Quantified Distribution of the Noradrenaline Innervation in the
... reachesits destination via 3 main pathways: the fimbria-fornix, the fasciculuscinguli, and the ventral amygdaloid bundle. The functional properties and role of this afferent systemhave received considerableattention (for reviews, seeFoote et al., 1983, and Saper, 1987). At a cellular level, 4 subtyp ...
... reachesits destination via 3 main pathways: the fimbria-fornix, the fasciculuscinguli, and the ventral amygdaloid bundle. The functional properties and role of this afferent systemhave received considerableattention (for reviews, seeFoote et al., 1983, and Saper, 1987). At a cellular level, 4 subtyp ...
Chapter 3
... • Series of rapidly occurring events that change and then restore the membrane potential of a cell to its resting state • Ion channels open, Na+ rushes in (depolarization), K+ rushes out (repolarization) • All-or-none principal = with stimulation, either happens one specific way or not at all (lasts ...
... • Series of rapidly occurring events that change and then restore the membrane potential of a cell to its resting state • Ion channels open, Na+ rushes in (depolarization), K+ rushes out (repolarization) • All-or-none principal = with stimulation, either happens one specific way or not at all (lasts ...
Facial whisker pattern is not sufficient to instruct a
... sensory trigeminal nucleus (dPrV). Input from mystacial whiskers is relayed by the maxillary branch and forms a topographic representation of rows and whiskers in the ventral PrV (vPrV). To investigate peripheral organisation in imposing a brain topographic pattern, we analysed Edn1−/− mice, which p ...
... sensory trigeminal nucleus (dPrV). Input from mystacial whiskers is relayed by the maxillary branch and forms a topographic representation of rows and whiskers in the ventral PrV (vPrV). To investigate peripheral organisation in imposing a brain topographic pattern, we analysed Edn1−/− mice, which p ...
Ch 12
... • Series of rapidly occurring events that change and then restore the membrane potential of a cell to its resting state • Ion channels open, Na+ rushes in (depolarization), K+ rushes out (repolarization) • All-or-none principal = with stimulation, either happens one specific way or not at all (lasts ...
... • Series of rapidly occurring events that change and then restore the membrane potential of a cell to its resting state • Ion channels open, Na+ rushes in (depolarization), K+ rushes out (repolarization) • All-or-none principal = with stimulation, either happens one specific way or not at all (lasts ...
Fig. - Development - The Company of Biologists
... sensory trigeminal nucleus (dPrV). Input from mystacial whiskers is relayed by the maxillary branch and forms a topographic representation of rows and whiskers in the ventral PrV (vPrV). To investigate peripheral organisation in imposing a brain topographic pattern, we analysed Edn1−/− mice, which p ...
... sensory trigeminal nucleus (dPrV). Input from mystacial whiskers is relayed by the maxillary branch and forms a topographic representation of rows and whiskers in the ventral PrV (vPrV). To investigate peripheral organisation in imposing a brain topographic pattern, we analysed Edn1−/− mice, which p ...
Chapter 7 - Psychology
... signals that travel to the spinal cord and brain. action potential - is the technical term for when a neuron "fires." In response to sufficient amounts of neurotransmitters, or physical stimulation (for the primary afferents), a signal travels down the neuron's axon and causes release of neurotransm ...
... signals that travel to the spinal cord and brain. action potential - is the technical term for when a neuron "fires." In response to sufficient amounts of neurotransmitters, or physical stimulation (for the primary afferents), a signal travels down the neuron's axon and causes release of neurotransm ...
Hopfield Networks - liacs
... • If we pick unit i and the firing rule does not change its Si, it will not change E. • If we pick unit i and the firing rule does change its Si, it will decrease E. ...
... • If we pick unit i and the firing rule does not change its Si, it will not change E. • If we pick unit i and the firing rule does change its Si, it will decrease E. ...
Structural Changes in AMPA-Receptive Neurons in the Nucleus of
... pressure to homeostatic values. Although the underlying of hypertension is likely to be heterogeneous, at least some forms of hypertension may be caused by, or lead to, dysfunction within the central baroreceptor reflex arc.4,5 Functional changes in properties of NTS neurons as well as altered blood ...
... pressure to homeostatic values. Although the underlying of hypertension is likely to be heterogeneous, at least some forms of hypertension may be caused by, or lead to, dysfunction within the central baroreceptor reflex arc.4,5 Functional changes in properties of NTS neurons as well as altered blood ...
chapter 12. schizophrenia 12.4 schizophrenia
... polymorphisms (RFLP) reported linkage between two markers on the long arm of chromosome 5 (5q1113) and schizophrenia. Subsequently, a number of other groups using separate cohorts were unable to replicate this, and several were able to clearly reject linkage to loci from 5q. While this failure dampe ...
... polymorphisms (RFLP) reported linkage between two markers on the long arm of chromosome 5 (5q1113) and schizophrenia. Subsequently, a number of other groups using separate cohorts were unable to replicate this, and several were able to clearly reject linkage to loci from 5q. While this failure dampe ...
Cerebellar control of the inferior olive
... to the cerebellum. This nucleo-olivary projection follows the zonal and, probably also, the microzonal arrangement of the cerebellum so that closed loops are formed between the neurones in the olive, the cerebellar cortex and the nuclei. The nucleo-olivary pathway is GABAergic, but several investiga ...
... to the cerebellum. This nucleo-olivary projection follows the zonal and, probably also, the microzonal arrangement of the cerebellum so that closed loops are formed between the neurones in the olive, the cerebellar cortex and the nuclei. The nucleo-olivary pathway is GABAergic, but several investiga ...
Common and specific inhibitory motor neurons innervate
... anastomosis with the transverse nerve. Within N1B and its side branches the two axons could be followed into M59 where they further divided and formed terminals on fibres of this muscle (Fig.·2C) (N=6). In no case could we observe the immunoreactive axons in N1B to proceed beyond M59 (N=16), which c ...
... anastomosis with the transverse nerve. Within N1B and its side branches the two axons could be followed into M59 where they further divided and formed terminals on fibres of this muscle (Fig.·2C) (N=6). In no case could we observe the immunoreactive axons in N1B to proceed beyond M59 (N=16), which c ...
The Computation and Comparison of Value in Goal
... capacity to make good choices in a large variety of environments, but not in all of them. In particular, organisms are susceptible to the influence of environmental variables that interfere with their ability to compute accurate values or select the best actions. Knowledge of the decision circuitry’ ...
... capacity to make good choices in a large variety of environments, but not in all of them. In particular, organisms are susceptible to the influence of environmental variables that interfere with their ability to compute accurate values or select the best actions. Knowledge of the decision circuitry’ ...
WHEN THE visual cortex in the occipital lobe is electrically
... each. The nature and possible consequences of these experimental studies were fully explained to them before informed consent was obtained. The patients had been on various anticonvulsive medications which were tapered 48-72 h before surgery and were withheld on the morning of surgery. Preoperative ...
... each. The nature and possible consequences of these experimental studies were fully explained to them before informed consent was obtained. The patients had been on various anticonvulsive medications which were tapered 48-72 h before surgery and were withheld on the morning of surgery. Preoperative ...
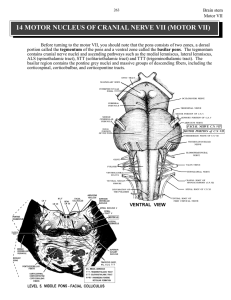
14 MOTOR NUCLEUS OF CRANIAL NERVE VII (MOTOR VII)
... I touched on some of the connections and functions of the cerebellum when discussing the accessory cuneate nucleus (POINT #5) and the inferior olivary complex (POINT # 6). There will also be several lectures on the cerebellum. Right now, you need to know that CORTICOPONTINE fibers convey information ...
... I touched on some of the connections and functions of the cerebellum when discussing the accessory cuneate nucleus (POINT #5) and the inferior olivary complex (POINT # 6). There will also be several lectures on the cerebellum. Right now, you need to know that CORTICOPONTINE fibers convey information ...
The Role of Selective Transport in Neuronal Protein
... Neurons are compartmentalized into two molecularly and functionally distinct domains, axons and dendrites. The precise targeting and localization of proteins within these domains is critical for every aspect of neuronal function, from the localization of signaling molecules that govern axonal guidan ...
... Neurons are compartmentalized into two molecularly and functionally distinct domains, axons and dendrites. The precise targeting and localization of proteins within these domains is critical for every aspect of neuronal function, from the localization of signaling molecules that govern axonal guidan ...
The Cognitive Neuroscience of Human Decision Making: A Review
... Weber, Hsee, & Welch, 2001). Such reports have emphasized impairments in the emotional aspect of decision making. Empirical studies of elements of decision making following frontal lobe damage have been undertaken more recently (e.g., Godefroy & Rousseaux, 1996, 1997; Miller, 1992; Miller & Milner, ...
... Weber, Hsee, & Welch, 2001). Such reports have emphasized impairments in the emotional aspect of decision making. Empirical studies of elements of decision making following frontal lobe damage have been undertaken more recently (e.g., Godefroy & Rousseaux, 1996, 1997; Miller, 1992; Miller & Milner, ...
Full Text - Cerebral Cortex
... pressing responses was the delivery of different kinds of rewards in a fixed order of (1) orange juice, (2) water, (3) grape juice and (4) no reward. The animal had to press the key even on no-reward trials to advance to the next trial. In the ‘Cued food reward’ task (Fig. 1b), food rewards instead ...
... pressing responses was the delivery of different kinds of rewards in a fixed order of (1) orange juice, (2) water, (3) grape juice and (4) no reward. The animal had to press the key even on no-reward trials to advance to the next trial. In the ‘Cued food reward’ task (Fig. 1b), food rewards instead ...
Identification of Dopaminergic Neurons of Nigral and Ventral
... difficult to identify the two subtypes in fetal ventral mesencephalon (VM) grafts and trace their axonal projections. Here, we have made use of a transgenic mouse expressing green fluorescent protein (GFP) under the tyrosine hydroxylase promoter. The expression of the GFP reporter allowed for visual ...
... difficult to identify the two subtypes in fetal ventral mesencephalon (VM) grafts and trace their axonal projections. Here, we have made use of a transgenic mouse expressing green fluorescent protein (GFP) under the tyrosine hydroxylase promoter. The expression of the GFP reporter allowed for visual ...
ling411-10-MEG
... zero, the wires become superconductive The magnetometer wires are housed in a thermally insulated drum (dewar) filled with liquid helium The liquid helium keeps the wires at a temperature of about ...
... zero, the wires become superconductive The magnetometer wires are housed in a thermally insulated drum (dewar) filled with liquid helium The liquid helium keeps the wires at a temperature of about ...
Kazumi TAKAHASHI†*, Jian-Sheng LIN† and Kazuya - HAL
... potential, slow single isolated firing, and an antidromic response to cortical stimulation, whereas TI-Rs neurons were characterized by a narrow action potential and high frequency burst discharge in association with theta waves in PS. These data suggest that the forebrain sleep/waking switch is reg ...
... potential, slow single isolated firing, and an antidromic response to cortical stimulation, whereas TI-Rs neurons were characterized by a narrow action potential and high frequency burst discharge in association with theta waves in PS. These data suggest that the forebrain sleep/waking switch is reg ...
Neuronal Activity in the Hippocampus During Delayed Non
... types of discrimination and a variety of complex learning tasks (Eichenbaum et al., 1992a; 1992b). However, selective aspiration of the hippocampus does not produce an impairment in object-cued DNMS tasks in rats (Aggleton et al., 1986; Rothblat and Kromer, 1991). Furthermore, we recently found that ...
... types of discrimination and a variety of complex learning tasks (Eichenbaum et al., 1992a; 1992b). However, selective aspiration of the hippocampus does not produce an impairment in object-cued DNMS tasks in rats (Aggleton et al., 1986; Rothblat and Kromer, 1991). Furthermore, we recently found that ...
State-Dependent TMS Reveals a Hierarchical
... that action understanding takes place in the ventral part of the dorsal stream (Rizzolatti and Matelli 2003), others claim that actions are fully recognized and categorized outside the motor system, in the ventral stream (Mahon and Caramazza 2008). In order to further investigate the relative contri ...
... that action understanding takes place in the ventral part of the dorsal stream (Rizzolatti and Matelli 2003), others claim that actions are fully recognized and categorized outside the motor system, in the ventral stream (Mahon and Caramazza 2008). In order to further investigate the relative contri ...
Bimal K
... explain how it generated a particular output. Again, for continuous output signals, the solution is only approximately similar to fuzzy logic computation. The learning for pattern recognition in a feedforward network will be illustrated by the optical character recognition (OCR) problem [43]. as sho ...
... explain how it generated a particular output. Again, for continuous output signals, the solution is only approximately similar to fuzzy logic computation. The learning for pattern recognition in a feedforward network will be illustrated by the optical character recognition (OCR) problem [43]. as sho ...
Task-dependent plasticity of spectrotemporal receptive fields in
... occurs in very diVerent tasks, and learning situations, suggests that “it is a general process of information storage and representation”. Each of these earlier studies measured changes in receptive Weld properties of A1 neurons that arose from behavior – we highlight two speciWc results from the ea ...
... occurs in very diVerent tasks, and learning situations, suggests that “it is a general process of information storage and representation”. Each of these earlier studies measured changes in receptive Weld properties of A1 neurons that arose from behavior – we highlight two speciWc results from the ea ...
Synaptic gating

Synaptic gating is the ability of neural circuits to gate inputs by either suppressing or facilitating specific synaptic activity. Selective inhibition of certain synapses has been studied thoroughly (see Gate theory of pain), and recent studies have supported the existence of permissively gated synaptic transmission. In general, synaptic gating involves a mechanism of central control over neuronal output. It includes a sort of gatekeeper neuron, which has the ability to influence transmission of information to selected targets independently of the parts of the synapse upon which it exerts its action (see also neuromodulation).Bistable neurons have the ability to oscillate between a hyperpolarized (down state) and a depolarized (up state) resting membrane potential without firing an action potential. These neurons can thus be referred to as up/down neurons. According to one model, this ability is linked to the presence of NMDA and AMPA glutamate receptors. External stimulation of the NMDA receptors is responsible for moving the neuron from the down state to the up state, while the stimulation of AMPA receptors allows the neuron to reach and surpass the threshold potential. Neurons that have this bistable ability have the potential to be gated because outside gatekeeper neurons can modulate the membrane potential of the gated neuron by selectively shifting them from the up state to the down state. Such mechanisms have been observed in the nucleus accumbens, with gatekeepers originating in the cortex, thalamus and basal ganglia.