Chapter 43
... • Two ways to increase velocity of conduction – Axon has a large diameter • Less resistance to current flow • Found primarily in invertebrates – Axon is myelinated • Action potential is only produced at the nodes of Ranvier • Impulse jumps from node to node (see next slide) • Saltatory conduction ...
... • Two ways to increase velocity of conduction – Axon has a large diameter • Less resistance to current flow • Found primarily in invertebrates – Axon is myelinated • Action potential is only produced at the nodes of Ranvier • Impulse jumps from node to node (see next slide) • Saltatory conduction ...
Unit 2: Nervous System
... • Brain divided into lobes • Spinal cord = communication highway • All nerves communicate through Spine ...
... • Brain divided into lobes • Spinal cord = communication highway • All nerves communicate through Spine ...
Sensory neurons
... Sensory Neurons are a part of the bodies nervous system that are responsible for detecting external signals. These neurons are rather important and special as they do not receive signals from the body, but from external sources like sound, light and temperature. In complex organisms like Humans, mos ...
... Sensory Neurons are a part of the bodies nervous system that are responsible for detecting external signals. These neurons are rather important and special as they do not receive signals from the body, but from external sources like sound, light and temperature. In complex organisms like Humans, mos ...
Anatomy Questions 3/2/16 1. The dorsal gray horns of the spinal
... 1. The dorsal gray horns of the spinal cord contain _____________________________. i. Visceral sensory soma ii. Somatic motor soma iii. Somatic sensory soma iv. Visceral motor soma a. 1 and 3 b. 2 and 4 c. All of the above d. None of the above 2. The soma of visceral motor neurons are found in the _ ...
... 1. The dorsal gray horns of the spinal cord contain _____________________________. i. Visceral sensory soma ii. Somatic motor soma iii. Somatic sensory soma iv. Visceral motor soma a. 1 and 3 b. 2 and 4 c. All of the above d. None of the above 2. The soma of visceral motor neurons are found in the _ ...
The Generation of Brain Waves
... postsynaptic potential (IPSP) results from the hyperpolarization of the cell membrane. The current flow in this case is fiom the inside of the cell outwards making the outside of the cell more positive preventing transmission of the impulse, opposite to that of the EPSp (7). Available evidence sugge ...
... postsynaptic potential (IPSP) results from the hyperpolarization of the cell membrane. The current flow in this case is fiom the inside of the cell outwards making the outside of the cell more positive preventing transmission of the impulse, opposite to that of the EPSp (7). Available evidence sugge ...
Visual Field - Warren`s Science Page
... internal organs enter same segments of spinal cord Skin encounters more pain than organs, so brain may interpret most sensory input as arriving from skin ...
... internal organs enter same segments of spinal cord Skin encounters more pain than organs, so brain may interpret most sensory input as arriving from skin ...
Peripheral nervous system
... but the inside is still very + Sodium-potassium pumps then use ATP to move Na+ out of the neuron and K+ in to return the charges inside and outside of the neuron to “normal” repolarization All or Nothing Response ...
... but the inside is still very + Sodium-potassium pumps then use ATP to move Na+ out of the neuron and K+ in to return the charges inside and outside of the neuron to “normal” repolarization All or Nothing Response ...
General principle of nervous system
... • The spinal cord (all level) • The reticular substance of the lower brain • Thalamus • Celebellum • Cerebral cortex ...
... • The spinal cord (all level) • The reticular substance of the lower brain • Thalamus • Celebellum • Cerebral cortex ...
nerves
... nerve ring. Within each arm, the radial nerve is linked to a nerve net from which it receives input and to which it sends signals controlling motor activity. ...
... nerve ring. Within each arm, the radial nerve is linked to a nerve net from which it receives input and to which it sends signals controlling motor activity. ...
Spinal Cord-Evoked Potentials and Muscle Responses Evoked by
... three subjects, the D wave and the first I wave of the SCEP were recruited simultaneously. In one subject, the D, I1 , and I2 waves were recruited simultaneously, and in another subject, the I1 and I2 waves were recruited simultaneously. In the remaining five subjects, only the I1 wave was recruited ...
... three subjects, the D wave and the first I wave of the SCEP were recruited simultaneously. In one subject, the D, I1 , and I2 waves were recruited simultaneously, and in another subject, the I1 and I2 waves were recruited simultaneously. In the remaining five subjects, only the I1 wave was recruited ...
What is EEG? Elana Zion
... Illustration 4: EEG activity in response to different types of images. About 170 milliseconds after the appearance of the stimulus, differences are apparent in the brain’s response to human monkey faces, compared to watches. This phenomenon is called the “N170” response, and indicates a neural proce ...
... Illustration 4: EEG activity in response to different types of images. About 170 milliseconds after the appearance of the stimulus, differences are apparent in the brain’s response to human monkey faces, compared to watches. This phenomenon is called the “N170” response, and indicates a neural proce ...
Nerves, structures, and organs of the head 1. Left cerebral
... Spinal cord (19) A soft oval-shaped cylinder about 45 cm long, and about as big around as the little finger. This structure is protected by the spinal column and is composed of afferent and efferent neurons and internucial neurons. Thalamus (8) Two rounded lobes of gray matter that serves as a major ...
... Spinal cord (19) A soft oval-shaped cylinder about 45 cm long, and about as big around as the little finger. This structure is protected by the spinal column and is composed of afferent and efferent neurons and internucial neurons. Thalamus (8) Two rounded lobes of gray matter that serves as a major ...
Central Nervous System
... areas - occipital lobes contain primary visual cortex (receive information from retina) and ...
... areas - occipital lobes contain primary visual cortex (receive information from retina) and ...
unit 5: the nervous and endocrine systems
... 1) Reflex actions: These are quick and automatic and the brain is not involved. Sensory information only reaches the spinal cord, so a response is rapid and automatic. They take place when a rapid response is required, for example, pulling your hand away when you burn it. In reflex actions, the thre ...
... 1) Reflex actions: These are quick and automatic and the brain is not involved. Sensory information only reaches the spinal cord, so a response is rapid and automatic. They take place when a rapid response is required, for example, pulling your hand away when you burn it. In reflex actions, the thre ...
Peripheral Nervous System
... Nervous System 1. Central Nervous System • The brain + the spinal cord – The center of integration and control 2. Peripheral Nervous System ...
... Nervous System 1. Central Nervous System • The brain + the spinal cord – The center of integration and control 2. Peripheral Nervous System ...
Motor Areas - Motlow State Community College
... tracts having common origin or destination and carrying similar information over long distances sensory tracts ...
... tracts having common origin or destination and carrying similar information over long distances sensory tracts ...
Nervous System Notes
... d. synapse – space between the receptors and the axon e. receptors – detect changes inside and outside the body f. motor neurons- neurons that send impulses from the brain and spinal cord to other body systems g. nerves- send and receive info h. brain- think, control movement, store info and memorie ...
... d. synapse – space between the receptors and the axon e. receptors – detect changes inside and outside the body f. motor neurons- neurons that send impulses from the brain and spinal cord to other body systems g. nerves- send and receive info h. brain- think, control movement, store info and memorie ...
p. A46 (5a) - Viktor`s Notes for the Neurosurgery Resident
... Spinal Cord - somatic motor system (motor units) Last updated: May 12, 2017 Normal and abnormal motor units (two adjacent units are shown): Segmental demyelination: random myelin internodes are injured and are remyelinated by multiple Schwann cells, while axon and myocytes remain intact. Axonal dege ...
... Spinal Cord - somatic motor system (motor units) Last updated: May 12, 2017 Normal and abnormal motor units (two adjacent units are shown): Segmental demyelination: random myelin internodes are injured and are remyelinated by multiple Schwann cells, while axon and myocytes remain intact. Axonal dege ...
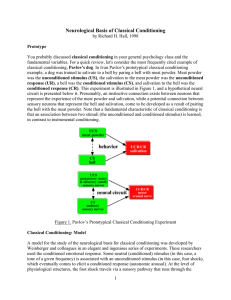
Neurological Basis of Classical Conditioning
... In order to test the viability of the neurological model presented above, Weinberger and colleagues began by establishing the tonotopic frequency of a set of neurons within the auditory system, in particular the auditory cortex. Many cells in the auditory system are "tuned" to a given frequency, tha ...
... In order to test the viability of the neurological model presented above, Weinberger and colleagues began by establishing the tonotopic frequency of a set of neurons within the auditory system, in particular the auditory cortex. Many cells in the auditory system are "tuned" to a given frequency, tha ...
FIGURE LEGNEDS FIGURE 24.1 A dorsal root ganglion cell is a
... usually by overvigorous contraction of the muscle. (B) Muscle spindle afferents (Ia and II) terminate on the noncontractile portions of intrafusal muscle fibers. They are arranged in parallel with working muscle fibers and respond to stretch of the entire muscle. Specialized motoneurons (γ) provide ...
... usually by overvigorous contraction of the muscle. (B) Muscle spindle afferents (Ia and II) terminate on the noncontractile portions of intrafusal muscle fibers. They are arranged in parallel with working muscle fibers and respond to stretch of the entire muscle. Specialized motoneurons (γ) provide ...
Chapter 11- 14 Integration of Nervous System Functions
... • SC and brain stem contains no. of sensory pathway • They transmit action potentials from periphery to various parts of brain • Each pathway involved with specific modality (type of information transmitted) • Names of ascending pathway or tracts in CNS indicate their origin & termination • First h ...
... • SC and brain stem contains no. of sensory pathway • They transmit action potentials from periphery to various parts of brain • Each pathway involved with specific modality (type of information transmitted) • Names of ascending pathway or tracts in CNS indicate their origin & termination • First h ...