The Nervous System in Lumbriculus variegatus
... conduction along the entire fiber. The giant nerve fibers in Lumbriculus are tightly wrapped by glial cell membranes, except at points where small branches emerge ventrally from the fibers (see anterior left LGF in Fig. 2). This glial wrapping gives the same appearance and probably serves the same f ...
... conduction along the entire fiber. The giant nerve fibers in Lumbriculus are tightly wrapped by glial cell membranes, except at points where small branches emerge ventrally from the fibers (see anterior left LGF in Fig. 2). This glial wrapping gives the same appearance and probably serves the same f ...
Imitation: is cognitive neuroscience solving the correspondence
... As outlined above, generalist theories assume that imitation is based on general purpose learning and motor control mechanisms. They also assume that imitation is achieved by activation of motor representations through observation of action. One would not expect the operation of such a mechanism to ...
... As outlined above, generalist theories assume that imitation is based on general purpose learning and motor control mechanisms. They also assume that imitation is achieved by activation of motor representations through observation of action. One would not expect the operation of such a mechanism to ...
ANATOMY OF THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM
... conduction along the entire fiber. The giant nerve fibers in Lumbriculus are tightly wrapped by glial cell membranes, except at points where small branches emerge ventrally from the fibers (see anterior left LGF in Fig. 2). This glial wrapping gives the same appearance and probably serves the same f ...
... conduction along the entire fiber. The giant nerve fibers in Lumbriculus are tightly wrapped by glial cell membranes, except at points where small branches emerge ventrally from the fibers (see anterior left LGF in Fig. 2). This glial wrapping gives the same appearance and probably serves the same f ...
Amyloid-Beta Induced Changes in Vesicular Transport of BDNF in
... provide insights into the cellular mechanism underlying, for example, Alzheimer’s disease (AD). To analyze the role of BDNF transport in AD, live cell imaging of fluorescently labeled BDNF was performed in hippocampal neurons of different AD model systems. BDNF and APP colocalized with low incidence ...
... provide insights into the cellular mechanism underlying, for example, Alzheimer’s disease (AD). To analyze the role of BDNF transport in AD, live cell imaging of fluorescently labeled BDNF was performed in hippocampal neurons of different AD model systems. BDNF and APP colocalized with low incidence ...
The Familial Dysautonomia disease gene, Ikbkap/Elp1, is required
... loss in the PNS is not due to failures in neural crest migration, the precursor cells that give rise to the majority of the peripheral nervous system, but rather to the apoptotic death of the sensory progenitors and neurons in the embryonic sensory and sympathetic ganglia (George et al., 2013; Jacks ...
... loss in the PNS is not due to failures in neural crest migration, the precursor cells that give rise to the majority of the peripheral nervous system, but rather to the apoptotic death of the sensory progenitors and neurons in the embryonic sensory and sympathetic ganglia (George et al., 2013; Jacks ...
Knockdown of the Dyslexia-Associated Gene
... 2000) suggests that deficits in temporal processing are not speech specific and reflect a more general dysfunction in temporal processing. Temporal processing deficits associated with dyslexia are theorized to result from abnormal firing in the central auditory system (Tallal 1980; Ahissar et al. 2000; T ...
... 2000) suggests that deficits in temporal processing are not speech specific and reflect a more general dysfunction in temporal processing. Temporal processing deficits associated with dyslexia are theorized to result from abnormal firing in the central auditory system (Tallal 1980; Ahissar et al. 2000; T ...
Unusual ultrastructural findings in dendrites of pyramidal
... pyramidal neurons of rabies-infected mice. Mice were inoculated intramuscularly with a street rabies virus of canine origin. The animals that showed an advanced stage of disease were fixed by perfusion with glutaraldehyde and paraformaldehyde. Brains were removed and cut on a vibratome to obtain cor ...
... pyramidal neurons of rabies-infected mice. Mice were inoculated intramuscularly with a street rabies virus of canine origin. The animals that showed an advanced stage of disease were fixed by perfusion with glutaraldehyde and paraformaldehyde. Brains were removed and cut on a vibratome to obtain cor ...
Disruption of experience-dependent synaptic modifications in striate
... eye afferents correlated with cortical activity, Ramoa et al. (1989) disinhibited the cortex by infusing low concentrations of the GABA, receptor antagonist bicuculline and found that the deprived eye inputs were retained in area 17. Finally, both Frtgnac et al. (1988) and Greuel et al. (1988) found ...
... eye afferents correlated with cortical activity, Ramoa et al. (1989) disinhibited the cortex by infusing low concentrations of the GABA, receptor antagonist bicuculline and found that the deprived eye inputs were retained in area 17. Finally, both Frtgnac et al. (1988) and Greuel et al. (1988) found ...
Read as PDF
... may play roles in locomotion and in the escape swimming network similar to those of Tritonia, because the animals share apparently homologous networks for these behaviors (Jing and Gillette, 1995; Jing et al., 1997; Jing and Gillette, 1998). In this animal, 5-HT stimulates multiple aspects of behavi ...
... may play roles in locomotion and in the escape swimming network similar to those of Tritonia, because the animals share apparently homologous networks for these behaviors (Jing and Gillette, 1995; Jing et al., 1997; Jing and Gillette, 1998). In this animal, 5-HT stimulates multiple aspects of behavi ...
Histochemical and lmmunocytochemical Compartments of the
... antibody CAT 301. Small GABA-immunoreactive cells and terminal-like puncta are highly concentrated in the rods but are dispersed in the matrix. In the matrix, all nonGABA cells are small, immunoreactive for 28-kDa calbindin, and not stained by CAT 301. They appear to form part of a wider system of c ...
... antibody CAT 301. Small GABA-immunoreactive cells and terminal-like puncta are highly concentrated in the rods but are dispersed in the matrix. In the matrix, all nonGABA cells are small, immunoreactive for 28-kDa calbindin, and not stained by CAT 301. They appear to form part of a wider system of c ...
Cholinergic Elements in the Zebrafish Central Nervous System
... the brain, retina, and spinal cord. AChE labeling was more abundant and more widely distributed than ChAT immunoreactivity. In the telencephalon, ChAT-immunoreactive (ChAT-ir) cells were absent, whereas AChE-positive neurons were observed in both the olfactory bulb and the telencephalic hemispheres. ...
... the brain, retina, and spinal cord. AChE labeling was more abundant and more widely distributed than ChAT immunoreactivity. In the telencephalon, ChAT-immunoreactive (ChAT-ir) cells were absent, whereas AChE-positive neurons were observed in both the olfactory bulb and the telencephalic hemispheres. ...
Medical Image Segmentation Using Artificial Neural Networks
... stimulus will fire in the first iteration. In this situation, the threshold values are high and it will take several iterations in which neurons are allowed to fire again. This iterative process will continue until the user stops it. There is no automatic procedure to stop the PCNN; this is a disadv ...
... stimulus will fire in the first iteration. In this situation, the threshold values are high and it will take several iterations in which neurons are allowed to fire again. This iterative process will continue until the user stops it. There is no automatic procedure to stop the PCNN; this is a disadv ...
BRAINSTEM
... Crossing-over of corticospinal (motor) tract at the level of the transition between medulla and spinal cord. Visible on the ventral brainstem surface. As a result of the decussation, one side of the brain controls the muscles of the opposite side. Ascending afferent axonal pathway in the brainstem ( ...
... Crossing-over of corticospinal (motor) tract at the level of the transition between medulla and spinal cord. Visible on the ventral brainstem surface. As a result of the decussation, one side of the brain controls the muscles of the opposite side. Ascending afferent axonal pathway in the brainstem ( ...
A circular model for song motor control in Serinus canaria
... by muscles. If the bursts in HVC projection neurons occur temporally close to significant motor instances (like the beginning of the syllables), it is tempting to conjecture that there is a relationship between these events. However, if the burst occurs simultaneously with the acoustic gesture, caus ...
... by muscles. If the bursts in HVC projection neurons occur temporally close to significant motor instances (like the beginning of the syllables), it is tempting to conjecture that there is a relationship between these events. However, if the burst occurs simultaneously with the acoustic gesture, caus ...
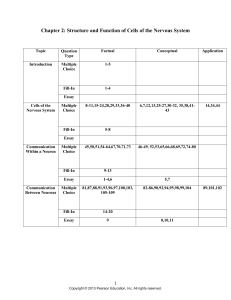
Exam 1
... Crossing-over of corticospinal (motor) tract at the level of the transition between medulla and spinal cord. Visible on the ventral brainstem surface. As a result of the decussation, one side of the brain controls the muscles of the opposite side. Ascending afferent axonal pathway in the brainstem ( ...
... Crossing-over of corticospinal (motor) tract at the level of the transition between medulla and spinal cord. Visible on the ventral brainstem surface. As a result of the decussation, one side of the brain controls the muscles of the opposite side. Ascending afferent axonal pathway in the brainstem ( ...
A Study on Various Sites of Supranuclear Facial Nerve
... Figure 3: Haemorrhage in thalamus and lentiform nucleus. ...
... Figure 3: Haemorrhage in thalamus and lentiform nucleus. ...
Sample
... a. Neurons have a high metabolic rate. b. The dendrites store nutrients and oxygen for the neuron. c. Dead neurons are consumed by other neurons. d. Neurons make up 29% of the volume of the brain. e. Neurons can survive for hours without oxygen. Difficulty: 2 Question ID: 2.1-31 Page Ref: 35 Topic: ...
... a. Neurons have a high metabolic rate. b. The dendrites store nutrients and oxygen for the neuron. c. Dead neurons are consumed by other neurons. d. Neurons make up 29% of the volume of the brain. e. Neurons can survive for hours without oxygen. Difficulty: 2 Question ID: 2.1-31 Page Ref: 35 Topic: ...
button - TestbankEbook
... a. Neurons have a high metabolic rate. b. The dendrites store nutrients and oxygen for the neuron. c. Dead neurons are consumed by other neurons. d. Neurons make up 29% of the volume of the brain. e. Neurons can survive for hours without oxygen. Difficulty: 2 Question ID: 2.1-31 Page Ref: 35 Topic: ...
... a. Neurons have a high metabolic rate. b. The dendrites store nutrients and oxygen for the neuron. c. Dead neurons are consumed by other neurons. d. Neurons make up 29% of the volume of the brain. e. Neurons can survive for hours without oxygen. Difficulty: 2 Question ID: 2.1-31 Page Ref: 35 Topic: ...
(2000). Cerebral hemisphere regulation of motivated behavior.
... intrinsic activity [327] that controls behavioral state — the sleep / wake cycle and levels of arousal within a particular state. Obviously, behavior is quite different when one is asleep or awake, and when awake there is a certain basic level of arousal or spontaneous activity that is independent o ...
... intrinsic activity [327] that controls behavioral state — the sleep / wake cycle and levels of arousal within a particular state. Obviously, behavior is quite different when one is asleep or awake, and when awake there is a certain basic level of arousal or spontaneous activity that is independent o ...
Cerebral hemisphere regulation of motivated
... intrinsic activity [327] that controls behavioral state — the sleep / wake cycle and levels of arousal within a particular state. Obviously, behavior is quite different when one is asleep or awake, and when awake there is a certain basic level of arousal or spontaneous activity that is independent o ...
... intrinsic activity [327] that controls behavioral state — the sleep / wake cycle and levels of arousal within a particular state. Obviously, behavior is quite different when one is asleep or awake, and when awake there is a certain basic level of arousal or spontaneous activity that is independent o ...
Predictions not commands: active inference in the motor system
... phrase (encoded in semantic areas) predicts words (encoded in lexical areas), which predicts letters (encoded in ventral occipital areas), which predict oriented lines and edges (encoded in visual areas). All these hierarchically deployed explanations for visual input are internally consistent and d ...
... phrase (encoded in semantic areas) predicts words (encoded in lexical areas), which predicts letters (encoded in ventral occipital areas), which predict oriented lines and edges (encoded in visual areas). All these hierarchically deployed explanations for visual input are internally consistent and d ...
Models and Measurements of Functional Maps in V1
... cortical activity and, instead, proposed an alternative description of cortical organization: rather than having several separable parameters mapped across the cortical surface, they suggested that primary visual cortex would be better characterized by a single map that encodes spatiotemporal energy ...
... cortical activity and, instead, proposed an alternative description of cortical organization: rather than having several separable parameters mapped across the cortical surface, they suggested that primary visual cortex would be better characterized by a single map that encodes spatiotemporal energy ...
Well That Frog Just Doesn`t Have The Nerve
... specific signals to target regions, the body would be unable to conduct the movements that keep every individual alive. As seen with the pithed frog, the spinal cord was disconnected from the brain. This inability to send a signal through the body made it impossible for the frog to sense pain or pro ...
... specific signals to target regions, the body would be unable to conduct the movements that keep every individual alive. As seen with the pithed frog, the spinal cord was disconnected from the brain. This inability to send a signal through the body made it impossible for the frog to sense pain or pro ...
Fut u re N
... neuropathological changes in cortical structures, including amyloid plaques and neurofibrillary tangles. Current treatments for Alzheimer’s disease offer only a small reduction in behavioral symptoms [1,2] and do not halt the temporal progression of the disease – emphasizing the need for a functiona ...
... neuropathological changes in cortical structures, including amyloid plaques and neurofibrillary tangles. Current treatments for Alzheimer’s disease offer only a small reduction in behavioral symptoms [1,2] and do not halt the temporal progression of the disease – emphasizing the need for a functiona ...
Pain
... c) Chemical Pain Rs: respond to noxious chemical stimuli. d) Polymodal Pain Rs: respond to a combination of mechanical, thermal, and chemical noxious stimuli ...
... c) Chemical Pain Rs: respond to noxious chemical stimuli. d) Polymodal Pain Rs: respond to a combination of mechanical, thermal, and chemical noxious stimuli ...
Synaptic gating

Synaptic gating is the ability of neural circuits to gate inputs by either suppressing or facilitating specific synaptic activity. Selective inhibition of certain synapses has been studied thoroughly (see Gate theory of pain), and recent studies have supported the existence of permissively gated synaptic transmission. In general, synaptic gating involves a mechanism of central control over neuronal output. It includes a sort of gatekeeper neuron, which has the ability to influence transmission of information to selected targets independently of the parts of the synapse upon which it exerts its action (see also neuromodulation).Bistable neurons have the ability to oscillate between a hyperpolarized (down state) and a depolarized (up state) resting membrane potential without firing an action potential. These neurons can thus be referred to as up/down neurons. According to one model, this ability is linked to the presence of NMDA and AMPA glutamate receptors. External stimulation of the NMDA receptors is responsible for moving the neuron from the down state to the up state, while the stimulation of AMPA receptors allows the neuron to reach and surpass the threshold potential. Neurons that have this bistable ability have the potential to be gated because outside gatekeeper neurons can modulate the membrane potential of the gated neuron by selectively shifting them from the up state to the down state. Such mechanisms have been observed in the nucleus accumbens, with gatekeepers originating in the cortex, thalamus and basal ganglia.