primary somatosensory thalamus (ventrobasal thalamus), sensory inputs deliver tactile information through the medial lemniscus tract. The transmission of sensory information through this pathway is affected by behavioral state. For instance, the relay of high- ...
Subacute combined degeneration of the spinal cord
... • the ventral and the dorsal roots join together and form the spinal nerve • spinal nerves get out of the spinal canal through the intervertebral foramina • the segmental level: • lower motor neuron cell bodies are located in the anterior horns (grey matter), for each segment, their axons form an an ...
... • the ventral and the dorsal roots join together and form the spinal nerve • spinal nerves get out of the spinal canal through the intervertebral foramina • the segmental level: • lower motor neuron cell bodies are located in the anterior horns (grey matter), for each segment, their axons form an an ...
State-dependent and cell type-specific temporal processing in
... (≤4 Hz) were observed particularly in deep channels whereas beta (12–30 Hz) frequency was relatively prominent around presumptive thalamic recipient layers compared to other layers. After BF stimulations (Fig. 3b), the delta component in deep layers decreased whereas the low gamma (30–50 Hz) compone ...
... (≤4 Hz) were observed particularly in deep channels whereas beta (12–30 Hz) frequency was relatively prominent around presumptive thalamic recipient layers compared to other layers. After BF stimulations (Fig. 3b), the delta component in deep layers decreased whereas the low gamma (30–50 Hz) compone ...
How and Why Brains Create Meaning from Sensory Information
... wave packet is triggered is of particular interest. When an animal or human receives sensory information, it is carried not by any small number of axons from receptors but by a massive barrage of action potentials. A glimpse of a face, for example, includes all of the detectors for motions, contours ...
... wave packet is triggered is of particular interest. When an animal or human receives sensory information, it is carried not by any small number of axons from receptors but by a massive barrage of action potentials. A glimpse of a face, for example, includes all of the detectors for motions, contours ...
Cerebellar Unit Activity and the Movement Disruption Induced by
... both structures during spontaneous reaching, low frequency electrical stimulation (0.1 ms, 5 to 20 V, 0.2 Hz), and reach-triggered electrical stimulation. With the electrodes used, the stimulus current ranged from 0.1 to 0.4 mA. Extension of the forepaw into the feeder was detected with a photoelect ...
... both structures during spontaneous reaching, low frequency electrical stimulation (0.1 ms, 5 to 20 V, 0.2 Hz), and reach-triggered electrical stimulation. With the electrodes used, the stimulus current ranged from 0.1 to 0.4 mA. Extension of the forepaw into the feeder was detected with a photoelect ...
Nervous System I
... The functioning of the neuron is dependent on the separation of positive and negative ions, keeping the negative charge on the inside and the positive charge on the outside. Neurons are typically at a resting state or resting potential: the amount of positive ions on one side and negative ions on th ...
... The functioning of the neuron is dependent on the separation of positive and negative ions, keeping the negative charge on the inside and the positive charge on the outside. Neurons are typically at a resting state or resting potential: the amount of positive ions on one side and negative ions on th ...
Lecture6 - Part 1 ANS student (2012).
... body to adapt to to changes in the external environment , ...
... body to adapt to to changes in the external environment , ...
ANS VS PNS
... Helps the body when it is in need of energy, under stress, and in emergency situation Does this by: increases blood pressure o decrease digestion o Increase heart beat o ...
... Helps the body when it is in need of energy, under stress, and in emergency situation Does this by: increases blood pressure o decrease digestion o Increase heart beat o ...
Spinal Cord - eCurriculum
... The peripheral distribution of spinal nerves follows a specific distribution pattern. The localization of segments involved in spinal cord lesions can be determined based upon knowledge of this peripheral distribution of spinal nerves from each segment of the cord. During development, each segment o ...
... The peripheral distribution of spinal nerves follows a specific distribution pattern. The localization of segments involved in spinal cord lesions can be determined based upon knowledge of this peripheral distribution of spinal nerves from each segment of the cord. During development, each segment o ...
Lab 6
... performing mental thought, memories, and dreaming. The electroencephalogram (EEG) is a recording from the surface of the scalp generated by many biopotentials in the cerebrum of the brain. More specifically, it is a recording of the action potentials and the postsynaptic potentials of cortical cells ...
... performing mental thought, memories, and dreaming. The electroencephalogram (EEG) is a recording from the surface of the scalp generated by many biopotentials in the cerebrum of the brain. More specifically, it is a recording of the action potentials and the postsynaptic potentials of cortical cells ...
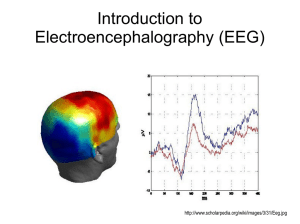
Introduction to Electroencephalography (EEG)
... commonly recognized components. Auditory components marked by roman numbers are the brainstem-evoked responses (BAEP). They are followed by mid-latency exogenous components (MAEP). The first peak in exogenous visual ERP comes from ERG (electroretinogram). Exogenous ERPs exhibit modality– specific fe ...
... commonly recognized components. Auditory components marked by roman numbers are the brainstem-evoked responses (BAEP). They are followed by mid-latency exogenous components (MAEP). The first peak in exogenous visual ERP comes from ERG (electroretinogram). Exogenous ERPs exhibit modality– specific fe ...
Saladin 5e Extended Outline
... up and down the cord. 2. Locomotion. Motor neurons in the brain initiate walking, but continued walking is coordinated by groups of neurons called central patterns generators in the cord. 3. Reflexes. Involuntary stereotyped responses to stimuli involve the brain, spinal cord, and peripheral nerves. ...
... up and down the cord. 2. Locomotion. Motor neurons in the brain initiate walking, but continued walking is coordinated by groups of neurons called central patterns generators in the cord. 3. Reflexes. Involuntary stereotyped responses to stimuli involve the brain, spinal cord, and peripheral nerves. ...
Multisensory contributions to low-level, `unisensory` processing
... feedback processes observed in V1 for ‘contextual surround’ [46] and visual selective attention [47] effects, both of which use feedback input and lag the initial feedforward sensory input. In any case, given that the requirements for integration [48] are met, a visual or somatosensory input could e ...
... feedback processes observed in V1 for ‘contextual surround’ [46] and visual selective attention [47] effects, both of which use feedback input and lag the initial feedforward sensory input. In any case, given that the requirements for integration [48] are met, a visual or somatosensory input could e ...
2. Organization of the Exam and Assessment Criteria
... electroencephalography, cardiography, electromyography, eye tracking, galvanic skin response, plethysmography, pneumography, etc., their relation to psychical processes and conditions, practical application. Polygraphy. 13. Electroencephalography and magnetoencephalography: ways of recording and met ...
... electroencephalography, cardiography, electromyography, eye tracking, galvanic skin response, plethysmography, pneumography, etc., their relation to psychical processes and conditions, practical application. Polygraphy. 13. Electroencephalography and magnetoencephalography: ways of recording and met ...
2. Organization of the Exam and Assessment Criteria
... electroencephalography, cardiography, electromyography, eye tracking, galvanic skin response, plethysmography, pneumography, etc., their relation to psychical processes and conditions, practical application. Polygraphy. 13. Electroencephalography and magnetoencephalography: ways of recording and met ...
... electroencephalography, cardiography, electromyography, eye tracking, galvanic skin response, plethysmography, pneumography, etc., their relation to psychical processes and conditions, practical application. Polygraphy. 13. Electroencephalography and magnetoencephalography: ways of recording and met ...