Supraspinal control of ejaculation
... Percentage of galanin cells that were Fos-ir after Home Cage, Anestrous Female, Mounts, M+I, 1 Ejac., 2 Ejacs ...
... Percentage of galanin cells that were Fos-ir after Home Cage, Anestrous Female, Mounts, M+I, 1 Ejac., 2 Ejacs ...
View Full Page PDF
... cells becomes asymmetric (skewed) with experience, a prediction that was confirmed experimentally (673). This example illustrates how a learning mechanism specifically depends on temporal correlations of neural firing activity. Correlated activity (coherent rhythms in particular) also plays an impor ...
... cells becomes asymmetric (skewed) with experience, a prediction that was confirmed experimentally (673). This example illustrates how a learning mechanism specifically depends on temporal correlations of neural firing activity. Correlated activity (coherent rhythms in particular) also plays an impor ...
Effects of galanin on wide-dynamic range neuron activity
... findings showing that galanin expression in primary sensory neurons was up-regulated, and that the inhibitory action of galanin enhanced after sciatic nerve injury [18]. Galantide (galanin (1–13)–substance P (5–11) amide), the antagonist of galanin, can block the inhibitory actions of galanin [19]. ...
... findings showing that galanin expression in primary sensory neurons was up-regulated, and that the inhibitory action of galanin enhanced after sciatic nerve injury [18]. Galantide (galanin (1–13)–substance P (5–11) amide), the antagonist of galanin, can block the inhibitory actions of galanin [19]. ...
Downloadable Full Text - DSpace@MIT
... on a different subpopulation of VTA DA neurons as well as on GABAergic cells in the RMTg. ChR2-EYFP expressing fibers from the LHb were found in medial posterior VTA in close proximity to DA neurons projecting to mPFC as well as in the RMTg (Supplementary Fig. 12, 13). Importantly, light-evoked EPSC ...
... on a different subpopulation of VTA DA neurons as well as on GABAergic cells in the RMTg. ChR2-EYFP expressing fibers from the LHb were found in medial posterior VTA in close proximity to DA neurons projecting to mPFC as well as in the RMTg (Supplementary Fig. 12, 13). Importantly, light-evoked EPSC ...
ch_12_lecture_outline_a
... perception, voluntary motor initiation, communication, memory storage, understanding • Each hemisphere connects to contralateral side of the body • There is lateralization of cortical function in the hemispheres ...
... perception, voluntary motor initiation, communication, memory storage, understanding • Each hemisphere connects to contralateral side of the body • There is lateralization of cortical function in the hemispheres ...
descending projections from the trigeminal ganglion and
... The overview is an updated survey of our current knowledge about the trigeminal primary afferent neurons involved in the somatosensory processing from the orofacial region. The types of neurons, located in the trigeminal ganglion (TG) and mesencephalic trigeminal nucleus (MTN), are reviewed. Critica ...
... The overview is an updated survey of our current knowledge about the trigeminal primary afferent neurons involved in the somatosensory processing from the orofacial region. The types of neurons, located in the trigeminal ganglion (TG) and mesencephalic trigeminal nucleus (MTN), are reviewed. Critica ...
Neurons
... Like a charged battery sitting on a shelf, a neuron in the resting state holds a store of potential energy that can be used to generate, or “fire,” a neural impulse in response to stimulation. It awaits a source of stimulation that will temporarily reverse the electrical charges within the cell, cau ...
... Like a charged battery sitting on a shelf, a neuron in the resting state holds a store of potential energy that can be used to generate, or “fire,” a neural impulse in response to stimulation. It awaits a source of stimulation that will temporarily reverse the electrical charges within the cell, cau ...
Physiological Plasticity of Single Neurons in Auditory Cortex of the
... (Birt, Nienhuis, & Olds, 1979; Birt & Olds, ...
... (Birt, Nienhuis, & Olds, 1979; Birt & Olds, ...
Title - HAL
... Neuronal dendrites display an astonishing diversity in shape. This part of the nerve cells is important for several reasons. Firstly, it strongly influences the information processing performed by the cell, though how this influence is exercised is still debated. Secondly, the shape of dendritic arb ...
... Neuronal dendrites display an astonishing diversity in shape. This part of the nerve cells is important for several reasons. Firstly, it strongly influences the information processing performed by the cell, though how this influence is exercised is still debated. Secondly, the shape of dendritic arb ...
Neurophysiological and Computational Principles of Cortical
... cells becomes asymmetric (skewed) with experience, a prediction that was confirmed experimentally (673). This example illustrates how a learning mechanism specifically depends on temporal correlations of neural firing activity. Correlated activity (coherent rhythms in particular) also plays an impor ...
... cells becomes asymmetric (skewed) with experience, a prediction that was confirmed experimentally (673). This example illustrates how a learning mechanism specifically depends on temporal correlations of neural firing activity. Correlated activity (coherent rhythms in particular) also plays an impor ...
MUSHROOM BODY MEMOIR: FROM MAPS TO MODELS
... not satisfied by maps. Rather, it asks for models that describe behavioural functions in terms of algorithms, which should allow them to be implemented in artificial systems. The step from maps to models has proven exceedingly difficult — not even the simplest, generally accepted model of the brain ...
... not satisfied by maps. Rather, it asks for models that describe behavioural functions in terms of algorithms, which should allow them to be implemented in artificial systems. The step from maps to models has proven exceedingly difficult — not even the simplest, generally accepted model of the brain ...
Pathfinding in Computer Games 1 Introduction
... E – Edges: A set of connections between the vertices, which can be either directed or not ...
... E – Edges: A set of connections between the vertices, which can be either directed or not ...
Signature - UNE Faculty/Staff Index Page
... epithalamus – posterior part of diencephalon Includes pineal gland and habenular nuclei (eating behavior) hypothalamus – inferior part of diencephalon Infundibulum connects to pituitary gland Includes nuclei to help regulate body temperature, fluid osmolarity thalamus – egg-shaped mass of nuclei in ...
... epithalamus – posterior part of diencephalon Includes pineal gland and habenular nuclei (eating behavior) hypothalamus – inferior part of diencephalon Infundibulum connects to pituitary gland Includes nuclei to help regulate body temperature, fluid osmolarity thalamus – egg-shaped mass of nuclei in ...
Ascending projections from spinal cord and brainstem to
... (VanderHorst et al., 1996), for better comparison, rostrocaudal levels in the different cases were matched at one reference level, indicated by a vertical line in figure 4. This level was defined as the most rostral level at which the ventrolateral border of the gray matter appears to be diagonally or ...
... (VanderHorst et al., 1996), for better comparison, rostrocaudal levels in the different cases were matched at one reference level, indicated by a vertical line in figure 4. This level was defined as the most rostral level at which the ventrolateral border of the gray matter appears to be diagonally or ...
attention - CMU Graphics
... ● Receptive field ● Changes strength of neurons’ response without changing underlying response properties ● Enhances synchronization of neuronal activity ● Spatial attention will increase the gain of all neurons whose receptive field overlaps the current attentional focus, creating an enhanced repre ...
... ● Receptive field ● Changes strength of neurons’ response without changing underlying response properties ● Enhances synchronization of neuronal activity ● Spatial attention will increase the gain of all neurons whose receptive field overlaps the current attentional focus, creating an enhanced repre ...
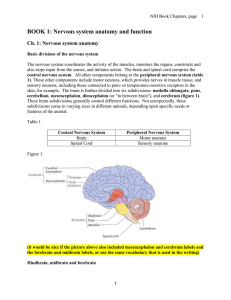
BOOK 1: Nervous system anatomy and function
... One type of monitoring approach is to use a microelectrode -- a small, microscopic probe typically made of glass or metal -- to record the number of action potentials a dopamine neuron generates. This technique is called electrophysiology or monitoring the “electrical functioning” of the neuron. The ...
... One type of monitoring approach is to use a microelectrode -- a small, microscopic probe typically made of glass or metal -- to record the number of action potentials a dopamine neuron generates. This technique is called electrophysiology or monitoring the “electrical functioning” of the neuron. The ...
Specialized Elements of Orbitofrontal Cortex in Primates
... of identifiable layers, the presence or absence of layer IV, neuronal density, and others. For example, areas that have fewer than six layers are different in type than areas that have six layers. To use an analogy, grouping by cortical type is like grouping people by similar height or weight. The p ...
... of identifiable layers, the presence or absence of layer IV, neuronal density, and others. For example, areas that have fewer than six layers are different in type than areas that have six layers. To use an analogy, grouping by cortical type is like grouping people by similar height or weight. The p ...
Role of Feedforward and Feedback Projections in Figure
... of computational modeling it was shown that the whole figure pops-out instantaneously and no filling-in process of the figural region takes place. Therefore, the model data also fit the idea of two independent mechanisms for local border and surface detection. Lamme showed onset latencies for figure ...
... of computational modeling it was shown that the whole figure pops-out instantaneously and no filling-in process of the figural region takes place. Therefore, the model data also fit the idea of two independent mechanisms for local border and surface detection. Lamme showed onset latencies for figure ...
kbook or W NEUROLOGICAL DISORDERS
... How likely is it that once we know exactly how the brain functions that we will be able to control another person’s brain? It sounds like science fiction, but we can actually do it right now, even with the limited knowledge we have. Transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) uses magnetic energy to sen ...
... How likely is it that once we know exactly how the brain functions that we will be able to control another person’s brain? It sounds like science fiction, but we can actually do it right now, even with the limited knowledge we have. Transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) uses magnetic energy to sen ...
Measurement of variability dynamics in cortical spike trains
... et al., 1967a, b; Tuckwell, 1988). Of particular interest is the class of renewal processes (Cox, 1962). Here, the intervals Xi between successive points (i.e. spikes) are independent and identically distributed (i.i.d.) with a fixed interval distribution f (x), implying a constant point process int ...
... et al., 1967a, b; Tuckwell, 1988). Of particular interest is the class of renewal processes (Cox, 1962). Here, the intervals Xi between successive points (i.e. spikes) are independent and identically distributed (i.i.d.) with a fixed interval distribution f (x), implying a constant point process int ...
Is Cell Death Primary or Secondary in the Pathophysiology of
... shown by others in DLB and Parkinson’s disease [41,50]. Looking at postsynaptic markers, an almost complete loss of drebrin was observed. Drebrin is an f-actin-binding postsynaptic protein known to be involved in the formation of dendritic spines [51]. By visualizing the dendritic tree of single cel ...
... shown by others in DLB and Parkinson’s disease [41,50]. Looking at postsynaptic markers, an almost complete loss of drebrin was observed. Drebrin is an f-actin-binding postsynaptic protein known to be involved in the formation of dendritic spines [51]. By visualizing the dendritic tree of single cel ...
Review The Neural Basis of Perceptual Learning
... outside the temporal lobe. One form of implicit memory, perceptual learning, involves improving one’s ability, with practice, to discriminate differences in the attributes of simple stimuli. Perceptual learning involves areas of neocortex upstream in the visual pathway from the temporal lobe, extend ...
... outside the temporal lobe. One form of implicit memory, perceptual learning, involves improving one’s ability, with practice, to discriminate differences in the attributes of simple stimuli. Perceptual learning involves areas of neocortex upstream in the visual pathway from the temporal lobe, extend ...
Developmental Changes Revealed by Immunohistochemical
... zones are present (Fig. IB). From ventricle to outer brain surface these are: the ventricular zone (VZ), which contains progenitor cells undergoing cell division; the intermediate zone (IZ), which can be further subdivided into the radiations (RA) and the subplate (SP); the cell-dense cortical plate ...
... zones are present (Fig. IB). From ventricle to outer brain surface these are: the ventricular zone (VZ), which contains progenitor cells undergoing cell division; the intermediate zone (IZ), which can be further subdivided into the radiations (RA) and the subplate (SP); the cell-dense cortical plate ...
Hypothalamic Regulation of Sleep
... Nambu et al. 1999). Because of the location of the hypocretin neurons in a region that has been implicated in feeding, this neuropeptide was initially thought to regulate appetite and energy metabolism (Sakurai et al. 1998). Application of hypocretin stimulates feeding (Dube et al. 1999; Sweet et al ...
... Nambu et al. 1999). Because of the location of the hypocretin neurons in a region that has been implicated in feeding, this neuropeptide was initially thought to regulate appetite and energy metabolism (Sakurai et al. 1998). Application of hypocretin stimulates feeding (Dube et al. 1999; Sweet et al ...
Synaptic gating

Synaptic gating is the ability of neural circuits to gate inputs by either suppressing or facilitating specific synaptic activity. Selective inhibition of certain synapses has been studied thoroughly (see Gate theory of pain), and recent studies have supported the existence of permissively gated synaptic transmission. In general, synaptic gating involves a mechanism of central control over neuronal output. It includes a sort of gatekeeper neuron, which has the ability to influence transmission of information to selected targets independently of the parts of the synapse upon which it exerts its action (see also neuromodulation).Bistable neurons have the ability to oscillate between a hyperpolarized (down state) and a depolarized (up state) resting membrane potential without firing an action potential. These neurons can thus be referred to as up/down neurons. According to one model, this ability is linked to the presence of NMDA and AMPA glutamate receptors. External stimulation of the NMDA receptors is responsible for moving the neuron from the down state to the up state, while the stimulation of AMPA receptors allows the neuron to reach and surpass the threshold potential. Neurons that have this bistable ability have the potential to be gated because outside gatekeeper neurons can modulate the membrane potential of the gated neuron by selectively shifting them from the up state to the down state. Such mechanisms have been observed in the nucleus accumbens, with gatekeepers originating in the cortex, thalamus and basal ganglia.