Ominous odors: olfactory control of instinctive fear and aggression in
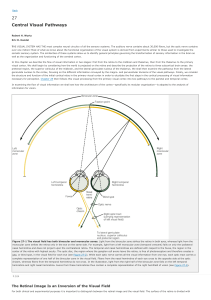
... Overlapping and distinct areas of the brain and modulating factors involved in pheromonal control of fear and aggression in mice. (a) Main areas of the brain and periphery that have been implicated in olfactory-mediated unconditioned fear (red), aggression (blue), or both (purple), as determined by ...
... Overlapping and distinct areas of the brain and modulating factors involved in pheromonal control of fear and aggression in mice. (a) Main areas of the brain and periphery that have been implicated in olfactory-mediated unconditioned fear (red), aggression (blue), or both (purple), as determined by ...
Phase Precession and Variable Spatial Scaling in a Periodic
... grid and conjunctive network connection matrix. The strength of excitatory connections from all neurons (y-axis), to all neurons (xaxis) are displayed. The first 100 neurons are grid cells, and the upper left block shows their recurrent connections. Neurons 101– 200 are ‘‘north’’ conjunctive cells, a ...
... grid and conjunctive network connection matrix. The strength of excitatory connections from all neurons (y-axis), to all neurons (xaxis) are displayed. The first 100 neurons are grid cells, and the upper left block shows their recurrent connections. Neurons 101– 200 are ‘‘north’’ conjunctive cells, a ...
Computing Action Potentials by Phase Interference in
... advanced invertebrates such as cephalopod molluscs [16] and decapod crustacea [15]. Thought processes in the vertebrates are known to occur very quickly. Simple shape recognition and learning has been timed to be less than 200ms removing motor input and output ...
... advanced invertebrates such as cephalopod molluscs [16] and decapod crustacea [15]. Thought processes in the vertebrates are known to occur very quickly. Simple shape recognition and learning has been timed to be less than 200ms removing motor input and output ...
Poster
... The SMN complex usually splices mRNA by the following process (see “An Inside Look at SMA”): A. Sm proteins and the SMN complex are located in the cytoplasm. Some SMN complexes can be found in the nucleus as well. The SMN complex preforms splicing functions in the cell. B. Sm proteins bind to SMN co ...
... The SMN complex usually splices mRNA by the following process (see “An Inside Look at SMA”): A. Sm proteins and the SMN complex are located in the cytoplasm. Some SMN complexes can be found in the nucleus as well. The SMN complex preforms splicing functions in the cell. B. Sm proteins bind to SMN co ...
Aging reduces total neuron number in the dorsal component of the
... slides were then dehydrated through increasing concentrations of ethanol, cleared with Citrisolv, and coverslipped under Permount. For immunohistochemistry, we used a mouse monoclonal antibody against GAD67 (MAB5406, clone 1G10.2; lot #LV1721349; Millipore, Bedford, MA). This antibody was raised aga ...
... slides were then dehydrated through increasing concentrations of ethanol, cleared with Citrisolv, and coverslipped under Permount. For immunohistochemistry, we used a mouse monoclonal antibody against GAD67 (MAB5406, clone 1G10.2; lot #LV1721349; Millipore, Bedford, MA). This antibody was raised aga ...
Sten Grillner
... thus demonstrated that the two basic modes of coordination could be generated by the spinal cord devoid of any influences from the brain. When the detailed motor pattern was recorded, in terms of electromyography (EMG) of the different limb muscles, the pattern was virtually identical to that of the ...
... thus demonstrated that the two basic modes of coordination could be generated by the spinal cord devoid of any influences from the brain. When the detailed motor pattern was recorded, in terms of electromyography (EMG) of the different limb muscles, the pattern was virtually identical to that of the ...
Chapter 3
... When there is damage to an axon, usually there are changes, called chromatolysis, which occur in the cell body of the affected cell; this causes swelling of the cell body and peaks between 10 and 20 days after injury. By the third to fifth day, degeneration of the distal portion of the neuronal proc ...
... When there is damage to an axon, usually there are changes, called chromatolysis, which occur in the cell body of the affected cell; this causes swelling of the cell body and peaks between 10 and 20 days after injury. By the third to fifth day, degeneration of the distal portion of the neuronal proc ...
Principles of Neural Science - Weizmann Institute of Science
... nucleus. The two most ventral layers of the nucleus contain relatively large cells and are known as the magnocellular layers; their main retinal input is from M ganglion cells. The four dorsal layers are known as parvocellular layers and receive input from P ganglion cells. Both the magnocellular an ...
... nucleus. The two most ventral layers of the nucleus contain relatively large cells and are known as the magnocellular layers; their main retinal input is from M ganglion cells. The four dorsal layers are known as parvocellular layers and receive input from P ganglion cells. Both the magnocellular an ...
Neuronal RNA Localization and the Cytoskeleton
... stoichiometry, and structural organization differ from that of the perikarya. Of fundamental interest is identification of how the cytoskeletal composition of the growth cone differs from the perikarya, and the identification of mechanisms involved in this sorting and assembly. One mechanism to prov ...
... stoichiometry, and structural organization differ from that of the perikarya. Of fundamental interest is identification of how the cytoskeletal composition of the growth cone differs from the perikarya, and the identification of mechanisms involved in this sorting and assembly. One mechanism to prov ...
Lecture 23. Pathophysiology of respiratory system
... • Injure of pleura; • Obstructive lung disease; • Restrictive lung disease. ...
... • Injure of pleura; • Obstructive lung disease; • Restrictive lung disease. ...
The human brain in numbers: a linearly scaled-up
... if one considers that although gorillas and orangutans overlap or exceed humans in body size, their brains amount to only about one-third of the size of the human brain. There are, however, several problems with the notion that the explanation for the superior cognitive abilities of the human specie ...
... if one considers that although gorillas and orangutans overlap or exceed humans in body size, their brains amount to only about one-third of the size of the human brain. There are, however, several problems with the notion that the explanation for the superior cognitive abilities of the human specie ...
Looking for the roots of cortical sensory computation in three
... and that the true response properties of DCx neurons have yet to be discovered. Until recently, functional experiments in PCx relied on sampling neuronal responses to limited sets of odors. Although these studies spanned stimulus sets large enough to identify the dispersion of RF selectivity across ...
... and that the true response properties of DCx neurons have yet to be discovered. Until recently, functional experiments in PCx relied on sampling neuronal responses to limited sets of odors. Although these studies spanned stimulus sets large enough to identify the dispersion of RF selectivity across ...
Kazumi TAKAHASHI†*, Jian-Sheng LIN† and Kazuya - HAL
... the transition from W to SWS. SWS was defined by sustained high-voltage slow waves in the EEG and lowered EMG activity. In the present study, D and SWS corresponded, respectively, to light and deep SWS. PS was defined by sustained theta waves and decreased delta waves in the EEG and the absence of E ...
... the transition from W to SWS. SWS was defined by sustained high-voltage slow waves in the EEG and lowered EMG activity. In the present study, D and SWS corresponded, respectively, to light and deep SWS. PS was defined by sustained theta waves and decreased delta waves in the EEG and the absence of E ...
Mental Processes -- How the Mind Arises from the Brain Roger Ellman
... and interpreting the logical construct of verbal statements. Although it was developed well before even the notion of digital computers had occurred or could have occurred, Boolean logic is the underlying principle on which digital computers operate. The letters A, B, etc., are called variables mean ...
... and interpreting the logical construct of verbal statements. Although it was developed well before even the notion of digital computers had occurred or could have occurred, Boolean logic is the underlying principle on which digital computers operate. The letters A, B, etc., are called variables mean ...
Topography of Visual Cortex Connections with Frontal Eye Field in
... current evoked an eye movement, the current level at which an eye movement could be evoked on 50% of the stimulus trains was taken as the threshold current. Eye movements evoked by intracortical microstimulation were monitored visually and agreed upon by two observers. Following recovery from anesth ...
... current evoked an eye movement, the current level at which an eye movement could be evoked on 50% of the stimulus trains was taken as the threshold current. Eye movements evoked by intracortical microstimulation were monitored visually and agreed upon by two observers. Following recovery from anesth ...
Surround suppression explained by long-range
... How does this reduction in response correlation come about, given the prevalence of strong spatial and temporal correlations present in natural visual scenes7, 8 , and given that neurons in a column share common preferences for visual features? Several neural models have been proposed to reduce corr ...
... How does this reduction in response correlation come about, given the prevalence of strong spatial and temporal correlations present in natural visual scenes7, 8 , and given that neurons in a column share common preferences for visual features? Several neural models have been proposed to reduce corr ...
Dynamics of Learning and Recall ... Recurrent Synapses and Cholinergic Modulation
... ramidal cells in the model were modified continuously according to learning rules dependent upon postsynaptic activity a, and presynaptic activity a,, in keeping with experimental evidence on the Hebbian nature of long-term potentiation (Kelso et al., 1986; Wigstrom et al., 1986). However, two versi ...
... ramidal cells in the model were modified continuously according to learning rules dependent upon postsynaptic activity a, and presynaptic activity a,, in keeping with experimental evidence on the Hebbian nature of long-term potentiation (Kelso et al., 1986; Wigstrom et al., 1986). However, two versi ...
A Review of Cell Assemblies by Huyck and
... fire at an elevated rate when the concept is perceived or in STM. An alternative to population coding is that a single cell represents a concept, commonly known as the grandmother cell (Barlow, 1972). However, a single neuron can not represent a concept because neurons die, and one would lose the co ...
... fire at an elevated rate when the concept is perceived or in STM. An alternative to population coding is that a single cell represents a concept, commonly known as the grandmother cell (Barlow, 1972). However, a single neuron can not represent a concept because neurons die, and one would lose the co ...
Disruption of the Blood-Brain Barrier and Neuronal Cell Death in
... activity and m2-muscarinic acetylcholine receptors (m2-AChR). Animals subjected to stress and chemicals exhibited both disruption of the BBB and neuronal cell death in the cingulate cortex, the dentate gyrus, the thalamus, and the hypothalamus. Other regions of the brain, although they demonstrated ...
... activity and m2-muscarinic acetylcholine receptors (m2-AChR). Animals subjected to stress and chemicals exhibited both disruption of the BBB and neuronal cell death in the cingulate cortex, the dentate gyrus, the thalamus, and the hypothalamus. Other regions of the brain, although they demonstrated ...
2016 prephd course work study material on development of BPN
... recognition successes of the Twentieth Century. It certainly sounds more exciting than a technical description such as “A network of weighted, additive values with nonlinear transfer functions”. However, despite the name, neural networks are far from “thinking machines” or “artificial brains”. A typ ...
... recognition successes of the Twentieth Century. It certainly sounds more exciting than a technical description such as “A network of weighted, additive values with nonlinear transfer functions”. However, despite the name, neural networks are far from “thinking machines” or “artificial brains”. A typ ...
Channelrhodopsin

Channelrhodopsins are a subfamily of retinylidene proteins (rhodopsins) that function as light-gated ion channels. They serve as sensory photoreceptors in unicellular green algae, controlling phototaxis: movement in response to light. Expressed in cells of other organisms, they enable light to control electrical excitability, intracellular acidity, calcium influx, and other cellular processes. Channelrhodopsin-1 (ChR1) and Channelrhodopsin-2 (ChR2) from the model organism Chlamydomonas reinhardtii are the first discovered channelrhodopsins. Variants have been cloned from other algal species, and more are expected.