Neural Oscillations
... receive only local inhibition (two spikes instead of four) – Here the timing of I spikes does not affect the range of delays over which the synchrony is stable – System in general is more tricky and can have some weird aperiodic or high frequency solutions – On the other hand non-homogeneous network ...
... receive only local inhibition (two spikes instead of four) – Here the timing of I spikes does not affect the range of delays over which the synchrony is stable – System in general is more tricky and can have some weird aperiodic or high frequency solutions – On the other hand non-homogeneous network ...
Artificial Neural Networks - University of Northampton
... pointed out that training to a low error can sometimes cause “overfitting”, where the network performs well on the training data but poorly on the test data The alternative is to divide the data into three sets, the extra one being the validation set ...
... pointed out that training to a low error can sometimes cause “overfitting”, where the network performs well on the training data but poorly on the test data The alternative is to divide the data into three sets, the extra one being the validation set ...
Realizing Biological Spiking Network Models in a Configurable
... the choice for having more vertical than horizontal lanes becomes apparent. Each signal occupies only one horizontal lane but many vertical ones. In the examples shown later, the condition of convex connection areas is always met since the networks are either fully connected (every chip is connected ...
... the choice for having more vertical than horizontal lanes becomes apparent. Each signal occupies only one horizontal lane but many vertical ones. In the examples shown later, the condition of convex connection areas is always met since the networks are either fully connected (every chip is connected ...
State-Dependent Computation Using Coupled Recurrent Networks
... receives excitatory inputs from its neighboring units as well as an inhibitory input that is proportional to the total activity of all units (Dayan & Abbott, 2001; Douglas & Martin, 2007). We use the term map to indicate that the elements of the WTA network are not functionally independent. Rather, ...
... receives excitatory inputs from its neighboring units as well as an inhibitory input that is proportional to the total activity of all units (Dayan & Abbott, 2001; Douglas & Martin, 2007). We use the term map to indicate that the elements of the WTA network are not functionally independent. Rather, ...
Lemniscal recurrent and transcortical influences on
... dorsal column fibers at cervical levels.8. and 39. The primary afferents terminate mostly within the clusters zone32 or cellular bricks8 where lemniscal-projecting neurons predominate.21., 27. and 32. The local neurons of this region have larger and more proximal cutaneous receptive fields than the ...
... dorsal column fibers at cervical levels.8. and 39. The primary afferents terminate mostly within the clusters zone32 or cellular bricks8 where lemniscal-projecting neurons predominate.21., 27. and 32. The local neurons of this region have larger and more proximal cutaneous receptive fields than the ...
PowerPoint-Präsentation
... in the sum for the net input The network will correct errors and so the pattern is an attractor All starting configurations with more than half the bits different from the original pattern will end up in the reversed state - i , which leaves to a symmetrically divided configuration spaces into two ...
... in the sum for the net input The network will correct errors and so the pattern is an attractor All starting configurations with more than half the bits different from the original pattern will end up in the reversed state - i , which leaves to a symmetrically divided configuration spaces into two ...
NT Notes
... you will have a reference sheet to look at while you do your WS. This is a class set so please do not take them with you. It is also available on the webpage along with this powerpoint. ...
... you will have a reference sheet to look at while you do your WS. This is a class set so please do not take them with you. It is also available on the webpage along with this powerpoint. ...
- Stem-cell and Brain Research Institute
... encode both the spatial (retinotopic) location of sequence elements, and their context or rank in the sequence. This suggested that recurrent connections in the cortex could allow neural activity related to previous sequence elements to influence the coding of the current element, thus yielding the ...
... encode both the spatial (retinotopic) location of sequence elements, and their context or rank in the sequence. This suggested that recurrent connections in the cortex could allow neural activity related to previous sequence elements to influence the coding of the current element, thus yielding the ...
Self-Organizing Feature Maps with Lateral Connections: Modeling
... the cortex, and thereby help form dynamic representations of coherent input areas [16]; (3) by learning correlations in input during development, they can potentially form long-term representations of input regularities such as gestalt rules [19]; and (4) by combining such representations with input ...
... the cortex, and thereby help form dynamic representations of coherent input areas [16]; (3) by learning correlations in input during development, they can potentially form long-term representations of input regularities such as gestalt rules [19]; and (4) by combining such representations with input ...
5-Autonomic Nervous System
... The sympathetic & parasympathetic division are made up of 2 parts: preganglia and postpanglia with the ganglion being the part that connects them. ...
... The sympathetic & parasympathetic division are made up of 2 parts: preganglia and postpanglia with the ganglion being the part that connects them. ...
THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM
... potassium ions to rush out of the neuron. The potassium ions, which have a positive charge as well, create a negatively charged cell interior by their absence. This event stops the depolarization process. The sodium ions are pumped more slowly to the cell exterior by active transport, resulting in t ...
... potassium ions to rush out of the neuron. The potassium ions, which have a positive charge as well, create a negatively charged cell interior by their absence. This event stops the depolarization process. The sodium ions are pumped more slowly to the cell exterior by active transport, resulting in t ...
Physiology Ch 55 p667-678 [4-25
... -a few fibers DON’T cross and end up passing ipsilaterally through ventral corticospinal tracts -most of these fibers cross in neck or thoracic region (control bilateral posture) -largest fibers in corticospinal tract are large, myelinated fibers with 16um diameter, originate from giant pyramidal ce ...
... -a few fibers DON’T cross and end up passing ipsilaterally through ventral corticospinal tracts -most of these fibers cross in neck or thoracic region (control bilateral posture) -largest fibers in corticospinal tract are large, myelinated fibers with 16um diameter, originate from giant pyramidal ce ...
Kaan Yücel M.D., Ph.D. http://fhs122.org
... postsynaptic neuron. The space between these two structures is called the synaptic cleft. Another feature of this neuronal connection is the presynaptic terminal. Most of the time, the signal is transmitted from one neuron to another via neurotransmitters. Rarely, the connection is electrical. Popul ...
... postsynaptic neuron. The space between these two structures is called the synaptic cleft. Another feature of this neuronal connection is the presynaptic terminal. Most of the time, the signal is transmitted from one neuron to another via neurotransmitters. Rarely, the connection is electrical. Popul ...
Wider Than the Sky: The Phenomenal Gift of Consciousness
... chemistry underlying neuronal activity. All this will be necessary to confront a number of critical questions and principles: Is the brain a computer? How is it built during development? How complex are its transactions? Are there new principles of organization unique to the brain that were selected ...
... chemistry underlying neuronal activity. All this will be necessary to confront a number of critical questions and principles: Is the brain a computer? How is it built during development? How complex are its transactions? Are there new principles of organization unique to the brain that were selected ...
Slide 1
... (depicted in tracings on the right). Postulated inhibitory connections are shown as red circles; postulated excitatory connections as green circles; and cholinergic pontine nuclei are shown as blue circles. It should be noted that the actual synaptic signs of many of the aminergic and reticular path ...
... (depicted in tracings on the right). Postulated inhibitory connections are shown as red circles; postulated excitatory connections as green circles; and cholinergic pontine nuclei are shown as blue circles. It should be noted that the actual synaptic signs of many of the aminergic and reticular path ...
decision-making in the primate brain
... Once this is learned, the same stimuli are subsequently paired with two novel stimuli (X and Y), and, in this second stage of the experiment, the joint stimuli AX and BY are both paired with rewards. If learning were merely associative, the subject would respond to both novel stimuli X and Y as if t ...
... Once this is learned, the same stimuli are subsequently paired with two novel stimuli (X and Y), and, in this second stage of the experiment, the joint stimuli AX and BY are both paired with rewards. If learning were merely associative, the subject would respond to both novel stimuli X and Y as if t ...
Study Guides/Part_4
... Strabismus: misalignment of the visual axis with respect to an object causes the two images of the object to fall on non-corresponding area of the retina---disparity Problem is when subject, even with actively “fixating” an object, fails to align both foveas on it Ambylopia: reduced vision in an eye ...
... Strabismus: misalignment of the visual axis with respect to an object causes the two images of the object to fall on non-corresponding area of the retina---disparity Problem is when subject, even with actively “fixating” an object, fails to align both foveas on it Ambylopia: reduced vision in an eye ...
Spinal nerves 1
... • basic unit of nervous tissue • receive, process and transmit signals • size: from 5 µm (granular cells of cerebellum) to 150 µm (Purkinje cells of cerebellum) • some can multiply even after birth • synapsis interconnects neurons ...
... • basic unit of nervous tissue • receive, process and transmit signals • size: from 5 µm (granular cells of cerebellum) to 150 µm (Purkinje cells of cerebellum) • some can multiply even after birth • synapsis interconnects neurons ...
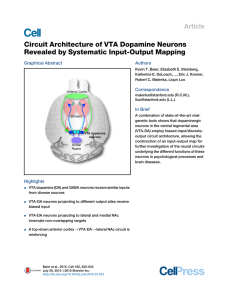
Circuit Architecture of VTA Dopamine Neurons Revealed by
... glycoprotein (G), were injected into the VTA of these mice (Figure 1A) (Miyamichi et al., 2013). Two weeks later, we injected EnvA-pseudotyped, G-deleted, and GFP-expressing rabies virus (RVdG). RVdG could only infect TC-expressing mammalian cells due to the EnvA pseudotype. Co-expression of G enabl ...
... glycoprotein (G), were injected into the VTA of these mice (Figure 1A) (Miyamichi et al., 2013). Two weeks later, we injected EnvA-pseudotyped, G-deleted, and GFP-expressing rabies virus (RVdG). RVdG could only infect TC-expressing mammalian cells due to the EnvA pseudotype. Co-expression of G enabl ...
Decision Making in Recurrent Neuronal Circuits
... this computational perspective. The focus will be on basic computations: (1) accumulation of evidence (what is the cellular basis of temporal accumulation of information?), (2) formation of a categorical choice (what is the termination rule for a deliberation process in neuronal terms?); (3) reward- ...
... this computational perspective. The focus will be on basic computations: (1) accumulation of evidence (what is the cellular basis of temporal accumulation of information?), (2) formation of a categorical choice (what is the termination rule for a deliberation process in neuronal terms?); (3) reward- ...
Homework 12
... 10. Ahad Israfil lost the right side of his brain as a result of an accidental gun discharge at the age of 14 and was able to graduate a university. What would be your prediction on Ahad’s future accomplishments, if Ahad was to lose his left hemisphere? ...
... 10. Ahad Israfil lost the right side of his brain as a result of an accidental gun discharge at the age of 14 and was able to graduate a university. What would be your prediction on Ahad’s future accomplishments, if Ahad was to lose his left hemisphere? ...
PPT2
... The processes for computing the region and the boundary are tightly coupled The regional properties diffuse within each region and tend to become constant The interruption of the spreading of regional information by boundaries results in sharp discontinuities in the responses across two different re ...
... The processes for computing the region and the boundary are tightly coupled The regional properties diffuse within each region and tend to become constant The interruption of the spreading of regional information by boundaries results in sharp discontinuities in the responses across two different re ...
CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM Sensory Pathway (PNS
... coordination and locomotor ability spatial perception ...
... coordination and locomotor ability spatial perception ...
Afferents of dopamine neurons
... Bevan, Booth, Eaton, and Bolam. (1998) J. Neurosci. 18: 9438-9452 Sadek, Magill and Bolam unpublished ...
... Bevan, Booth, Eaton, and Bolam. (1998) J. Neurosci. 18: 9438-9452 Sadek, Magill and Bolam unpublished ...
moth`s nervous system - Wageningen UR E
... £10,£12,Z14-16:AL input channel and do not respond differently when the complete, natural blend is presented to the antenna. These cells may therefore be involved in mediating general arousal in response to sex pheromone but apparently do not contribute to species recognition. In contrast, we refer ...
... £10,£12,Z14-16:AL input channel and do not respond differently when the complete, natural blend is presented to the antenna. These cells may therefore be involved in mediating general arousal in response to sex pheromone but apparently do not contribute to species recognition. In contrast, we refer ...
Synaptic gating

Synaptic gating is the ability of neural circuits to gate inputs by either suppressing or facilitating specific synaptic activity. Selective inhibition of certain synapses has been studied thoroughly (see Gate theory of pain), and recent studies have supported the existence of permissively gated synaptic transmission. In general, synaptic gating involves a mechanism of central control over neuronal output. It includes a sort of gatekeeper neuron, which has the ability to influence transmission of information to selected targets independently of the parts of the synapse upon which it exerts its action (see also neuromodulation).Bistable neurons have the ability to oscillate between a hyperpolarized (down state) and a depolarized (up state) resting membrane potential without firing an action potential. These neurons can thus be referred to as up/down neurons. According to one model, this ability is linked to the presence of NMDA and AMPA glutamate receptors. External stimulation of the NMDA receptors is responsible for moving the neuron from the down state to the up state, while the stimulation of AMPA receptors allows the neuron to reach and surpass the threshold potential. Neurons that have this bistable ability have the potential to be gated because outside gatekeeper neurons can modulate the membrane potential of the gated neuron by selectively shifting them from the up state to the down state. Such mechanisms have been observed in the nucleus accumbens, with gatekeepers originating in the cortex, thalamus and basal ganglia.