Chapter 44
... – Dopamine is used in some areas of the brain that control body movements – Serotonin is involved in the regulation of sleep ...
... – Dopamine is used in some areas of the brain that control body movements – Serotonin is involved in the regulation of sleep ...
Peripheral Nervous System
... Peripheral Nerves (repetitio est…) Definition: bundles of axons. AKA tracts in CNS ...
... Peripheral Nerves (repetitio est…) Definition: bundles of axons. AKA tracts in CNS ...
Nervous System
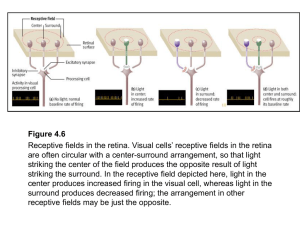
... Rods and Cones • ~ 125 million rod cells –Rod cells are light sensitive but do not distinguish colors • ~ 6 million cone cells –Not as light sensitive as rods but provide color vision –Most highly concentrated on the fovea – area of retina lacking rods ...
... Rods and Cones • ~ 125 million rod cells –Rod cells are light sensitive but do not distinguish colors • ~ 6 million cone cells –Not as light sensitive as rods but provide color vision –Most highly concentrated on the fovea – area of retina lacking rods ...
The Brain: Your Crowning Glory
... We begin our tour of the brain at the lowest level, the hindbrain — the part of the brain where the spinal cord enters the skull and widens. We then work our way upward, first to the midbrain, which lies above the hindbrain, and then to the forebrain, which lies in the highest part of the brain. Con ...
... We begin our tour of the brain at the lowest level, the hindbrain — the part of the brain where the spinal cord enters the skull and widens. We then work our way upward, first to the midbrain, which lies above the hindbrain, and then to the forebrain, which lies in the highest part of the brain. Con ...
chapter 44 lecture slides
... Nervous System Organization • Vertebrates have three types of neurons 1. Sensory neurons (afferent neurons) carry impulses to central nervous system (CNS) 2. Motor neurons (efferent neurons) carry impulses from CNS to effectors (muscles and glands) 3. Interneurons (association neurons) provide more ...
... Nervous System Organization • Vertebrates have three types of neurons 1. Sensory neurons (afferent neurons) carry impulses to central nervous system (CNS) 2. Motor neurons (efferent neurons) carry impulses from CNS to effectors (muscles and glands) 3. Interneurons (association neurons) provide more ...
chapter 44 lecture slides
... Nervous System Organization • Vertebrates have three types of neurons 1. Sensory neurons (afferent neurons) carry impulses to central nervous system (CNS) 2. Motor neurons (efferent neurons) carry impulses from CNS to effectors (muscles and glands) 3. Interneurons (association neurons) provide more ...
... Nervous System Organization • Vertebrates have three types of neurons 1. Sensory neurons (afferent neurons) carry impulses to central nervous system (CNS) 2. Motor neurons (efferent neurons) carry impulses from CNS to effectors (muscles and glands) 3. Interneurons (association neurons) provide more ...
Functional Organization of Nervous Tissue
... medial epicondyle of the humerus will produce strong tingling sensations along the forearm and hand. (a) Radial (b) Median (c) Phrenic (d) Femoral (e) Ulnar ...
... medial epicondyle of the humerus will produce strong tingling sensations along the forearm and hand. (a) Radial (b) Median (c) Phrenic (d) Femoral (e) Ulnar ...
Study Guide Chapter 10 in Fox
... Understand the difference between “sensory receptors” and “ligand receptors” Most sensory receptors are either ______________ or _______________ These receptors receive some form of ___________ and convert it into action potentials. Because they convert energy from one form to another, receptors are ...
... Understand the difference between “sensory receptors” and “ligand receptors” Most sensory receptors are either ______________ or _______________ These receptors receive some form of ___________ and convert it into action potentials. Because they convert energy from one form to another, receptors are ...
Endocrine System: Overview
... b. Click the “Contents” button. c. Open the Nervous System File. d. Click Animations. e. Click Somatic Sensory and Motor Pathways. Introduction ...
... b. Click the “Contents” button. c. Open the Nervous System File. d. Click Animations. e. Click Somatic Sensory and Motor Pathways. Introduction ...
The Peripheral Nervous System
... Pass through small foramina (holes) in the cranial cavity and skull Identified by names and numbers ...
... Pass through small foramina (holes) in the cranial cavity and skull Identified by names and numbers ...
Document
... • Magnitude estimation—intensity is coded in the frequency of impulses • Spatial discrimination—identifying the site or pattern of the stimulus (studied by the two-point discrimination test) ...
... • Magnitude estimation—intensity is coded in the frequency of impulses • Spatial discrimination—identifying the site or pattern of the stimulus (studied by the two-point discrimination test) ...
Central Nervous System
... Association's in brain and spinal cord Interpreting the info and passing on To move the motor neurons carry to the body Bring it to the glands Bring it to the muscles...oh oh oh oh oh Nervous System Spinal cord, brain, and nerves... oh oh oh oh oh The Nervous System ...
... Association's in brain and spinal cord Interpreting the info and passing on To move the motor neurons carry to the body Bring it to the glands Bring it to the muscles...oh oh oh oh oh Nervous System Spinal cord, brain, and nerves... oh oh oh oh oh The Nervous System ...
BIOL 2402 Lecture Outline Chapter 5
... each full cycle lasts about 90 minutes, and in each successive cycle the amount of paradoxical/REM sleep increases paradoxical sleep involves low muscle tone, increased cortical activity, and dreaming switching between slow wave/NREM and paradoxical/REM is controlled by paradoxical/REM “sleep-on” ne ...
... each full cycle lasts about 90 minutes, and in each successive cycle the amount of paradoxical/REM sleep increases paradoxical sleep involves low muscle tone, increased cortical activity, and dreaming switching between slow wave/NREM and paradoxical/REM is controlled by paradoxical/REM “sleep-on” ne ...
BRAIN ANATOMY Central Nervous System (CNS) is the brain and
... 3. Posterior to pons is the Cerebellum which is responsible for controlling movement (balance, coordination, timing and rhythm ) There is a nucleus that spans from the medulla up to the midbrain and a little bit of thalamus called the reticular formation also known as reticular activating system and ...
... 3. Posterior to pons is the Cerebellum which is responsible for controlling movement (balance, coordination, timing and rhythm ) There is a nucleus that spans from the medulla up to the midbrain and a little bit of thalamus called the reticular formation also known as reticular activating system and ...
Nervous System PowerPoint
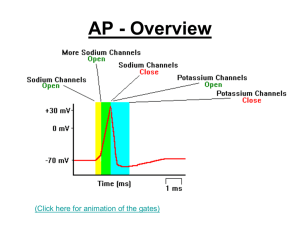
... After the impulse, the gates return to the resting condition with extra potassium gates open. The flow of potassium ions out of the cell restores the resting potential. The Na+/K+ pump continues to pump the sodium and potassium across the membrane against the concentration gradient to restore th ...
... After the impulse, the gates return to the resting condition with extra potassium gates open. The flow of potassium ions out of the cell restores the resting potential. The Na+/K+ pump continues to pump the sodium and potassium across the membrane against the concentration gradient to restore th ...
The Nervous System
... Cells of the Nervous System Neurons/nerve cells: receive stimuli and transmit action potentials (send and receive information) Cell Body: contains the nucleus and two extensions Dendrites: shorter, more numerous, and receives information (Action Potentials) Axons: single, long “fiber” whic ...
... Cells of the Nervous System Neurons/nerve cells: receive stimuli and transmit action potentials (send and receive information) Cell Body: contains the nucleus and two extensions Dendrites: shorter, more numerous, and receives information (Action Potentials) Axons: single, long “fiber” whic ...
Introduction
... (a) Input from the right half of the visual field strikes the left side of each retina and is transmitted to the left hemisphere (shown in red). Input from the left half of the visual field strikes the right side of each retina and is transmitted to the right hemisphere (shown in green). The nerve f ...
... (a) Input from the right half of the visual field strikes the left side of each retina and is transmitted to the left hemisphere (shown in red). Input from the left half of the visual field strikes the right side of each retina and is transmitted to the right hemisphere (shown in green). The nerve f ...
7-1_SegmOrgSpinCord_BogdanyP
... The segmental organization of the spinal cord Oral presentation by Peter Bogdány The spinal cord is a part of the central nervous system. It collects data from the peripherical nervous system – sensory information - , and innervate skeletal and smooth muscles – motoric function - that mediate volunt ...
... The segmental organization of the spinal cord Oral presentation by Peter Bogdány The spinal cord is a part of the central nervous system. It collects data from the peripherical nervous system – sensory information - , and innervate skeletal and smooth muscles – motoric function - that mediate volunt ...
Human Biology - St Mary's College, Wallasey
... to develop, while pathways that are not used are eventually destroyed. This is why we become better at certain tasks when we practice them more often. ...
... to develop, while pathways that are not used are eventually destroyed. This is why we become better at certain tasks when we practice them more often. ...
D. Vertebrate Nervous Systems
... Short-term memory stored in the frontal lobes. The establishment of long-term memory involves the hippocampus. The transfer of information from short-term to long-term memory. Is enhanced by repetition (remember that when you are preparing for an exam). Influenced by emotional states medi ...
... Short-term memory stored in the frontal lobes. The establishment of long-term memory involves the hippocampus. The transfer of information from short-term to long-term memory. Is enhanced by repetition (remember that when you are preparing for an exam). Influenced by emotional states medi ...
Behavioral Neuroscience: The NeuroPsychological approach
... corpus-callosum) and found that each hemisphere is a conscious system in its own right, even in conflicting mental processes. Object in the left visual field, will not be vocally named, but can be handled with the ______ hand. Reasoning and calculation with the left hemisphere ...
... corpus-callosum) and found that each hemisphere is a conscious system in its own right, even in conflicting mental processes. Object in the left visual field, will not be vocally named, but can be handled with the ______ hand. Reasoning and calculation with the left hemisphere ...
AP Biology Study Guide
... 6. Explain (a) how an action potential propagates itself along a neuron, (b) why action potentials move in only one direction, and (c) how action potentials relay different intensities of information. 7. Compare the structures, functions, and locations of electrical and chemical synapses. 8. Compare ...
... 6. Explain (a) how an action potential propagates itself along a neuron, (b) why action potentials move in only one direction, and (c) how action potentials relay different intensities of information. 7. Compare the structures, functions, and locations of electrical and chemical synapses. 8. Compare ...
Second exam study questions
... 5.What is the functional anatomy of a taste receptor cell? What are the types of taste receptors and what they respond to? How do taste cells stimulate sensory neurons and how is taste information carried to and within the brain? 6. What properties of sound waves are detected as volume and pitch? Wh ...
... 5.What is the functional anatomy of a taste receptor cell? What are the types of taste receptors and what they respond to? How do taste cells stimulate sensory neurons and how is taste information carried to and within the brain? 6. What properties of sound waves are detected as volume and pitch? Wh ...
AP – All or nothing
... and the action potential is propagated along the neurone. • The wave travels the whole length of the neurone. ...
... and the action potential is propagated along the neurone. • The wave travels the whole length of the neurone. ...