Introduction_to_nerv..
... Types of Neurons There are three types of neurons: 1.The motor neuron transmits nerve impulses from the CNS to the effectors 2.The sensory neuron transmits nerve impulses from the receptors to the CNS 3.The relay neuron connects the sensory neuron to the motor neuron and also neurons in the CNS ...
... Types of Neurons There are three types of neurons: 1.The motor neuron transmits nerve impulses from the CNS to the effectors 2.The sensory neuron transmits nerve impulses from the receptors to the CNS 3.The relay neuron connects the sensory neuron to the motor neuron and also neurons in the CNS ...
semicircular canals
... Iris: dilates and constricts thereby regulating the amount of light that enters to posterior chamber of the eye. Ciliary body: muscular – pulls on suspensory ligaments and causes the lens to bend and change focus. Fovea centralis: area having the densest amount of photoreceptors Optic Disk (blind sp ...
... Iris: dilates and constricts thereby regulating the amount of light that enters to posterior chamber of the eye. Ciliary body: muscular – pulls on suspensory ligaments and causes the lens to bend and change focus. Fovea centralis: area having the densest amount of photoreceptors Optic Disk (blind sp ...
The Nervous System
... The cells that transmit the electrical signals of the nervous system are called neurons Sensory neurons carry information (impulses) from the sense organs to the central nervous system (CNS). Motor neurons carry information (impulses) from the central nervous system (CNS) to the muscles and glands. ...
... The cells that transmit the electrical signals of the nervous system are called neurons Sensory neurons carry information (impulses) from the sense organs to the central nervous system (CNS). Motor neurons carry information (impulses) from the central nervous system (CNS) to the muscles and glands. ...
Biology 30 NERVOUS SYSTEM
... The reflex arc also involves a one-way flow of information. Sensory neurons may stimulate a number of inter-neurons, which take impulses to different parts of the central nervous system. This is why we are usually conscious of stimuli that we reflexively react to. ...
... The reflex arc also involves a one-way flow of information. Sensory neurons may stimulate a number of inter-neurons, which take impulses to different parts of the central nervous system. This is why we are usually conscious of stimuli that we reflexively react to. ...
nervoussystemwebquest
... Sensory neuron transmits information from a sensory receptor to a motor neuron, which signals an effector cell to carry out the response. The knee jerking reaction goes through the sensory neurons which relays the information to the stretch receptor in the thigh muscle, to interneurons in the spinal ...
... Sensory neuron transmits information from a sensory receptor to a motor neuron, which signals an effector cell to carry out the response. The knee jerking reaction goes through the sensory neurons which relays the information to the stretch receptor in the thigh muscle, to interneurons in the spinal ...
Revision material
... How do cells in the ventral spinal cord respond to differing levels of Shh? The genomic sequence of the “AMPA” receptor encodes a Ca2+ channel but most AMPA receptors are only permeable to Na+. Explain. Describe briefly the optical factors that affect visual acuity. Write short notes on two of the f ...
... How do cells in the ventral spinal cord respond to differing levels of Shh? The genomic sequence of the “AMPA” receptor encodes a Ca2+ channel but most AMPA receptors are only permeable to Na+. Explain. Describe briefly the optical factors that affect visual acuity. Write short notes on two of the f ...
File
... common among psychologists. One psychologist might say to another, "But how exactly is this mental activity carried out? Does the homunculus do it?" This is a way of saying, "You have not given us an adequate explanation!" ...
... common among psychologists. One psychologist might say to another, "But how exactly is this mental activity carried out? Does the homunculus do it?" This is a way of saying, "You have not given us an adequate explanation!" ...
53 XIX BLY 122 Lecture Notes (O`Brien)
... 1. Connection between two neurons 2. Electrical signal from one neuron is converted to a chemical signal = neurotransmitter 3. Neurotransmitters cross space between neurons & cause changes in 2nd cell’s membrane potential C. Organization of vertebrate nervous system 1. Central nervous system (CNS) c ...
... 1. Connection between two neurons 2. Electrical signal from one neuron is converted to a chemical signal = neurotransmitter 3. Neurotransmitters cross space between neurons & cause changes in 2nd cell’s membrane potential C. Organization of vertebrate nervous system 1. Central nervous system (CNS) c ...
Nervous System Crossword Puzzle
... 39. NS part of the autonomic nervous system and tends to depress secretion, decrease the tone and contractility of smooth muscle, and increase heart rate 42. cortex responsible for memory, brooch's area, recognition 43. nerves mixed nerve, which carries motor, sensory, and autonomic signals between ...
... 39. NS part of the autonomic nervous system and tends to depress secretion, decrease the tone and contractility of smooth muscle, and increase heart rate 42. cortex responsible for memory, brooch's area, recognition 43. nerves mixed nerve, which carries motor, sensory, and autonomic signals between ...
Nervous System Crossword Puzzle
... contains nerve pathways between the cerebral hemispheres and the medulla oblongata as well as nuclei; the center for visual reflexes such as moving the head and eyes 40. links the medulla oblongata and the ...
... contains nerve pathways between the cerebral hemispheres and the medulla oblongata as well as nuclei; the center for visual reflexes such as moving the head and eyes 40. links the medulla oblongata and the ...
Ch 9 Sensory System
... from parts of body not actually stimulated −common with viscera pain receptors = often dull − Ex. Heart, Gallbladder, or Bladder ...
... from parts of body not actually stimulated −common with viscera pain receptors = often dull − Ex. Heart, Gallbladder, or Bladder ...
Neural Basis of Motor Control
... Concept 7: Transportation of sensory information to the brain • Sensory neural pathway (ascending track) – Passes through the spinal cord to brain stem to thalamus to the sensory areas of cerebral cortex and to the cerebellum – There are different specific ascending tracks: • Vision has it’s ow ...
... Concept 7: Transportation of sensory information to the brain • Sensory neural pathway (ascending track) – Passes through the spinal cord to brain stem to thalamus to the sensory areas of cerebral cortex and to the cerebellum – There are different specific ascending tracks: • Vision has it’s ow ...
PD233-Lecture6
... electrical potential difference between inside and outside of cells known as resting potential. ...
... electrical potential difference between inside and outside of cells known as resting potential. ...
HUMAN PHYSIOLOGY
... 1. describe the structure of a neuron and explain the functional significance of its principal regions. 2. explain what is meant by the blood-brain barrier and discuss its significance. 3. describe the sheath of Schwann and explain how it functions in the regeneration of cut peripheral nerve fibers. ...
... 1. describe the structure of a neuron and explain the functional significance of its principal regions. 2. explain what is meant by the blood-brain barrier and discuss its significance. 3. describe the sheath of Schwann and explain how it functions in the regeneration of cut peripheral nerve fibers. ...
Control Coordination
... living things, plant or animal Specialized structures inside a cell that have specific functions ...
... living things, plant or animal Specialized structures inside a cell that have specific functions ...
Chapter_03_4E
... • Motor responses can originate from any one of three levels – Spinal cord – Lower regions of the brain – Motor areas of the cerebral cortex • Motor responses for more complex movement patterns typically originate in the motor cortex • A motor reflex is a preprogrammed response that is integrated by ...
... • Motor responses can originate from any one of three levels – Spinal cord – Lower regions of the brain – Motor areas of the cerebral cortex • Motor responses for more complex movement patterns typically originate in the motor cortex • A motor reflex is a preprogrammed response that is integrated by ...
A Journey Through the Central Nervous System
... • Pain and temperature info to the somatosensory cortex ...
... • Pain and temperature info to the somatosensory cortex ...
Chapter 3
... • Motor cortex is just posterior • Followed by Central Sulcus • Function: • Motor nerves from left motor cortex control right side of the body • Broca’s area very important in speech production • Until 1960s, pre-frontal lobotomy was surgery that intended to minimize dysfunction and calm moods of me ...
... • Motor cortex is just posterior • Followed by Central Sulcus • Function: • Motor nerves from left motor cortex control right side of the body • Broca’s area very important in speech production • Until 1960s, pre-frontal lobotomy was surgery that intended to minimize dysfunction and calm moods of me ...
Spinal Cord
... Decussate in medulla into medial lemniscal tract Allows discriminative touch and proprioception Uses 1st, 2nd, & 3rd order neurons 1st order neurons synapse with interneruons at level of spine entry creating reflex arcs ...
... Decussate in medulla into medial lemniscal tract Allows discriminative touch and proprioception Uses 1st, 2nd, & 3rd order neurons 1st order neurons synapse with interneruons at level of spine entry creating reflex arcs ...
Ch 14: Peripheral Nervous System
... Sensory Receptors! Motor Endings! Cranial Nerves! The Four Plexuses ...
... Sensory Receptors! Motor Endings! Cranial Nerves! The Four Plexuses ...
Unit10 Nervous Wk 1
... 1. The ANS is further divided into » Parasympathetic nervous system works in actions that do not require a fast response (rest and digest response) » Sympathetic nervous system works in actions that do require a fast response (fight or fight response) ...
... 1. The ANS is further divided into » Parasympathetic nervous system works in actions that do not require a fast response (rest and digest response) » Sympathetic nervous system works in actions that do require a fast response (fight or fight response) ...
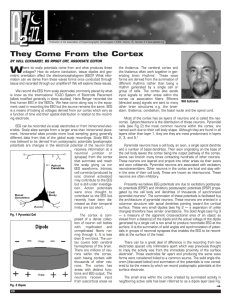
They Come From the Cortex - American Association of Sleep
... polarity of the potential pointed at them. Each orientation will produce a unique result because of the effect on the solid angle (see Fig. 3) the dipole presents to the recording electrodes. The surface area of the dipole layer and the orientation of the layer with respect to the electrodes have pr ...
... polarity of the potential pointed at them. Each orientation will produce a unique result because of the effect on the solid angle (see Fig. 3) the dipole presents to the recording electrodes. The surface area of the dipole layer and the orientation of the layer with respect to the electrodes have pr ...