Neuronal correlates of movement dynamics in the dorsal and ventral
... functional overlaps between PMd and M1 (Riehle and Requin 1989; Crammond and Kalaska 1994, 1996; Johnson et al. 1996, 1999; Scott and Kalaska 1997; Scott et al. 1997). Regarding the hypothesis of dynamics-related activity in PMd, the most relevant study by Werner et al. found that the activity of 26 ...
... functional overlaps between PMd and M1 (Riehle and Requin 1989; Crammond and Kalaska 1994, 1996; Johnson et al. 1996, 1999; Scott and Kalaska 1997; Scott et al. 1997). Regarding the hypothesis of dynamics-related activity in PMd, the most relevant study by Werner et al. found that the activity of 26 ...
Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation: Decomposing the
... stimulation of cortical tissue through the intact scalp of a participant. The technique induces a short-lived (~200 µs) electrical current of up to 5 kA in a stimulation coil placed over the scalp of the participant, which in turn will generate a perpendicular magnetic field (i.e., directed to the c ...
... stimulation of cortical tissue through the intact scalp of a participant. The technique induces a short-lived (~200 µs) electrical current of up to 5 kA in a stimulation coil placed over the scalp of the participant, which in turn will generate a perpendicular magnetic field (i.e., directed to the c ...
An Introduction To Human Neuroanatomy
... Myelin is a protein which increases the speed of information flow along axons. Axons are a nerve cell’s output fiber. The oligodendrocyte on the left is reaching out and wrapping its myelin-filled cell membrane around two nerve cell axons (labeled A1 and A2). In the right hand picture, we see severa ...
... Myelin is a protein which increases the speed of information flow along axons. Axons are a nerve cell’s output fiber. The oligodendrocyte on the left is reaching out and wrapping its myelin-filled cell membrane around two nerve cell axons (labeled A1 and A2). In the right hand picture, we see severa ...
Limitations in anti-obesity drug development: the critical role of
... involved in the regulation of energy balance. In the brain, the hypothalamus (small boxed area in mid-sagittal view of the brain) contains two critical subsets of neurons (enlarged in boxed area): the neuropeptide Y/agouti-related protein/γ-amino butyric acid (NPY/AgRP/GABA) neurons, which, when act ...
... involved in the regulation of energy balance. In the brain, the hypothalamus (small boxed area in mid-sagittal view of the brain) contains two critical subsets of neurons (enlarged in boxed area): the neuropeptide Y/agouti-related protein/γ-amino butyric acid (NPY/AgRP/GABA) neurons, which, when act ...
Cognitive neuroscience of self-regulation failure
... behavior [38]. A recent meta-analysis of 75 articles found that implicit cognition is a strong and reliable predictor of substance use [39]. From this perspective, cognition that is spontaneously activated by stimuli from the environment alters how people act in a given situation. The ability to tra ...
... behavior [38]. A recent meta-analysis of 75 articles found that implicit cognition is a strong and reliable predictor of substance use [39]. From this perspective, cognition that is spontaneously activated by stimuli from the environment alters how people act in a given situation. The ability to tra ...
Full Text - Harvard University
... Opposite to Hull, Skinner approached the study of motivation entirely based on empirical observations. One of Skinner’s key contributions was that response rates and motivation levels of animals can be controlled by schedules of reinforcement imposed by the experimenter. Specifically, he observed th ...
... Opposite to Hull, Skinner approached the study of motivation entirely based on empirical observations. One of Skinner’s key contributions was that response rates and motivation levels of animals can be controlled by schedules of reinforcement imposed by the experimenter. Specifically, he observed th ...
Dynamical systems view
... An epic, twenty-year battle was fought over the cortical representation of movement. Do motor cortex neurons represent the direction of the hand during reaching, or do they represent other features of movement such as joint rotation or muscle output? Graziano 2011 The role of the motor system is to ...
... An epic, twenty-year battle was fought over the cortical representation of movement. Do motor cortex neurons represent the direction of the hand during reaching, or do they represent other features of movement such as joint rotation or muscle output? Graziano 2011 The role of the motor system is to ...
Transgenic mice overexpressing the full
... TgNTRK3 per line and 7 wild type mice) with the aid of CASTGRID software package adapted to an OLYMPUS BX51 microscope (Olympus, Denmark), through the substantia nigra pars compacta (SNc) and pars reticulata (SNr) (Bregma − 2.46 mm to − 4.04 mm) and LC (Bregma − 5.34 mm to − 5.8 mm) according to the ...
... TgNTRK3 per line and 7 wild type mice) with the aid of CASTGRID software package adapted to an OLYMPUS BX51 microscope (Olympus, Denmark), through the substantia nigra pars compacta (SNc) and pars reticulata (SNr) (Bregma − 2.46 mm to − 4.04 mm) and LC (Bregma − 5.34 mm to − 5.8 mm) according to the ...
THE CINGULATE CORTEX AND HUMAN MEMORY PROCESSES
... why the overdeveloped anterior cingulate cortex correlates with a decrease in memory errors, such as confabulations, but also with a decrease in overall recall: conservative decision-making criteria filter the noise and lower the number of “false alarms” as well as lowering the number of “hits.” On ...
... why the overdeveloped anterior cingulate cortex correlates with a decrease in memory errors, such as confabulations, but also with a decrease in overall recall: conservative decision-making criteria filter the noise and lower the number of “false alarms” as well as lowering the number of “hits.” On ...
PDF
... completing the training paradigm, we tested the cats using three experiments. Experiment 1 was a 100-trial session including 50 ICMS-absent trials and 10 trials each of 20, 40, 60, 80, and 100 µA pulse amplitude. This experiment was designed to test the cats’ performance in ICMS detection at differe ...
... completing the training paradigm, we tested the cats using three experiments. Experiment 1 was a 100-trial session including 50 ICMS-absent trials and 10 trials each of 20, 40, 60, 80, and 100 µA pulse amplitude. This experiment was designed to test the cats’ performance in ICMS detection at differe ...
Altered fear learning across development in both mouse and human
... PSYCHOLOGICAL AND COGNITIVE SCIENCES ...
... PSYCHOLOGICAL AND COGNITIVE SCIENCES ...
stretch reflex 2
... Supraspinal Control of Stretch Reflex At the cortical level, the net effect of area 4 & area 6 & area 4s on the stretch reflex & muscle tone is inhibitory, so a lesion causing damage of area 4, 4s & 6 (UMNL) leads to increase in muscle tone •In animals the separation between the cerebral cortex & b ...
... Supraspinal Control of Stretch Reflex At the cortical level, the net effect of area 4 & area 6 & area 4s on the stretch reflex & muscle tone is inhibitory, so a lesion causing damage of area 4, 4s & 6 (UMNL) leads to increase in muscle tone •In animals the separation between the cerebral cortex & b ...
Separate Representations of Target and Timing Cue Locations in
... Submitted 23 June 2008; accepted in final form 8 November 2008 ...
... Submitted 23 June 2008; accepted in final form 8 November 2008 ...
Abnormal Neurotransmitter Release Underlying Behavioral and
... including the presynaptic neurophysiological and intracellular signaling mechanisms that control the neurotransmitter synthesis, storage, and release, the regulation of relevant transporters, and presynaptic and postsynaptic signaling pathways are described elsewhere (eg, Cooper et al, 2003). Abnorm ...
... including the presynaptic neurophysiological and intracellular signaling mechanisms that control the neurotransmitter synthesis, storage, and release, the regulation of relevant transporters, and presynaptic and postsynaptic signaling pathways are described elsewhere (eg, Cooper et al, 2003). Abnorm ...
Glycine Binding Sites of Presynaptic NMDA Receptors May
... the open-channel NMDA-R blocker, dizocilpine maleate (MK801; 1 mM), in the recording pipette as described by Berretta and Jones (1996). Blockade of the postsynaptic NMDA-Rs with MK-801 completely abolished the NMDA component of mEPSCs (Fig. 5). Inclusion of 7-Cl KYNA (20 M) under these conditions r ...
... the open-channel NMDA-R blocker, dizocilpine maleate (MK801; 1 mM), in the recording pipette as described by Berretta and Jones (1996). Blockade of the postsynaptic NMDA-Rs with MK-801 completely abolished the NMDA component of mEPSCs (Fig. 5). Inclusion of 7-Cl KYNA (20 M) under these conditions r ...
The dynamic spatio-temporal behavior of visual responses in
... evidence accumulated not later than around 1970 [6,57,61,72], indicate that visual information processing must be a process utilizing recurrent loops and involving massive dynamic interactions. It is thus puzzling that visual cortical receptive fields were for a very long time regarded as rather sta ...
... evidence accumulated not later than around 1970 [6,57,61,72], indicate that visual information processing must be a process utilizing recurrent loops and involving massive dynamic interactions. It is thus puzzling that visual cortical receptive fields were for a very long time regarded as rather sta ...
Heterogeneous Integration of Bilateral Whisker Signals by Neurons
... et al. (2000) showed that the relative contribution of temporal interactions between neurons increases with the number of whiskers to be discriminated. Inhibitory intercolumnar interactions have also been suggested to maintain a dynamic range and prevent response saturation (Mirabella et al. 2001). ...
... et al. (2000) showed that the relative contribution of temporal interactions between neurons increases with the number of whiskers to be discriminated. Inhibitory intercolumnar interactions have also been suggested to maintain a dynamic range and prevent response saturation (Mirabella et al. 2001). ...
Biomimetic approaches to the control of underwater walking machines
... Amplitude modulation affects the number, size and discharge frequency of the active motor neurons. Phase-modulating reflexes operate at the level of the neuronal oscillator and can perturb an ongoing rhythm on a cycle-by-cycle basis (Pinsker & Ayers 1983). Intersegmental exteroceptive reflexes modulat ...
... Amplitude modulation affects the number, size and discharge frequency of the active motor neurons. Phase-modulating reflexes operate at the level of the neuronal oscillator and can perturb an ongoing rhythm on a cycle-by-cycle basis (Pinsker & Ayers 1983). Intersegmental exteroceptive reflexes modulat ...
A transcription factor network controls cell migration
... (Turner and Cepko, 1987). While numerous genes that govern this process have been uncovered, precise mechanisms that produce different neuron types remain elusive (for review see Cepko, 2014). ...
... (Turner and Cepko, 1987). While numerous genes that govern this process have been uncovered, precise mechanisms that produce different neuron types remain elusive (for review see Cepko, 2014). ...
Neural Prostheses - Gert Cauwenberghs
... intervals varying from 1 to 10 s. (d) Voltage traces showing membrane depolarization and spikes in a current-clamped hippocampal neuron (left) evoked by 1-s periods of light (gray bar). Right, properties of the first spike elicited (n = 10): latency to spike threshold, latency to spike peak, and jit ...
... intervals varying from 1 to 10 s. (d) Voltage traces showing membrane depolarization and spikes in a current-clamped hippocampal neuron (left) evoked by 1-s periods of light (gray bar). Right, properties of the first spike elicited (n = 10): latency to spike threshold, latency to spike peak, and jit ...
Anatomofunctional organization of the ventral primary motor and
... eyes. We further checked whether different types of movements (i.e. scratching, grooming or spontaneous finger flexion movements) were equally effective in triggering neuronal discharge in order to establish whether the activity was related to simple movements or motor acts. Grasping-related respons ...
... eyes. We further checked whether different types of movements (i.e. scratching, grooming or spontaneous finger flexion movements) were equally effective in triggering neuronal discharge in order to establish whether the activity was related to simple movements or motor acts. Grasping-related respons ...
Developing an Effective Parenting Style
... • The genes’ instructions are lifelong • Genes affect some parts of growth and development more than others • Some genes determine whether a person will have a trait • Other genes affect the range of a trait ...
... • The genes’ instructions are lifelong • Genes affect some parts of growth and development more than others • Some genes determine whether a person will have a trait • Other genes affect the range of a trait ...
Slide 1 - Brainstem Wiki
... FIG. 6. Course of the laterally projecting component of the spinothalamic tract in a macaque monkey. The cells of origin of the part of the spinothalamic tract that projects to the lateral thalamus are concentrated in laminae I and V of the spinal cord dorsal horn. The axons cross the midline in the ...
... FIG. 6. Course of the laterally projecting component of the spinothalamic tract in a macaque monkey. The cells of origin of the part of the spinothalamic tract that projects to the lateral thalamus are concentrated in laminae I and V of the spinal cord dorsal horn. The axons cross the midline in the ...
child development - Goodheart
... • The genes’ instructions are lifelong • Genes affect some parts of growth and development more than others • Some genes determine whether a person will have a trait • Other genes affect the range of a trait ...
... • The genes’ instructions are lifelong • Genes affect some parts of growth and development more than others • Some genes determine whether a person will have a trait • Other genes affect the range of a trait ...
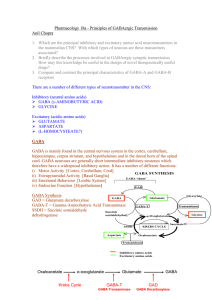
Pharmacology 18a – Priciples of GABAergic Transmission
... GABA is stored in vesicles in nerve terminals (like any other neurotransmitter) and is released by exocytosis upon influx of calcium ions. GABA Receptors There are 2 types of GABA receptor: GABAA Generally POSTsynaptic When activated by GABA cause influx of Cl- ions This causes the cell to hyp ...
... GABA is stored in vesicles in nerve terminals (like any other neurotransmitter) and is released by exocytosis upon influx of calcium ions. GABA Receptors There are 2 types of GABA receptor: GABAA Generally POSTsynaptic When activated by GABA cause influx of Cl- ions This causes the cell to hyp ...
Synaptic gating

Synaptic gating is the ability of neural circuits to gate inputs by either suppressing or facilitating specific synaptic activity. Selective inhibition of certain synapses has been studied thoroughly (see Gate theory of pain), and recent studies have supported the existence of permissively gated synaptic transmission. In general, synaptic gating involves a mechanism of central control over neuronal output. It includes a sort of gatekeeper neuron, which has the ability to influence transmission of information to selected targets independently of the parts of the synapse upon which it exerts its action (see also neuromodulation).Bistable neurons have the ability to oscillate between a hyperpolarized (down state) and a depolarized (up state) resting membrane potential without firing an action potential. These neurons can thus be referred to as up/down neurons. According to one model, this ability is linked to the presence of NMDA and AMPA glutamate receptors. External stimulation of the NMDA receptors is responsible for moving the neuron from the down state to the up state, while the stimulation of AMPA receptors allows the neuron to reach and surpass the threshold potential. Neurons that have this bistable ability have the potential to be gated because outside gatekeeper neurons can modulate the membrane potential of the gated neuron by selectively shifting them from the up state to the down state. Such mechanisms have been observed in the nucleus accumbens, with gatekeepers originating in the cortex, thalamus and basal ganglia.