Lecture 5 - Brain I - Linn
... emotion, nonnon-verbal language, “tone.” “ Holistic and recognition” ...
... emotion, nonnon-verbal language, “tone.” “ Holistic and recognition” ...
Mental activities
... ◦ Stretch receptors—two types; muscle spindles and Golgi tendon receptors operate to provide body with information concerning muscle length and strength of muscle contraction Muscle spindle—composed of 5 to 10 intrafusal fibers lying between and parallel to regular (extrafusal) muscle fibers If ...
... ◦ Stretch receptors—two types; muscle spindles and Golgi tendon receptors operate to provide body with information concerning muscle length and strength of muscle contraction Muscle spindle—composed of 5 to 10 intrafusal fibers lying between and parallel to regular (extrafusal) muscle fibers If ...
Subthalamic High-frequency Deep Brain Stimulation Evaluated in a
... prone in a Siemens/CTI ECAT EXACT HR47 tomograph and scanned with three times 15Ooxygen and three times 15O-water before the stimulation ("baseline"). The electrode was then ...
... prone in a Siemens/CTI ECAT EXACT HR47 tomograph and scanned with three times 15Ooxygen and three times 15O-water before the stimulation ("baseline"). The electrode was then ...
Principles of Sensory Coding
... their own separate channels. An animal might encounter very different environments depending on where it is born; for example, a city rat and a country rat will likely encounter very different odors. So sensory systems need to adapt themselves to the experiences of different animals. In contrast, co ...
... their own separate channels. An animal might encounter very different environments depending on where it is born; for example, a city rat and a country rat will likely encounter very different odors. So sensory systems need to adapt themselves to the experiences of different animals. In contrast, co ...
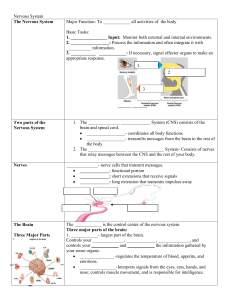
The Nervous System
... • Impulses are transmitted from cell to cell by the release of chemicals called ...
... • Impulses are transmitted from cell to cell by the release of chemicals called ...
TMS Slideshow - Specialty Center TMS
... new neural connections throughout life. It allows the neurons in the brain to compensate for the injury and disease, and to adjust their activities in response to new situations or to changes in their ...
... new neural connections throughout life. It allows the neurons in the brain to compensate for the injury and disease, and to adjust their activities in response to new situations or to changes in their ...
Nervous System
... ii. If you like, colour in the diagram as suggested below. Axon - purple; Myelin sheath - yellow; Cell body - blue; Dendrites - green; Muscle fibers – red; iii. Now indicate the direction that the nerve impulse travels. ...
... ii. If you like, colour in the diagram as suggested below. Axon - purple; Myelin sheath - yellow; Cell body - blue; Dendrites - green; Muscle fibers – red; iii. Now indicate the direction that the nerve impulse travels. ...
Biology 12 - Excretion
... A MOTOR neuron has a long axon and short dendrites. In the first part of the nerve impulse, the ion SODIUM moves to the inside of the neuron. The junction between one neuron and another is called a SYNAPSE. Each division of the autonomic nervous system controls the same organs, but they generally ha ...
... A MOTOR neuron has a long axon and short dendrites. In the first part of the nerve impulse, the ion SODIUM moves to the inside of the neuron. The junction between one neuron and another is called a SYNAPSE. Each division of the autonomic nervous system controls the same organs, but they generally ha ...
Spinal Cord – Gross Anatomy
... Divided into three columns namely, anterior, posterior and lateral funiculus ...
... Divided into three columns namely, anterior, posterior and lateral funiculus ...
Central Nervous System Part 2
... cerebellum and spinal cord to keep the cortex alert and conscious. Also acts as a filter for sensory input to the cortex … filters out 99% of sensory input as unimportant. RAS: arousal system Complex polysynaptic path in brainstem and thalamus RF Receives messages from neurons on spine and other par ...
... cerebellum and spinal cord to keep the cortex alert and conscious. Also acts as a filter for sensory input to the cortex … filters out 99% of sensory input as unimportant. RAS: arousal system Complex polysynaptic path in brainstem and thalamus RF Receives messages from neurons on spine and other par ...
Peripheral Nervous System
... (Brain and Spinal Cord) The Peripheral Nervous System made up of nerves that lie outside the central nervous system. Carries impulses to and from the central nervous system ...
... (Brain and Spinal Cord) The Peripheral Nervous System made up of nerves that lie outside the central nervous system. Carries impulses to and from the central nervous system ...
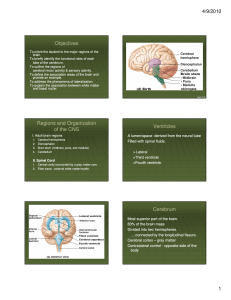
Brain Regions
... sensory, motor, and association areas of the cortex. • Processing and integration occurs w/i the nuclei and then info is sent from the globus pallidus to the motor cortex via the thalamus. • The basal nuclei alter motor commands issued by the cerebral cortex via this feedback loop. ...
... sensory, motor, and association areas of the cortex. • Processing and integration occurs w/i the nuclei and then info is sent from the globus pallidus to the motor cortex via the thalamus. • The basal nuclei alter motor commands issued by the cerebral cortex via this feedback loop. ...
Nervous System PPT 4 - PNS
... impulses that travel in sensory axons to the spinal cord. Interneurons integrate data from sensory neurons and then relay signals to motor axons. Motor axons convey nerve impulses from the spinal cord to a sketetal muscle, which contracts. Movement of the hand away from the pin is the response to th ...
... impulses that travel in sensory axons to the spinal cord. Interneurons integrate data from sensory neurons and then relay signals to motor axons. Motor axons convey nerve impulses from the spinal cord to a sketetal muscle, which contracts. Movement of the hand away from the pin is the response to th ...
brain - Austin Community College
... Neuroglia are specialized nervous tissue cells that are smaller and more numerous than neurons. They serve to carry out support functions such as vascularization, phagocytosis and myelinization. There are four types found in the CNS - Astrocytes - star shaped with many processes, participate in the ...
... Neuroglia are specialized nervous tissue cells that are smaller and more numerous than neurons. They serve to carry out support functions such as vascularization, phagocytosis and myelinization. There are four types found in the CNS - Astrocytes - star shaped with many processes, participate in the ...
Answers to Questions — neurons
... 3. Hyponatremia occurs when people have very low amounts of sodium in their body. How might the nervous system be affected if the person had this condition? Sodium is important in generating action potentials, thus low amounts of sodium would make it so neurons are less able to transmit signals. In ...
... 3. Hyponatremia occurs when people have very low amounts of sodium in their body. How might the nervous system be affected if the person had this condition? Sodium is important in generating action potentials, thus low amounts of sodium would make it so neurons are less able to transmit signals. In ...
Nerve Impulses - Tamalpais Union High School District
... muscle fiber is not dependent upon the strength of the stimulus. If a stimulus is above a certain threshold, a nerve or muscle fiber will fire. Full response or no response at all. ...
... muscle fiber is not dependent upon the strength of the stimulus. If a stimulus is above a certain threshold, a nerve or muscle fiber will fire. Full response or no response at all. ...
Sensation & Perception
... retina: where the image is focused. The retina is like a movie screen. ...
... retina: where the image is focused. The retina is like a movie screen. ...
File
... Sensation : is a state of awareness of a stimulus. Sensation requires:1) A stimulus : Any changes in the environment, either internal or external , e.g. body temp, pH, light, sound, pressure ….. etc. 2) Receptor : which receive stimulus 3) Conduction of nerve impulse to the CNS 4) Translation at di ...
... Sensation : is a state of awareness of a stimulus. Sensation requires:1) A stimulus : Any changes in the environment, either internal or external , e.g. body temp, pH, light, sound, pressure ….. etc. 2) Receptor : which receive stimulus 3) Conduction of nerve impulse to the CNS 4) Translation at di ...
Chapter 8 - Missouri State University
... Each vertebral segment gives rise to a ________________ of spinal ...
... Each vertebral segment gives rise to a ________________ of spinal ...
File
... There are 31 pairs of spinal nerves…… If you can memorize all 31 in 2 minutes, then you get an ec slip….BUT If you don’t get them all, then you have to lose 5 participation points from your grade. ...
... There are 31 pairs of spinal nerves…… If you can memorize all 31 in 2 minutes, then you get an ec slip….BUT If you don’t get them all, then you have to lose 5 participation points from your grade. ...
ANPS 019 Beneyto-Santonja 10-31
... o Descending motor axons from cortex and red nucleus (in midbrain) o Ascending sensory axons from body AND face Cranial nerves – V, VI, VII, VIII Cerebellar Peduncles axons linking the cerebellum & brainstem Inferior Input (ICP) – unconscious proprioception info (what you are doing) o Info fro ...
... o Descending motor axons from cortex and red nucleus (in midbrain) o Ascending sensory axons from body AND face Cranial nerves – V, VI, VII, VIII Cerebellar Peduncles axons linking the cerebellum & brainstem Inferior Input (ICP) – unconscious proprioception info (what you are doing) o Info fro ...
Physiology SENSORY PHYSIOLOGY Sensory Receptors Martin Paré
... Sensory transduction converts stimuli into graded potentials. Such changes in receptor membrane potential are known as the receptor potential and the generator potential. ...
... Sensory transduction converts stimuli into graded potentials. Such changes in receptor membrane potential are known as the receptor potential and the generator potential. ...
Ch 14: Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves
... Sensory Receptors Motor Endings Cranial Nerves The Four Plexuses Extremities ...
... Sensory Receptors Motor Endings Cranial Nerves The Four Plexuses Extremities ...