Neurons
... • Nerves—cablelike organs in the PNS • Consists of numerous axons wrapped in connective ...
... • Nerves—cablelike organs in the PNS • Consists of numerous axons wrapped in connective ...
prenatal formation of cortical input and development of
... observations). Thus, at least the earlier generated layer 5 neurons have had ample time to migrate to the cortex and to elaborate efferent axons that reach the nearby neostriaturn. Our findings are also in general agreement with the timing of development of efferent subcortical connections from the ...
... observations). Thus, at least the earlier generated layer 5 neurons have had ample time to migrate to the cortex and to elaborate efferent axons that reach the nearby neostriaturn. Our findings are also in general agreement with the timing of development of efferent subcortical connections from the ...
Neuroscience of Addiction Review
... The neuronal interaction responsible for cocaine reinforcement and the motivation to seek the drug appears to reside within the nucleus accumbens (Chang et al., 1994; Carelli and Deadwyler, 1996; Peoples et al., 1997). Electrophysiological recordings in animals receiving intravenous cocaine by self- ...
... The neuronal interaction responsible for cocaine reinforcement and the motivation to seek the drug appears to reside within the nucleus accumbens (Chang et al., 1994; Carelli and Deadwyler, 1996; Peoples et al., 1997). Electrophysiological recordings in animals receiving intravenous cocaine by self- ...
The Cerebellum Anatomically consists of two hemispheres and
... A.Afferent from other parts of brain: 1.From cerebral cortex through the corticosponto cerebellar pathway, the largest source of Mossy fibers which transmit information about muscle movements planned by cortex. 2.From olivary nucleus through olivocerebellar tract. From vestibular apparatus or from b ...
... A.Afferent from other parts of brain: 1.From cerebral cortex through the corticosponto cerebellar pathway, the largest source of Mossy fibers which transmit information about muscle movements planned by cortex. 2.From olivary nucleus through olivocerebellar tract. From vestibular apparatus or from b ...
Cerebellar Unit Activity and the Movement Disruption Induced by
... Sixteen male albino rats of the Wistar strain, about 3 months old, were reduced to 85 % of original body weight (200—250 g) and trained to reach for 20 mg pellets of Larsen's diet into a narrow (11 mm internal diameter) horizontal feeder attached to the front wall of a plexiglass chamber (Megirian e ...
... Sixteen male albino rats of the Wistar strain, about 3 months old, were reduced to 85 % of original body weight (200—250 g) and trained to reach for 20 mg pellets of Larsen's diet into a narrow (11 mm internal diameter) horizontal feeder attached to the front wall of a plexiglass chamber (Megirian e ...
Morphological Identification of Cell Death in Dorsal Root Ganglion
... neurons after the surgical repair of their peripheral processes. Methods: Animals (male Wistar rats) were exposed to models of sciatic nerve transection, direct epineurial suture repair of sciatic nerve, autograft repair of sciatic nerve, and sham operated. After 1 and 12 weeks of the surgery, the n ...
... neurons after the surgical repair of their peripheral processes. Methods: Animals (male Wistar rats) were exposed to models of sciatic nerve transection, direct epineurial suture repair of sciatic nerve, autograft repair of sciatic nerve, and sham operated. After 1 and 12 weeks of the surgery, the n ...
Viral vector-based tools advance knowledge of basal ganglia
... glutamatergic input from the prefrontal cortex (PFC), hippocampus, and amygdala and dopaminergic innervation from the VTA (Russo and Nestler 2013). It also receives serotonergic input from the dorsal raphe and noradrenergic input from the locus coeruleus (Lorrain et al. 1999; Unemoto et al. 1985; Yo ...
... glutamatergic input from the prefrontal cortex (PFC), hippocampus, and amygdala and dopaminergic innervation from the VTA (Russo and Nestler 2013). It also receives serotonergic input from the dorsal raphe and noradrenergic input from the locus coeruleus (Lorrain et al. 1999; Unemoto et al. 1985; Yo ...
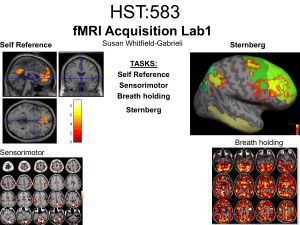
HST:583 fMRI Acquisition Lab1 Susan Whitfield
... 16-second periods of breath holding and normal breathing. During the off-block, the subject sees a green screen during which they are to breathe normally. During the last 2s of the off-block, the screen becomes yellow, signifying to the subject to take a deep breath in and hold. During the on-block ...
... 16-second periods of breath holding and normal breathing. During the off-block, the subject sees a green screen during which they are to breathe normally. During the last 2s of the off-block, the screen becomes yellow, signifying to the subject to take a deep breath in and hold. During the on-block ...
diencephalon - ugur baran kasirga web pages
... Functions of the Diencephalon • The diencephalon ("interbrain") is the region of the vertebrate neural tube that gives rise to posterior forebrain structures. • In development, the forebrain develops from the prosencephalon , the most anterior vesicle of the neural tube that later forms both the di ...
... Functions of the Diencephalon • The diencephalon ("interbrain") is the region of the vertebrate neural tube that gives rise to posterior forebrain structures. • In development, the forebrain develops from the prosencephalon , the most anterior vesicle of the neural tube that later forms both the di ...
Chapter 48
... • Opening other types of ion channels triggers a depolarization, a reduction in the magnitude of the membrane potential • For example, depolarization occurs if gated Na+ channels open and Na+ diffuses into the cell ...
... • Opening other types of ion channels triggers a depolarization, a reduction in the magnitude of the membrane potential • For example, depolarization occurs if gated Na+ channels open and Na+ diffuses into the cell ...
resting potential
... • Opening other types of ion channels triggers a depolarization, a reduction in the magnitude of the membrane potential • For example, depolarization occurs if gated Na+ channels open and Na+ diffuses into the cell ...
... • Opening other types of ion channels triggers a depolarization, a reduction in the magnitude of the membrane potential • For example, depolarization occurs if gated Na+ channels open and Na+ diffuses into the cell ...
Neural Control of Interappendage Phase During Locomotion
... network. Any given network can display one property without showing the other property. The fact that the swimmem system is both central and distributed is extremely useful and will be be discussed later in this paper. It is not possible in some preparations to isolate totally a portion of the CNS f ...
... network. Any given network can display one property without showing the other property. The fact that the swimmem system is both central and distributed is extremely useful and will be be discussed later in this paper. It is not possible in some preparations to isolate totally a portion of the CNS f ...
Autonomic Nervous System
... Normally, the sympathetic and parasympathetic systems are continually active, and the basal rates of activity are known, respectively, as sympathetic tone and parasympathetic tone. The value of tone is that it allows a single nervous system both to increase and to decrease the activity of a stimulat ...
... Normally, the sympathetic and parasympathetic systems are continually active, and the basal rates of activity are known, respectively, as sympathetic tone and parasympathetic tone. The value of tone is that it allows a single nervous system both to increase and to decrease the activity of a stimulat ...
1 Revised 10/11/2016 The Physiology of the Senses Lecture 7
... Our conscious perception of touch begins in the primary somatosensory cortex (S1). This is somatotopically organized with the body surface laid down sequentially on the postcentral gyrus. This body map is distorted with the lips, tongue and fingertips having a large representation. This distortion r ...
... Our conscious perception of touch begins in the primary somatosensory cortex (S1). This is somatotopically organized with the body surface laid down sequentially on the postcentral gyrus. This body map is distorted with the lips, tongue and fingertips having a large representation. This distortion r ...
Positive sparse coding of natural images: a theory for simple cell
... tuned to the orientation and polarity of edges in visual stimuli [1]. While orientation tuning has been the subject of intense investigation, the polarity tuning of cells is poorly understood; a simple cell responds either to a bright edge with dark flanks, or to the opposite polarity, a dark edge w ...
... tuned to the orientation and polarity of edges in visual stimuli [1]. While orientation tuning has been the subject of intense investigation, the polarity tuning of cells is poorly understood; a simple cell responds either to a bright edge with dark flanks, or to the opposite polarity, a dark edge w ...
File
... mV to more negative values? The concentration gradient of potassium causes it to leave the cell, thereby leaving a negative charge inside the cell causing the membrane to become more negative. ...
... mV to more negative values? The concentration gradient of potassium causes it to leave the cell, thereby leaving a negative charge inside the cell causing the membrane to become more negative. ...
NEUROTRANSMISSION
... have some knowledge of neurotransmission. For those learning about it for the first time, expect some difficulties in understanding it. Neurotransmission is a very difficult topic for elementary school students. Our goal is for the students to have a basic understanding of the process by the end of ...
... have some knowledge of neurotransmission. For those learning about it for the first time, expect some difficulties in understanding it. Neurotransmission is a very difficult topic for elementary school students. Our goal is for the students to have a basic understanding of the process by the end of ...
Neurons in red nucleus and primary motor cortex exhibit similar
... A recent hypothesis proposes that the volitional motor system may act like an optimal feedback controller (Todorov and Jordan, 2002; Todorov, 2004). This framework highlights the importance of afferent feedback for voluntary control of movement and predicts that feedback will be modified based on th ...
... A recent hypothesis proposes that the volitional motor system may act like an optimal feedback controller (Todorov and Jordan, 2002; Todorov, 2004). This framework highlights the importance of afferent feedback for voluntary control of movement and predicts that feedback will be modified based on th ...
development of an artificial neural network for monitoring
... A neural network is a massively parallel distributed processor made up of simple processing units, which has a natural propensity for storing experiential knowledge and making it available for use. The knowledge is acquired by the networks from its environment through a learning process which is bas ...
... A neural network is a massively parallel distributed processor made up of simple processing units, which has a natural propensity for storing experiential knowledge and making it available for use. The knowledge is acquired by the networks from its environment through a learning process which is bas ...
A Real-Time Intrusion Detection System using Artificial Neural
... analyzer. Analysis means knowing whether the packet is a TCP, SMTP, UDP, etc. This was only the type of packet. There are also many other attributes of packets such as header-length, flag, fragmentation offset, TTL value, etc. So recognizing all the incoming packets along with all their attributes i ...
... analyzer. Analysis means knowing whether the packet is a TCP, SMTP, UDP, etc. This was only the type of packet. There are also many other attributes of packets such as header-length, flag, fragmentation offset, TTL value, etc. So recognizing all the incoming packets along with all their attributes i ...
52 Nerve Tissue
... dendritic branches, usually leave the parent axon at right angles. Axons also differ in that the diameter is constant throughout most of the length and the external surface generally is smooth. Axons end in several branches called telodendria, which vary in number and shape and may form a network or ...
... dendritic branches, usually leave the parent axon at right angles. Axons also differ in that the diameter is constant throughout most of the length and the external surface generally is smooth. Axons end in several branches called telodendria, which vary in number and shape and may form a network or ...
Neural plasticity and recovery of function
... effects of lesions on rats’ across the cortex. maze learning. • The larger the amount of cortex damaged, the more errors the rats made. ...
... effects of lesions on rats’ across the cortex. maze learning. • The larger the amount of cortex damaged, the more errors the rats made. ...
PPT Lecture Slides: January 22, 2002
... • Each is a visual module – connects to other areas – operates largely independently ...
... • Each is a visual module – connects to other areas – operates largely independently ...
Synaptic gating

Synaptic gating is the ability of neural circuits to gate inputs by either suppressing or facilitating specific synaptic activity. Selective inhibition of certain synapses has been studied thoroughly (see Gate theory of pain), and recent studies have supported the existence of permissively gated synaptic transmission. In general, synaptic gating involves a mechanism of central control over neuronal output. It includes a sort of gatekeeper neuron, which has the ability to influence transmission of information to selected targets independently of the parts of the synapse upon which it exerts its action (see also neuromodulation).Bistable neurons have the ability to oscillate between a hyperpolarized (down state) and a depolarized (up state) resting membrane potential without firing an action potential. These neurons can thus be referred to as up/down neurons. According to one model, this ability is linked to the presence of NMDA and AMPA glutamate receptors. External stimulation of the NMDA receptors is responsible for moving the neuron from the down state to the up state, while the stimulation of AMPA receptors allows the neuron to reach and surpass the threshold potential. Neurons that have this bistable ability have the potential to be gated because outside gatekeeper neurons can modulate the membrane potential of the gated neuron by selectively shifting them from the up state to the down state. Such mechanisms have been observed in the nucleus accumbens, with gatekeepers originating in the cortex, thalamus and basal ganglia.