Electrical stimulation of neural tissue to evoke behavioral responses
... estimate how far from the electrode tip current activates neural tissue mediating behaviors such as eating (Olds, 1958), self-stimulation (Wise, 1972; Fouriezos and Wise, 1984; Milner and Laferriere, 1986), and circling behavior (Yeomans et al., 1984, 1986). The method used by Fouriezos and Wise (19 ...
... estimate how far from the electrode tip current activates neural tissue mediating behaviors such as eating (Olds, 1958), self-stimulation (Wise, 1972; Fouriezos and Wise, 1984; Milner and Laferriere, 1986), and circling behavior (Yeomans et al., 1984, 1986). The method used by Fouriezos and Wise (19 ...
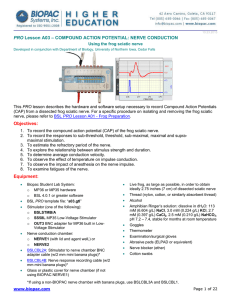
compound action potential: nerve conduction
... channels are also stimulated by the “+” voltage change and begin to slowly open. After inactivation of the NaC, the delayed-opening of the K-channels helps return the membrane voltage to the resting potential after the action potential has passed. For a short period of time, all NaC are inactivated ...
... channels are also stimulated by the “+” voltage change and begin to slowly open. After inactivation of the NaC, the delayed-opening of the K-channels helps return the membrane voltage to the resting potential after the action potential has passed. For a short period of time, all NaC are inactivated ...
Neurologic System The nervous system Central and peripheral
... Basal ganglia system Extrapyramidal pathway and processing station between the cerebral motor cortex and the upper brainstem Refine motor movements through interconnections with: Thalamus Motor cortex Reticular formation Spinal cord Cerebrum (Cont.) Aids in integration of voluntary movement to produ ...
... Basal ganglia system Extrapyramidal pathway and processing station between the cerebral motor cortex and the upper brainstem Refine motor movements through interconnections with: Thalamus Motor cortex Reticular formation Spinal cord Cerebrum (Cont.) Aids in integration of voluntary movement to produ ...
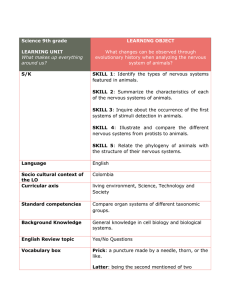
CHAPTER 48 NEURONS, SYNAPSES, AND SIGNALING Learning
... 8. Explain the role of mechanoreceptors in hearing and balance. 9. Describe the structure and function of invertebrate statocysts. 10. Explain how insects may detect sound. 11. Refer to a diagram of the human ear and give the function of each structure. 12. Explain how the mammalian ear functions as ...
... 8. Explain the role of mechanoreceptors in hearing and balance. 9. Describe the structure and function of invertebrate statocysts. 10. Explain how insects may detect sound. 11. Refer to a diagram of the human ear and give the function of each structure. 12. Explain how the mammalian ear functions as ...
Cranial Nerves: Assessment of Functions
... nasal half of each retina cross at the optic chiasma and are distributed to the contralateral brain stem, thalamus, and occipital cerebrum along with fibers from the ipsilateral temporal retina (see figure 1.2). Both eyes are represented in the occipital cortex of each cerebral hemisphere. In additi ...
... nasal half of each retina cross at the optic chiasma and are distributed to the contralateral brain stem, thalamus, and occipital cerebrum along with fibers from the ipsilateral temporal retina (see figure 1.2). Both eyes are represented in the occipital cortex of each cerebral hemisphere. In additi ...
Whisker sensory system – From receptor to decision
... presented to its right, and to inhibit licking when a sound is presented to its left. Thus, the brain stem can transmit left/right differences in neuronal firing pattern to the centers that control licking. But the same decorticate animal cannot be trained to approach a sound source, once localized, ...
... presented to its right, and to inhibit licking when a sound is presented to its left. Thus, the brain stem can transmit left/right differences in neuronal firing pattern to the centers that control licking. But the same decorticate animal cannot be trained to approach a sound source, once localized, ...
Effect of deep brain stimulation on substantia nigra neurons in a
... electrophoresed to the SNc at electrophoresis currents of 5–100 nA and stagnation currents of 5–10 nA. Except for Glu, other neurotransmitter detection solutions were electrophoresed using a positive charge. Unit neuron discharge was displayed on an oscilloscope after it was mediated and filtered th ...
... electrophoresed to the SNc at electrophoresis currents of 5–100 nA and stagnation currents of 5–10 nA. Except for Glu, other neurotransmitter detection solutions were electrophoresed using a positive charge. Unit neuron discharge was displayed on an oscilloscope after it was mediated and filtered th ...
Printable Activities
... The tendency of the invertebrates was to concentrate the nervous system in the anterior region, where brain cells are created. Later, the evolutionary trend was towards the formation of a nervous cord, capable of connecting the brain to the rest of the body. From the point of view of kinship (phylog ...
... The tendency of the invertebrates was to concentrate the nervous system in the anterior region, where brain cells are created. Later, the evolutionary trend was towards the formation of a nervous cord, capable of connecting the brain to the rest of the body. From the point of view of kinship (phylog ...
Auditory Brain Development in Children With Hearing Loss– Part One
... homa Health Sciences Center signal of interest from competing noise—occurs in groups of and Salus University. Ms. Smith, neurons at all levels of the auditory nervous system. right, is a founder and the exFrom the primary auditory cortex, auditory signals travel to the ecutive director of Hearts for ...
... homa Health Sciences Center signal of interest from competing noise—occurs in groups of and Salus University. Ms. Smith, neurons at all levels of the auditory nervous system. right, is a founder and the exFrom the primary auditory cortex, auditory signals travel to the ecutive director of Hearts for ...
The Nervous System
... in cortex fibers pass through bulges called pyramids on medulla oblongata - hence the name conduct impulses from motor cortex to motor nuclei of the cerebral nerves or to the ventral gray columns of spinal cord ...
... in cortex fibers pass through bulges called pyramids on medulla oblongata - hence the name conduct impulses from motor cortex to motor nuclei of the cerebral nerves or to the ventral gray columns of spinal cord ...
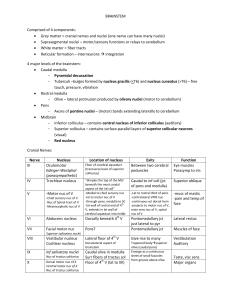
BRAINSTEM Comprised of 4 components: • Grey matter = cranial
... Comprised of 4 components: Grey matter = cranial nerves and nuclei (one nerve can have many nuclei) Suprasegmental nuclei – motor/sensory functions or relays to cerebellum White matter = fiber tracts Reticular formation – interneurons integration 4 major levels of the brainstem: Caudal m ...
... Comprised of 4 components: Grey matter = cranial nerves and nuclei (one nerve can have many nuclei) Suprasegmental nuclei – motor/sensory functions or relays to cerebellum White matter = fiber tracts Reticular formation – interneurons integration 4 major levels of the brainstem: Caudal m ...
Migraine photophobia originating in cone-driven
... for additional post-acquisition processing (see signal processing below). Preliminary real-time waveform discrimination was performed for initial characterization of neuronal responses using Spike2 software (CED), and was based on template creation from spontaneous and evoked action potentials. The ...
... for additional post-acquisition processing (see signal processing below). Preliminary real-time waveform discrimination was performed for initial characterization of neuronal responses using Spike2 software (CED), and was based on template creation from spontaneous and evoked action potentials. The ...
Neuro 04 Brainstem Student
... Loss of pain and temperature on the contralateral side (spinothalamic tract) Loss of pain and temperature on the same side of the face and nasal and oral cavities (uncrossed spinal trigeminal tract) Difficulty swallowing and a hoarse, weak voice. Due to damage to nucleus ambiguus Loss of gag reflex ...
... Loss of pain and temperature on the contralateral side (spinothalamic tract) Loss of pain and temperature on the same side of the face and nasal and oral cavities (uncrossed spinal trigeminal tract) Difficulty swallowing and a hoarse, weak voice. Due to damage to nucleus ambiguus Loss of gag reflex ...
Residual eye-movements in macaque and their effects on visual
... In all monkeys, the eyes moved throughout the course of the measurement. Figs. 1A–1C show, for eyes of three monkeys, X–Y plots of eye-position at 0.25-s intervals for 10 min. The eyes moved during the recording period, but generally without systematic progression (the movement shown in Fig. 1B—a st ...
... In all monkeys, the eyes moved throughout the course of the measurement. Figs. 1A–1C show, for eyes of three monkeys, X–Y plots of eye-position at 0.25-s intervals for 10 min. The eyes moved during the recording period, but generally without systematic progression (the movement shown in Fig. 1B—a st ...
Your Nervous System - Springfield Public Schools
... such as a flame? Most likely you have noticed that your hand automatically jerks away. This type of automatic response to your environment is called a reflex. A reflex action is shown in Figure 12. In some reflex actions, the actions of the skeletal muscles are controlled by the spinal cord only—not ...
... such as a flame? Most likely you have noticed that your hand automatically jerks away. This type of automatic response to your environment is called a reflex. A reflex action is shown in Figure 12. In some reflex actions, the actions of the skeletal muscles are controlled by the spinal cord only—not ...
Trigeminal nerve
... 3. inferior alveolar nerve : largest branch ,enter mandible through mandibular canal in association with inferior alveolar vein and artey • This nerve anteriorly through the mandibular canal until mental foramen and then divided in to two branches : mental and incisive 4.Mylohyoid nerve : branch fro ...
... 3. inferior alveolar nerve : largest branch ,enter mandible through mandibular canal in association with inferior alveolar vein and artey • This nerve anteriorly through the mandibular canal until mental foramen and then divided in to two branches : mental and incisive 4.Mylohyoid nerve : branch fro ...
Subconscious Stimulus Recognition and Processing During
... natural sleep and waking, recorded cortical unit responses to acoustic stimulation. Single units in both the primary and secondary auditory cortex decreased or increased their responses during sleep compared to wakefulness. Moreover, when the responses across neurons were averaged, sound-evoked acti ...
... natural sleep and waking, recorded cortical unit responses to acoustic stimulation. Single units in both the primary and secondary auditory cortex decreased or increased their responses during sleep compared to wakefulness. Moreover, when the responses across neurons were averaged, sound-evoked acti ...