Core Lab #1 - Reflex Responses
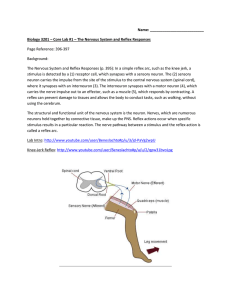
... stimulus is detected by a (1) receptor cell, which synapses with a sensory neuron. The (2) sensory neuron carries the impulse from the site of the stimulus to the central nervous system (spinal cord), where it synapses with an interneuron (3). The interneuron synapses with a motor neuron (4), which ...
... stimulus is detected by a (1) receptor cell, which synapses with a sensory neuron. The (2) sensory neuron carries the impulse from the site of the stimulus to the central nervous system (spinal cord), where it synapses with an interneuron (3). The interneuron synapses with a motor neuron (4), which ...
The Effects of Local Fetal Brain Extract Administration
... saturated response was recorded. At this location, the recorded CMAP were saved. Then, the recorded CMAP from animals, in each group and at each stage, were averaged and a printout of each was taken. Finally, the delay time (latency) of averaged records of experimental and control rats were measured ...
... saturated response was recorded. At this location, the recorded CMAP were saved. Then, the recorded CMAP from animals, in each group and at each stage, were averaged and a printout of each was taken. Finally, the delay time (latency) of averaged records of experimental and control rats were measured ...
Regulation of Action-Potential Firing in Spiny Neurons of the Rat
... but the reason for their differences in firing activity are unknown. We compared properties of spontaneously firing and silent spiny neurons in urethan-anesthetized rats. Neurons were identified as spiny projection neurons after labeling by intracellular injection of biocytin. The threshold for acti ...
... but the reason for their differences in firing activity are unknown. We compared properties of spontaneously firing and silent spiny neurons in urethan-anesthetized rats. Neurons were identified as spiny projection neurons after labeling by intracellular injection of biocytin. The threshold for acti ...
Regulation of Action-Potential Firing in Spiny Neurons of the Rat
... silent spiny neurons are not observed to fire in extracellular records made before penetration, their silence is not thought to be from the effects of impalement (Wilson and Groves 1981). Extracellular recording combined with iontophoretic application of excitatory neurotransmitters has also reveale ...
... silent spiny neurons are not observed to fire in extracellular records made before penetration, their silence is not thought to be from the effects of impalement (Wilson and Groves 1981). Extracellular recording combined with iontophoretic application of excitatory neurotransmitters has also reveale ...
Activity of Bipolar Potential Generation in Paramecium
... studied by T. Kamada, 1934[7]. The relation of membrane potential and motion of cilia is studied by Y. Naitoh and R. Eckert, 1969[8,9]. They showed that swimming directions are defined by positive (depolarization) and negative (hyperpolarization) potentials generated in a single cell. In florecence ...
... studied by T. Kamada, 1934[7]. The relation of membrane potential and motion of cilia is studied by Y. Naitoh and R. Eckert, 1969[8,9]. They showed that swimming directions are defined by positive (depolarization) and negative (hyperpolarization) potentials generated in a single cell. In florecence ...
CHAPTER 11: NERVOUS SYSTEM II: DIVISIONS OF THE
... Describe the structures around the spinal cord (i.e. dorsal root, ventral root, spinal nerve, white ramus communicans, gray ramus communicans, paravertebral (chain) ganglia, and ...
... Describe the structures around the spinal cord (i.e. dorsal root, ventral root, spinal nerve, white ramus communicans, gray ramus communicans, paravertebral (chain) ganglia, and ...
Neuroanatomy - TechnionMed
... 1. Anterolateral spinothalamic pathway fibers in the brain are called a. spinal lamnisucus b. NOT lateral lamniscus c. NOT medial lamniscus d. NOT spinothalamic tract 2. What is true about fibers from the antero-lateral spinothalamic tract a. Metseltabis? Near the spinal segment where the afferent n ...
... 1. Anterolateral spinothalamic pathway fibers in the brain are called a. spinal lamnisucus b. NOT lateral lamniscus c. NOT medial lamniscus d. NOT spinothalamic tract 2. What is true about fibers from the antero-lateral spinothalamic tract a. Metseltabis? Near the spinal segment where the afferent n ...
The Central Nervous System
... The ANS always displays two neurons in the motor pathway from CNS to the effector organ. - This contrasts with the situation in the somatic-efferent system where there is one neuron in the path from CNS to a skeletal muscle effector. The two ANS neurons are designated the pre- and post-ganglionic n ...
... The ANS always displays two neurons in the motor pathway from CNS to the effector organ. - This contrasts with the situation in the somatic-efferent system where there is one neuron in the path from CNS to a skeletal muscle effector. The two ANS neurons are designated the pre- and post-ganglionic n ...
Wind Direction Coding in the Cockroach Escape Response: Winner
... measurements somewhat underestimated the movements of the CF joints of the front legs, because these front legs are held at an angle oblique to the view of the camera. We transformed these data into a single parameter that could describe turn direction. For this, we combined the data from all six le ...
... measurements somewhat underestimated the movements of the CF joints of the front legs, because these front legs are held at an angle oblique to the view of the camera. We transformed these data into a single parameter that could describe turn direction. For this, we combined the data from all six le ...
Science - Princeton University
... tissue receives and processes visual information from both the ipsilateral and the contralateral occipital lobes (15) and, perhaps, from the pulvinar as well. Thus, inferotemporal cortex may be an integrating mechanism for information about "what the stimulus is." received from the geniculostriate s ...
... tissue receives and processes visual information from both the ipsilateral and the contralateral occipital lobes (15) and, perhaps, from the pulvinar as well. Thus, inferotemporal cortex may be an integrating mechanism for information about "what the stimulus is." received from the geniculostriate s ...
Meninges,Cerebrospinal Fluid, and the spinal cord
... Myelinated ascending (sensory) & descending (motor) tracts Tracts located in 3 white columns (funiculi) on each side ...
... Myelinated ascending (sensory) & descending (motor) tracts Tracts located in 3 white columns (funiculi) on each side ...
Chapter 15
... for the last 3 years. She was originally admitted to the nursing home following amputation of both legs below the knee. This was necessary secondary to diabetes that results in gradual neuropathy and loss of vascular circulation in the extremities. A recent visit by the primary care physician reveal ...
... for the last 3 years. She was originally admitted to the nursing home following amputation of both legs below the knee. This was necessary secondary to diabetes that results in gradual neuropathy and loss of vascular circulation in the extremities. A recent visit by the primary care physician reveal ...
The Nervous System
... When skeletal muscles contract, they do so in response to stimuli from the nervous system. We plan our movement in the brain, and the ner vous system transmits that plan to the muscles. At the muscles, the nervous system stimulates contraction but stimulates only those motor units needed for that pa ...
... When skeletal muscles contract, they do so in response to stimuli from the nervous system. We plan our movement in the brain, and the ner vous system transmits that plan to the muscles. At the muscles, the nervous system stimulates contraction but stimulates only those motor units needed for that pa ...
ASCENDING PATHWAYS - University of Kansas Medical Center
... Secondary axons make up the lateral spinothalamic tract traveling in the lateral column of the spinal cord. ...
... Secondary axons make up the lateral spinothalamic tract traveling in the lateral column of the spinal cord. ...
Chapter 13: The Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves, and Spinal Reflexes
... nerve (of the lateral cord), the median nerve (of lateral and medial cords), the ulnar nerve (of the medial cord), axillary nerve (of the posterior cord) and the radial nerve (of the posterior cord). Table 13-2 summarizes the structures of the brachial plexus. ...
... nerve (of the lateral cord), the median nerve (of lateral and medial cords), the ulnar nerve (of the medial cord), axillary nerve (of the posterior cord) and the radial nerve (of the posterior cord). Table 13-2 summarizes the structures of the brachial plexus. ...
Lab #6: Neurophysiology Simulation
... potential is recorded. A threshold stimulus is just intense enough to depolarize a few neurons in the nerve to threshold and cause them to undergo an action potential, so a very weak compound action potential is recorded. If stimulus intensity is increased above threshold, the amplitude of the compo ...
... potential is recorded. A threshold stimulus is just intense enough to depolarize a few neurons in the nerve to threshold and cause them to undergo an action potential, so a very weak compound action potential is recorded. If stimulus intensity is increased above threshold, the amplitude of the compo ...
Nervous System - IHMC Public Cmaps
... 1. CONTROL OF ALL BODY FUNCTIONS: Nervous system is the master system of human body. It controls the activity of all other systems in such a way that all the systems collectively make a human being. Without a controlling system, there is no concept of life because in such case there will be no coord ...
... 1. CONTROL OF ALL BODY FUNCTIONS: Nervous system is the master system of human body. It controls the activity of all other systems in such a way that all the systems collectively make a human being. Without a controlling system, there is no concept of life because in such case there will be no coord ...
spinal nerves - Coastal Bend College
... • SC gives rise to 31 pairs of spinal nerves that exit the vertebral column thru intervertebral foramen or the sacral foramina • 2 regions of enlargement ...
... • SC gives rise to 31 pairs of spinal nerves that exit the vertebral column thru intervertebral foramen or the sacral foramina • 2 regions of enlargement ...
Chapter 12 - Coastal Bend College
... • SC gives rise to 31 pairs of spinal nerves that exit the vertebral column thru intervertebral foramen or the sacral foramina • 2 regions of enlargement ...
... • SC gives rise to 31 pairs of spinal nerves that exit the vertebral column thru intervertebral foramen or the sacral foramina • 2 regions of enlargement ...
Nervous System: Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves
... -spinal nerves branch off cord near to what they innervate -cervical and lumbar enlargements of cord house cell bodies of motor neurons for muscles of appendages -Dermatome = region of skin surface innervated by one pair spinal nerves ...
... -spinal nerves branch off cord near to what they innervate -cervical and lumbar enlargements of cord house cell bodies of motor neurons for muscles of appendages -Dermatome = region of skin surface innervated by one pair spinal nerves ...
Atonia-Related Regions in the Rodent Pons and Medulla
... SNEX-100) that were moved stereotaxically in 0.3-mm steps from H2.8 to 0.0 between A0.7–P0.3 and L0.2–1.5 mm in the pons and from H2.0 to ⫺0.7 between P2.0 –P3.3 and L0.0 – 0.6 in the medulla according to Paxinos and Watson (1986). These regions correspond to the approximate anatomical levels of the ...
... SNEX-100) that were moved stereotaxically in 0.3-mm steps from H2.8 to 0.0 between A0.7–P0.3 and L0.2–1.5 mm in the pons and from H2.0 to ⫺0.7 between P2.0 –P3.3 and L0.0 – 0.6 in the medulla according to Paxinos and Watson (1986). These regions correspond to the approximate anatomical levels of the ...
Reflexes - Sinoe Medical Association
... The white matter of the spinal cord consists of ascending and descending fiber tracts, with the ascending tracts transmitting sensory information (from receptors in the skin, skin skeletal muscles muscles, tendons tendons, joints joints, & various visceral receptors) and the descending tracts transm ...
... The white matter of the spinal cord consists of ascending and descending fiber tracts, with the ascending tracts transmitting sensory information (from receptors in the skin, skin skeletal muscles muscles, tendons tendons, joints joints, & various visceral receptors) and the descending tracts transm ...
Chapter 13 PowerPoint - Hillsborough Community College
... – Aspects of sensory perception: • Perceptual detection: ability to detect a stimulus (requires summation of impulses) • Magnitude estimation: intensity coded in frequency of impulses • Spatial discrimination: identifying site or pattern of stimulus (studied by two-point discrimination test) © 2016 ...
... – Aspects of sensory perception: • Perceptual detection: ability to detect a stimulus (requires summation of impulses) • Magnitude estimation: intensity coded in frequency of impulses • Spatial discrimination: identifying site or pattern of stimulus (studied by two-point discrimination test) © 2016 ...
pdf
... humans (19) and has been found to be associated with auditory attention (1, 20, 41) resulting in top-down modulation of auditory processing (25). This finding was further confirmed by electrophysiological data indicating that tinnitus might occur as the result of a dysfunction in the top-down inhibito ...
... humans (19) and has been found to be associated with auditory attention (1, 20, 41) resulting in top-down modulation of auditory processing (25). This finding was further confirmed by electrophysiological data indicating that tinnitus might occur as the result of a dysfunction in the top-down inhibito ...