Central Nervous System (CNS)
... •Meissner’s (gracile and corpuscles cuneate tract) Finger or toe •Muscle spindle Dorsal column of the patient •Pacinian corpuscles (gracile and •Golgi tendon organs cuneate tract) ...
... •Meissner’s (gracile and corpuscles cuneate tract) Finger or toe •Muscle spindle Dorsal column of the patient •Pacinian corpuscles (gracile and •Golgi tendon organs cuneate tract) ...
BIO201 Crimando Vocab 6 BIO201 Nervous System I Vocabulary
... Cation more concentrated in extracellular fluid (ECF): ____________________ Cation more concentrated in intracellular fluid (ICF): ____________________ Ion channel that opens in response to chemical binding: ____________________ Ion channel that opens in response to local change in membrane voltage: ...
... Cation more concentrated in extracellular fluid (ECF): ____________________ Cation more concentrated in intracellular fluid (ICF): ____________________ Ion channel that opens in response to chemical binding: ____________________ Ion channel that opens in response to local change in membrane voltage: ...
Chapter 16A
... • Pain receptors (nociceptors) are located in nearly every body tissue except the brain • Stimulated by excessive distension, muscle spasm & inadequate blood flow • Tissue injury releases chemicals such as K+, kinins & prostaglandins that stimulate nociceptors ...
... • Pain receptors (nociceptors) are located in nearly every body tissue except the brain • Stimulated by excessive distension, muscle spasm & inadequate blood flow • Tissue injury releases chemicals such as K+, kinins & prostaglandins that stimulate nociceptors ...
Unit B6 Key Words
... A chemical messenger secreted by gland that brings about a slow change in the body A change in the environment that causes a response Cells that detect changes in the environment The long tine part of a neuron Tissues and organs in the body that control the body’s responses to stimuli A set of nerve ...
... A chemical messenger secreted by gland that brings about a slow change in the body A change in the environment that causes a response Cells that detect changes in the environment The long tine part of a neuron Tissues and organs in the body that control the body’s responses to stimuli A set of nerve ...
Checkpoint Answers
... 1. The brain and spinal cord comprise the *A. central nervous system. B. peripheral nervous system. C. peripheral ganglia. D. spinal nerves. 2. Ganglia are clusters of nerve cell bodies located in the CNS. false 3. Sensory neurons A. are multipolar and carry impulses toward the CNS. *B. are pseudoun ...
... 1. The brain and spinal cord comprise the *A. central nervous system. B. peripheral nervous system. C. peripheral ganglia. D. spinal nerves. 2. Ganglia are clusters of nerve cell bodies located in the CNS. false 3. Sensory neurons A. are multipolar and carry impulses toward the CNS. *B. are pseudoun ...
Concept Mapping Back Print
... answer: Two factors that influence the speed with which an impulse is conducted are the diameter of the axon and whether or not it is myelinated. In the absence of myelination, increasing the diameter of the axon will increase the speed of impulse conduction. The large axons in the organisms are res ...
... answer: Two factors that influence the speed with which an impulse is conducted are the diameter of the axon and whether or not it is myelinated. In the absence of myelination, increasing the diameter of the axon will increase the speed of impulse conduction. The large axons in the organisms are res ...
Motor Cortex
... during planning (targeting) & execution (trigger stimulus) PM active before movement ~ ...
... during planning (targeting) & execution (trigger stimulus) PM active before movement ~ ...
Neurons and Networks. An Introduction to Behavioral Neuroscience, Second Edition Brochure
... solid foundation of understanding and knowledge required for further study. The new edition retains the features that made the first edition so attractive: consistent emphasis on results and concepts that have stood the test of time; abundant high-quality illustrations; exceptionally clear explanati ...
... solid foundation of understanding and knowledge required for further study. The new edition retains the features that made the first edition so attractive: consistent emphasis on results and concepts that have stood the test of time; abundant high-quality illustrations; exceptionally clear explanati ...
Nervous System - El Camino College
... The area just behind central sulcus is the general Sensory Area to receive sensory input. Primary vision area lies in visual cortex in occipital lobe. Primary Gustatory Area lies on lateral side of frontal lobes and receives information about taste. Primary Auditory Area lies in temporal lobes and r ...
... The area just behind central sulcus is the general Sensory Area to receive sensory input. Primary vision area lies in visual cortex in occipital lobe. Primary Gustatory Area lies on lateral side of frontal lobes and receives information about taste. Primary Auditory Area lies in temporal lobes and r ...
The Nervous System
... The Peripheral Nervous System • All of the nerves that are not a part of the central nervous system. • Somatic nervous System - regulates activities that are under conscious control (muscles) and pain reflexes. • Autonomic Nervous System – regulates activities that are automatic or involuntary. • E ...
... The Peripheral Nervous System • All of the nerves that are not a part of the central nervous system. • Somatic nervous System - regulates activities that are under conscious control (muscles) and pain reflexes. • Autonomic Nervous System – regulates activities that are automatic or involuntary. • E ...
The Nervous System
... unilateral facial paralysis due to disorder of facial nerve partial paralysis & lack of muscular coordination due to damage to cerebrum during birth ...
... unilateral facial paralysis due to disorder of facial nerve partial paralysis & lack of muscular coordination due to damage to cerebrum during birth ...
Neurons, Hormones, and the Brain
... • Neural circuits linked to neural pathways that run up and down the spinal cord= 2 and from the brain, As a result reflexes effected by thoughts and emotions • For example erection in men • However you can control your knee from jerking when it is tapped; and most men can learn to voluntarily delay ...
... • Neural circuits linked to neural pathways that run up and down the spinal cord= 2 and from the brain, As a result reflexes effected by thoughts and emotions • For example erection in men • However you can control your knee from jerking when it is tapped; and most men can learn to voluntarily delay ...
Class Topics
... • all nerves outside of CNS – cranial nerves - from brain » 12 pairs – spinal nerves - from spinal cord Page: 3 ...
... • all nerves outside of CNS – cranial nerves - from brain » 12 pairs – spinal nerves - from spinal cord Page: 3 ...
The Evaluation of Weakness in the
... 1st stimulus: 60 quanta 2nd stimulus: 56 quanta 3rd stimulus: 53 quanta 4th stimulus: 55 quanta as reserve quanta become available Accounts for decrease in EPP and results in increase risk of failure (blocking) over four repetitive stimulations at 2 Hz ...
... 1st stimulus: 60 quanta 2nd stimulus: 56 quanta 3rd stimulus: 53 quanta 4th stimulus: 55 quanta as reserve quanta become available Accounts for decrease in EPP and results in increase risk of failure (blocking) over four repetitive stimulations at 2 Hz ...
Chapter 33
... The nerve impulse travels along the axon or dendrites as an electrical current gathered by ions moving in and out of the neuron through voltage-gated channels. Voltage-gated channels – protein channels in the membrane that open & close in response to an electrical ...
... The nerve impulse travels along the axon or dendrites as an electrical current gathered by ions moving in and out of the neuron through voltage-gated channels. Voltage-gated channels – protein channels in the membrane that open & close in response to an electrical ...
Note
... Estimating the discriminability of two stimuli from the neural responses proceeds by calculating the distribution of responses to the two stimuli P(n|v) from data (where n = NT , the number of spikes); the stimuli v are noise (n) and tone plus noise (t). The discrimination task is to detect the ton ...
... Estimating the discriminability of two stimuli from the neural responses proceeds by calculating the distribution of responses to the two stimuli P(n|v) from data (where n = NT , the number of spikes); the stimuli v are noise (n) and tone plus noise (t). The discrimination task is to detect the ton ...
10 - Karmayog .org
... instruction is given by the spinal cord (without waiting for brain reaction) these are reflex actions. Babies have a similar gripping reflex. If you put any thing in their hand they grip it. They are born with this reflex. The knee jerk reflex is the one most often tested when you visit a doctor it ...
... instruction is given by the spinal cord (without waiting for brain reaction) these are reflex actions. Babies have a similar gripping reflex. If you put any thing in their hand they grip it. They are born with this reflex. The knee jerk reflex is the one most often tested when you visit a doctor it ...
EQ2.5 - major divisions of the nervous system
... The two major divisions of the nervous system are the central and the peripheral nervous system. The central nervous system is divided in two parts : the brain and the spinal chord. The Peripheral nervous system includes all the nerves in the body. The function of the central nervous system is to ma ...
... The two major divisions of the nervous system are the central and the peripheral nervous system. The central nervous system is divided in two parts : the brain and the spinal chord. The Peripheral nervous system includes all the nerves in the body. The function of the central nervous system is to ma ...
Optogenetic Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging (ofMRI
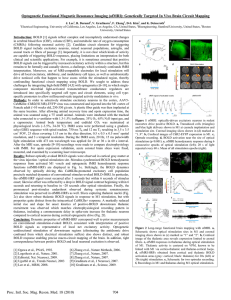
... the same location. After allowing animal recovery time and opsin expression time, the animal was scanned using a 7T small animal. Animals were intubated with the tracheal tube connected to a ventilator with 1.3-1.5% isoflurane, 35% O2, 65% N2O input gas, and a capnometer. Animal body temperature and ...
... the same location. After allowing animal recovery time and opsin expression time, the animal was scanned using a 7T small animal. Animals were intubated with the tracheal tube connected to a ventilator with 1.3-1.5% isoflurane, 35% O2, 65% N2O input gas, and a capnometer. Animal body temperature and ...
Objectives: The student shall know the facts, understand the
... SOMATIC SENSATION (continued) Somatosensory pathways Peripheral nerve regeneration Peripheral nerve fields Dermatome: define & characteristics Dorsal column & anterolateral ascending divisions Spinal cord pathways & effects of spinal cord lesions Modalities subserved Primary sensory cortex location ...
... SOMATIC SENSATION (continued) Somatosensory pathways Peripheral nerve regeneration Peripheral nerve fields Dermatome: define & characteristics Dorsal column & anterolateral ascending divisions Spinal cord pathways & effects of spinal cord lesions Modalities subserved Primary sensory cortex location ...