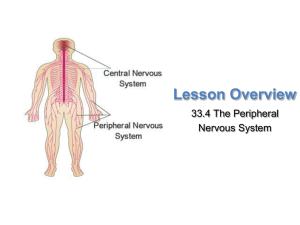
The Peripheral Nervous System
... skeletal muscles, stimulates the sweat glands, and slows down the contractions of smooth muscles in the digestive system. ...
... skeletal muscles, stimulates the sweat glands, and slows down the contractions of smooth muscles in the digestive system. ...
Chapter 9 powerpoint file
... Brain Function: Sensory Information Primary somatic sensory cortex- found on the postcentral gyrus (parietal lobe) Skin, musculoskeletal system, and visceracomponents that send information to this region when a stimulus activates a sensory receptor Somatosensory pathways – carry information o ...
... Brain Function: Sensory Information Primary somatic sensory cortex- found on the postcentral gyrus (parietal lobe) Skin, musculoskeletal system, and visceracomponents that send information to this region when a stimulus activates a sensory receptor Somatosensory pathways – carry information o ...
Cranial Nerves
... tissue coursing together outside the central nervous system. 3. Axon- the usually single, long process of a nerve cell that propagates a nerve impulse toward the axon terminals. 4. Dendrite- a neuronal process that carries electrical signals usually graded potentials, toward the cell body. 5. Synaps ...
... tissue coursing together outside the central nervous system. 3. Axon- the usually single, long process of a nerve cell that propagates a nerve impulse toward the axon terminals. 4. Dendrite- a neuronal process that carries electrical signals usually graded potentials, toward the cell body. 5. Synaps ...
Interactions Between the Lateral Hypothalamus and the
... and in the nucleus raphe magnus or its adjacent region, the nucleus magnocellularis. In nearly all experiments, a glass electrode containing 100 mM glutamic acid (monosodium L-glutamate) was glued to the stimulating electrode placed in the LH. Pressure of l-5 psi was used to inject glutamic acid. In ...
... and in the nucleus raphe magnus or its adjacent region, the nucleus magnocellularis. In nearly all experiments, a glass electrode containing 100 mM glutamic acid (monosodium L-glutamate) was glued to the stimulating electrode placed in the LH. Pressure of l-5 psi was used to inject glutamic acid. In ...
Capturing Brain Dynamics: a combined neuroscience and
... synchronization on a larger spatial scale Neuroengineering ...
... synchronization on a larger spatial scale Neuroengineering ...
Autonomic Nervous System
... Impulses originating in the brain are carried through the spinal cord, where they synapse with the dendrites of motor neurons. ...
... Impulses originating in the brain are carried through the spinal cord, where they synapse with the dendrites of motor neurons. ...
The Nervous System
... continues to move toward the cell body 8. Impulses travel faster when fibers have a myelin sheath ...
... continues to move toward the cell body 8. Impulses travel faster when fibers have a myelin sheath ...
- Neuro-Optometric Rehabilitation Association
... Retinal processing problems affect a majority of patients following traumatic brain injury (TBI) [1,2]. Sensory, motor, emotional and cognitive systems interact and process stimuli transmitted via retinal fiber pathways [3]; therefore, these systems are susceptible to TBI-related retinal processing dy ...
... Retinal processing problems affect a majority of patients following traumatic brain injury (TBI) [1,2]. Sensory, motor, emotional and cognitive systems interact and process stimuli transmitted via retinal fiber pathways [3]; therefore, these systems are susceptible to TBI-related retinal processing dy ...
motor pathways i-iii
... c) Vestibular nuclei respond to vestibular stimuli elicited by movements and changes in position of the head. They give rise to medial and lateral vestibulospinal tracts. d) These pathways provide a motor system parallel to the pyramidal system for activation of the LMNs. They descend through the br ...
... c) Vestibular nuclei respond to vestibular stimuli elicited by movements and changes in position of the head. They give rise to medial and lateral vestibulospinal tracts. d) These pathways provide a motor system parallel to the pyramidal system for activation of the LMNs. They descend through the br ...
Slide 1
... • Descending influence on RJM from cortical sites occurs. Input may activate the trigeminal motor pool during the initial phases of preparing and positioning of the food. • Such inputs also activate the CPG which modulated descending inputs from the motor cortex, and acts directly on the motor pool ...
... • Descending influence on RJM from cortical sites occurs. Input may activate the trigeminal motor pool during the initial phases of preparing and positioning of the food. • Such inputs also activate the CPG which modulated descending inputs from the motor cortex, and acts directly on the motor pool ...
A new view of the motor cortex
... sometimes directly to layer 5 of cortex, the output layer. The assumption seems to have been that this punctate stimulation could serve as a method of anatomical tract tracing. It could reveal the pathway of interest from cortex to muscles with a relay in the spinal cord, while avoiding the complica ...
... sometimes directly to layer 5 of cortex, the output layer. The assumption seems to have been that this punctate stimulation could serve as a method of anatomical tract tracing. It could reveal the pathway of interest from cortex to muscles with a relay in the spinal cord, while avoiding the complica ...
מצגת של PowerPoint
... - Less neurons with evoked inhibitory responses. - Lower evoked response amplitudes. - Lower spontaneous response frequencies (but similar amplitudes). ...
... - Less neurons with evoked inhibitory responses. - Lower evoked response amplitudes. - Lower spontaneous response frequencies (but similar amplitudes). ...
The Nervous System Introduction Organization of Neural Tissue
... • Integrate diverse information ...
... • Integrate diverse information ...
TRIGEMINAL NUCLEUS - eCurriculum
... modality to which a sense organ responds optimally. • Generator Potentials are depolarizations in receptors that are graded relative to the intensity and form of the stimulus. ...
... modality to which a sense organ responds optimally. • Generator Potentials are depolarizations in receptors that are graded relative to the intensity and form of the stimulus. ...
INTERNAL CAPSULE
... • a- descending branch : ventral and lateral reticulospinal tracts : spinal cord • b- ascending branch : reticular activating system (RAS) to cerebral cortex ...
... • a- descending branch : ventral and lateral reticulospinal tracts : spinal cord • b- ascending branch : reticular activating system (RAS) to cerebral cortex ...
Modulation of visceral function by selective stimulation of the left
... to the outputs of the stimulator a special cable was developed. At one end of the cable to be connected to the common connector was a switching module designed to fit its pins. The switching module permitted a certain GTE to be connected to the stimulator individually or in combination with other GT ...
... to the outputs of the stimulator a special cable was developed. At one end of the cable to be connected to the common connector was a switching module designed to fit its pins. The switching module permitted a certain GTE to be connected to the stimulator individually or in combination with other GT ...
video slide - ScienceToGo
... hyperpolarizations that move the membrane potential farther from threshold After release, the neurotransmitter ...
... hyperpolarizations that move the membrane potential farther from threshold After release, the neurotransmitter ...
The Brain - Personal
... task management Working memory for object-recall tasks Solving complex, multitask problems ...
... task management Working memory for object-recall tasks Solving complex, multitask problems ...
"Touch". In: Encyclopedia of Life Sciences (ELS)
... Touch is defined as direct contact between two physical bodies. In neuroscience, touch describes the special sense by which contact with the body is perceived in the conscious mind. Touch allows us to recognise objects held in the hand, and use them as tools. Because the skin is elastic, it forms a ...
... Touch is defined as direct contact between two physical bodies. In neuroscience, touch describes the special sense by which contact with the body is perceived in the conscious mind. Touch allows us to recognise objects held in the hand, and use them as tools. Because the skin is elastic, it forms a ...
GABA-antagonist inverts movement and object detection in flies
... spatial wavelength of grating 13"; contrast 30%; stimulus frequency 3 Hz). The flies were stimulated repetitively with a constant sequence of visual stimuli. This consisted of motion from back to front. counterphase flicker, motion from front to back and again counterphase flicker. Each stimulus las ...
... spatial wavelength of grating 13"; contrast 30%; stimulus frequency 3 Hz). The flies were stimulated repetitively with a constant sequence of visual stimuli. This consisted of motion from back to front. counterphase flicker, motion from front to back and again counterphase flicker. Each stimulus las ...
Motor Systems - Neuroanatomy
... reflexes are a basic building block of movement. Dorsal root inputs provide the sensory input for spinal reflexes, and the LMNs provide the motor output pathway. One of the simplest and best studied reflexes is the stretch reflex - stretch a muscle and the reflex circuit leads to contraction of the ...
... reflexes are a basic building block of movement. Dorsal root inputs provide the sensory input for spinal reflexes, and the LMNs provide the motor output pathway. One of the simplest and best studied reflexes is the stretch reflex - stretch a muscle and the reflex circuit leads to contraction of the ...
Sliding
... pre then post->LTP: easy, the AP “boosts” the activation of the NMDAR by reducing the Mg block post then pre-> LTD: several hypothesis 1) Ca entry during the AP. Ca is not fully removed by the time synapses are activated and help to bring [Ca]i to the LTD threshold 2) Ca entry during the AP desensit ...
... pre then post->LTP: easy, the AP “boosts” the activation of the NMDAR by reducing the Mg block post then pre-> LTD: several hypothesis 1) Ca entry during the AP. Ca is not fully removed by the time synapses are activated and help to bring [Ca]i to the LTD threshold 2) Ca entry during the AP desensit ...
Spring 2002
... healthy individuals, BCI experiments were also performed with patients with an amputated upper limb, spinal cord injury, and Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS). The Neil Squire Foundation in Canada is a non-profit organization whose purpose is to create opportunities for independence for individua ...
... healthy individuals, BCI experiments were also performed with patients with an amputated upper limb, spinal cord injury, and Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS). The Neil Squire Foundation in Canada is a non-profit organization whose purpose is to create opportunities for independence for individua ...
PDF
... As an alternative to sound stimulation, electrical microstimulation can be used to better understand the brain’s natural circuitry by perturbing the circuitry to generate percepts (Stanley, 2013). The ability to perturb activity within a system can provide important insights into the contribution of ...
... As an alternative to sound stimulation, electrical microstimulation can be used to better understand the brain’s natural circuitry by perturbing the circuitry to generate percepts (Stanley, 2013). The ability to perturb activity within a system can provide important insights into the contribution of ...