Expert system, fuzzy logic, and neural network applications in power
... in solving fuzzy logic problems, its inability to solve pattem recognition and image processing type problems was seriously felt since the beginnning of the 1990’s. In fact, expert system techniques which held so much promise in the 1980’s, could not fulfill the expected computational needs. Therefo ...
... in solving fuzzy logic problems, its inability to solve pattem recognition and image processing type problems was seriously felt since the beginnning of the 1990’s. In fact, expert system techniques which held so much promise in the 1980’s, could not fulfill the expected computational needs. Therefo ...
Smelling on the fly: sensory cues and strategies for olfactory
... be easily depleted [31]. In addition, high odor concentrations tend to drive more activity in GABAergic interneurons [35], which further decreases the gain of ORNto-PN synapses [36,37]. GABAergic inhibition tends to prevent saturation of PN firing rates, and helps ensure that even intense stimuli re ...
... be easily depleted [31]. In addition, high odor concentrations tend to drive more activity in GABAergic interneurons [35], which further decreases the gain of ORNto-PN synapses [36,37]. GABAergic inhibition tends to prevent saturation of PN firing rates, and helps ensure that even intense stimuli re ...
PRESYNAPTIC IONOTROPIC RECEPTORS AND CONTROL OF
... VGCCs can enhance spontaneous neurotransmitter release, an effect that is sensitive to VGCC blockade. By contrast, effects of the activation of presynaptic anionic receptors on evoked release are more difficult to predict. Depolarization that activates VGCCs and enhances spontaneous release might di ...
... VGCCs can enhance spontaneous neurotransmitter release, an effect that is sensitive to VGCC blockade. By contrast, effects of the activation of presynaptic anionic receptors on evoked release are more difficult to predict. Depolarization that activates VGCCs and enhances spontaneous release might di ...
Reward-Related Responses in the Human Striatum
... synaptic input from cortical and subcortical afferents, such as motor cortical input and dopaminergic projections from substantia nigra (but also other midbrain nuclei, such as the ventral tegmental area2,4,5,7–9 ). The striatum can be further subdivided into dorsal and ventral components. The dorsa ...
... synaptic input from cortical and subcortical afferents, such as motor cortical input and dopaminergic projections from substantia nigra (but also other midbrain nuclei, such as the ventral tegmental area2,4,5,7–9 ). The striatum can be further subdivided into dorsal and ventral components. The dorsa ...
Cliff - USD Biology
... Tonic change to DA levels Covering a broad population of NAC neurons Modulate incoming presynaptic signals Therefore modulate the actions of D1, D2, and D3 receptors ...
... Tonic change to DA levels Covering a broad population of NAC neurons Modulate incoming presynaptic signals Therefore modulate the actions of D1, D2, and D3 receptors ...
View Full Page PDF
... thalamocortical system. Spindle waves are by far the best understood type of rhythmicity in this system, in part because they can be enhanced by anesthetics such as barbiturates (8, 81). The thalamic origin of spindles was first suggested by Bishop (28), who observed the suppression of rhythmic acti ...
... thalamocortical system. Spindle waves are by far the best understood type of rhythmicity in this system, in part because they can be enhanced by anesthetics such as barbiturates (8, 81). The thalamic origin of spindles was first suggested by Bishop (28), who observed the suppression of rhythmic acti ...
Conditioned tone control of brain reward behavior produces highly
... Primary sensory cortices have been assumed to serve as stimulus analyzers while cognitive functions such as learning and memory have been allocated to ‘‘higher” cortical areas. However, the primary auditory cortex (A1) is now known to encode the acquired significance of sound as indicated by associat ...
... Primary sensory cortices have been assumed to serve as stimulus analyzers while cognitive functions such as learning and memory have been allocated to ‘‘higher” cortical areas. However, the primary auditory cortex (A1) is now known to encode the acquired significance of sound as indicated by associat ...
Genetic Ablation of Orexin Neurons in Mice Results in Narcolepsy
... Recently, several reports implicate a dysfunction of the orexin system in the human sleep disorder narcolepsy. Narcolepsy is the only neurological disorder characterized by a primary disorganization of sleep and wakefulness. Patients with narcolepsy suffer from excessive daytime sleepiness, cataplex ...
... Recently, several reports implicate a dysfunction of the orexin system in the human sleep disorder narcolepsy. Narcolepsy is the only neurological disorder characterized by a primary disorganization of sleep and wakefulness. Patients with narcolepsy suffer from excessive daytime sleepiness, cataplex ...
Brainstem
... - rich vascularity gives its pinkish hue - involved in motor control - inputs -- from deep cerebellar nuclei -- from motor-related cortical areas (corticorubral fibers) - outputs -- spinal cord (rubrospinal fibers) --- project to the same laminae the corticospinal fibers terminate --- corticorubral ...
... - rich vascularity gives its pinkish hue - involved in motor control - inputs -- from deep cerebellar nuclei -- from motor-related cortical areas (corticorubral fibers) - outputs -- spinal cord (rubrospinal fibers) --- project to the same laminae the corticospinal fibers terminate --- corticorubral ...
09 - Pierce College
... d. Occipital lobes 29. Primary auditory cortex is located here: a. Frontal lobe b. Parietal lobes c. Temporal lobes d. Occipital lobes 30. The part of your brain that receives, interprets and acts on action potentials from the eyes is located in which lobe? a. Frontal b. Parietal c. Temporal d. Occ ...
... d. Occipital lobes 29. Primary auditory cortex is located here: a. Frontal lobe b. Parietal lobes c. Temporal lobes d. Occipital lobes 30. The part of your brain that receives, interprets and acts on action potentials from the eyes is located in which lobe? a. Frontal b. Parietal c. Temporal d. Occ ...
Different neurotrophins are expressed and act in a developmental
... raised the issue of whether similar correlations between target field innervation, neurotrophin synthesis and neuronal responsiveness exist for these more recently identified neurotrophins. This is especially pertinent as these neurotrophins, in contrast to NGF, have additional roles in neuronal dev ...
... raised the issue of whether similar correlations between target field innervation, neurotrophin synthesis and neuronal responsiveness exist for these more recently identified neurotrophins. This is especially pertinent as these neurotrophins, in contrast to NGF, have additional roles in neuronal dev ...
Repetition suppression - Philosophical Transactions of the Royal
... Figure 2. Effect of interleaving stimuli on repetition suppression. Mean percentage change in neuron response to visual stimulus presentation relative to spontaneous activity as a function of the number of interleaved stimuli in (a) area TE, (b) perirhinal cortex, and (c) entorhinal cortex. With an ...
... Figure 2. Effect of interleaving stimuli on repetition suppression. Mean percentage change in neuron response to visual stimulus presentation relative to spontaneous activity as a function of the number of interleaved stimuli in (a) area TE, (b) perirhinal cortex, and (c) entorhinal cortex. With an ...
No Binocular Rivalry in the LGN of Alert Macaque Monkeys
... formed by averaging them had a peak of <1.0. This happened because the maximum response was not at the same frequency for every unit. (For example, maximum response could occur at the stimulus frequency for one unit, and at the video frame rate for another unit. Averaging the spectra of these two un ...
... formed by averaging them had a peak of <1.0. This happened because the maximum response was not at the same frequency for every unit. (For example, maximum response could occur at the stimulus frequency for one unit, and at the video frame rate for another unit. Averaging the spectra of these two un ...
Visual Adaptation: Physiology, Mechanisms, and Functional Benefits
... by test stimuli presented at both adapted and unadapted locations within the RF. In MT, however, adaptation with a small stimulus affects only stimuli presented to the same spatial subregion of the RF. This suggests that changes in MT contrast sensitivity occur prior to the spatial integration of in ...
... by test stimuli presented at both adapted and unadapted locations within the RF. In MT, however, adaptation with a small stimulus affects only stimuli presented to the same spatial subregion of the RF. This suggests that changes in MT contrast sensitivity occur prior to the spatial integration of in ...
Chapter 2: Biological Bases of Behavior MULTIPLE CHOICE 1
... REF: 2.3 Neurons: Structure, Function, and Communication, Textbook | Animation - Neuron and Transmitters, Online OBJ: LO4 Identify the main functions of glial cells. MSC: TYPE: Easy 17. Which brain cells are responsible for providing insulation around the neuron? a. GABA cells c. axon cells b. curar ...
... REF: 2.3 Neurons: Structure, Function, and Communication, Textbook | Animation - Neuron and Transmitters, Online OBJ: LO4 Identify the main functions of glial cells. MSC: TYPE: Easy 17. Which brain cells are responsible for providing insulation around the neuron? a. GABA cells c. axon cells b. curar ...
Investigator/Program Director (Last, First, Middle): Nick, Teresa A.
... modulatory influence on the motor neurons that innervate them (Nick and Ribera, 2000). When synaptic communication was blocked with an acetylcholine antagonist, α-bungarotoxin, the motor neurons developed differently than if they were allowed to synaptically communicate with muscle. The Trk neurotro ...
... modulatory influence on the motor neurons that innervate them (Nick and Ribera, 2000). When synaptic communication was blocked with an acetylcholine antagonist, α-bungarotoxin, the motor neurons developed differently than if they were allowed to synaptically communicate with muscle. The Trk neurotro ...
Neurophysiological involvement in hypervolemic hyponatremia
... of 2% or 5% per hour over 2 h had a biphasic effect on AVP secretion: a short suppression (<60 min) followed by a rebound ...
... of 2% or 5% per hour over 2 h had a biphasic effect on AVP secretion: a short suppression (<60 min) followed by a rebound ...
nervous system physiology 4
... innervated by the axon from one motor neuron is called a motor unit. ...
... innervated by the axon from one motor neuron is called a motor unit. ...
Vdhjections InducedInto the Auditory Pathway of Ferrets. I
... subject of intense examination. However, it is not known whether cortical cells in different sensory cortices process information in a way that is specific to the modality of their input, or whether there are commonalities in processing circuitry across different cortices. In our laboratory, this qu ...
... subject of intense examination. However, it is not known whether cortical cells in different sensory cortices process information in a way that is specific to the modality of their input, or whether there are commonalities in processing circuitry across different cortices. In our laboratory, this qu ...
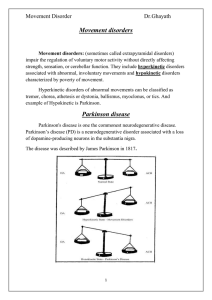
Movement disorders
... the half-life of the drug. This loss of benefit is known as the wearing-off effect. At the same time, many patients develop dyskinesia, these tend to occur at the time of maximal clinical benefit and peak plasma concentration (peak-dose dyskinesia). In more advanced states, patients may cycle betwee ...
... the half-life of the drug. This loss of benefit is known as the wearing-off effect. At the same time, many patients develop dyskinesia, these tend to occur at the time of maximal clinical benefit and peak plasma concentration (peak-dose dyskinesia). In more advanced states, patients may cycle betwee ...
The role of mirror neurons in speech perception and
... subset of apraxic patients also have pantomime recognition deficits (Heilman, Rothi, & Valenstein, 1982), which has been taken as evidence for overlap in the neural systems supporting action execution and action understanding (Gallese et al., 1996). Some studies of apraxic patients have linked actio ...
... subset of apraxic patients also have pantomime recognition deficits (Heilman, Rothi, & Valenstein, 1982), which has been taken as evidence for overlap in the neural systems supporting action execution and action understanding (Gallese et al., 1996). Some studies of apraxic patients have linked actio ...
Grid Cell Firing May Arise From Interference of Theta Frequency
... dynamics (Fuhs and Touretzky, 2006) cannot be derived from the constraints of this data on intrinsic oscillation frequency, and do not account for it in their present form. As shown in Figure 2, this model effectively links the frequency of mpo (Fig. 1A) to the grid cell field spacing (Hafting et al. ...
... dynamics (Fuhs and Touretzky, 2006) cannot be derived from the constraints of this data on intrinsic oscillation frequency, and do not account for it in their present form. As shown in Figure 2, this model effectively links the frequency of mpo (Fig. 1A) to the grid cell field spacing (Hafting et al. ...
HIERARCHICAL MODELS OF VARIANCE SOURCES Harri Valpola
... The additive Gaussian noise terms n(t) and m(t) are structure was as in Fig. 1(a). The sources were iniallowed to have non-zero bias. The model structure is tialised using PCA components calculated from the shown in Fig. 1(c). Note that it makes sense to have data. If the source model had dynamics, ...
... The additive Gaussian noise terms n(t) and m(t) are structure was as in Fig. 1(a). The sources were iniallowed to have non-zero bias. The model structure is tialised using PCA components calculated from the shown in Fig. 1(c). Note that it makes sense to have data. If the source model had dynamics, ...
AN INTEGRATIVE THEORY OF LOCUS
... system plays a more complex and specific role in the control of behavior than investigators previously thought. We review neurophysiological and modeling studies in monkey that support a new theory of LC-NE function. LC neurons exhibit two modes of activity, phasic and tonic. Phasic LC activation is ...
... system plays a more complex and specific role in the control of behavior than investigators previously thought. We review neurophysiological and modeling studies in monkey that support a new theory of LC-NE function. LC neurons exhibit two modes of activity, phasic and tonic. Phasic LC activation is ...
Table of Contents
... the membrane. Nevertheless, this depolarization still inhibits muscle contraction because the increase in chloride conductance creates a 'current shunt' for excitatory currents (Kuffler and Eyzaguirre, 1955). Specifically, the abundance of open chloride channels clamps the membrane voltage at the ch ...
... the membrane. Nevertheless, this depolarization still inhibits muscle contraction because the increase in chloride conductance creates a 'current shunt' for excitatory currents (Kuffler and Eyzaguirre, 1955). Specifically, the abundance of open chloride channels clamps the membrane voltage at the ch ...
Synaptic gating

Synaptic gating is the ability of neural circuits to gate inputs by either suppressing or facilitating specific synaptic activity. Selective inhibition of certain synapses has been studied thoroughly (see Gate theory of pain), and recent studies have supported the existence of permissively gated synaptic transmission. In general, synaptic gating involves a mechanism of central control over neuronal output. It includes a sort of gatekeeper neuron, which has the ability to influence transmission of information to selected targets independently of the parts of the synapse upon which it exerts its action (see also neuromodulation).Bistable neurons have the ability to oscillate between a hyperpolarized (down state) and a depolarized (up state) resting membrane potential without firing an action potential. These neurons can thus be referred to as up/down neurons. According to one model, this ability is linked to the presence of NMDA and AMPA glutamate receptors. External stimulation of the NMDA receptors is responsible for moving the neuron from the down state to the up state, while the stimulation of AMPA receptors allows the neuron to reach and surpass the threshold potential. Neurons that have this bistable ability have the potential to be gated because outside gatekeeper neurons can modulate the membrane potential of the gated neuron by selectively shifting them from the up state to the down state. Such mechanisms have been observed in the nucleus accumbens, with gatekeepers originating in the cortex, thalamus and basal ganglia.