Lecture 12b - Spinal Cord
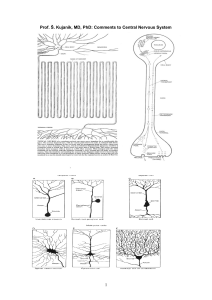
... • Gray matter is central • Thick layer of white matter covers it: – consists of ascending and descending axons – organized in columns – containing axon bundles with specific ...
... • Gray matter is central • Thick layer of white matter covers it: – consists of ascending and descending axons – organized in columns – containing axon bundles with specific ...
Lecture notes for October 9, 2015 FINAL
... The three major sensory tracts involve chains of neurons o First-order neuron Delivers sensations to the CNS The cell body is in the dorsal or cranial root ganglion o Second-order neuron An interneuron with the cell body in the spinal cord or brain o Third-order neuron Transmits information ...
... The three major sensory tracts involve chains of neurons o First-order neuron Delivers sensations to the CNS The cell body is in the dorsal or cranial root ganglion o Second-order neuron An interneuron with the cell body in the spinal cord or brain o Third-order neuron Transmits information ...
Lecture 12b - Spinal Cord
... • Gray matter is central • Thick layer of white matter covers it: – consists of ascending and descending axons – organized in columns – containing axon bundles with specific ...
... • Gray matter is central • Thick layer of white matter covers it: – consists of ascending and descending axons – organized in columns – containing axon bundles with specific ...
RL 19 - School of Informatics
... motivate a person to perform certain activities. It is released (particularly in areas such as the nucleus accumbens and prefrontal cortex) by rewarding experiences such as food, sex, drugs, and neutral stimuli that become associated with them Dopamine is closely associated with reward-seeking behav ...
... motivate a person to perform certain activities. It is released (particularly in areas such as the nucleus accumbens and prefrontal cortex) by rewarding experiences such as food, sex, drugs, and neutral stimuli that become associated with them Dopamine is closely associated with reward-seeking behav ...
Structural changes that occur during normal aging of primate
... pyramidal neurons. Also, large neurons have more lipofuscin than smaller ones, but this is not a rule, so that among the larger cortical neurons, the Meynert cells of visual cortex [27] come to contain little age pigment, while the Betz cells of motor cortex can become so full of pigment that their ...
... pyramidal neurons. Also, large neurons have more lipofuscin than smaller ones, but this is not a rule, so that among the larger cortical neurons, the Meynert cells of visual cortex [27] come to contain little age pigment, while the Betz cells of motor cortex can become so full of pigment that their ...
Sensory feedback for upper limb prostheses
... objects begin to slip in the hand, and provide sensory feedback to the user about increasing grip force. Clearly, this afferent system is important if the prosthesis is to be used to grasp and lift objects without crushing or dropping them. Under normal circumstances, the skin is densely innervated ...
... objects begin to slip in the hand, and provide sensory feedback to the user about increasing grip force. Clearly, this afferent system is important if the prosthesis is to be used to grasp and lift objects without crushing or dropping them. Under normal circumstances, the skin is densely innervated ...
A neuropsychological theory of metaphor
... 2. Comparison. A metaphor is a condensed statement of a similarity or analogy. The utterance of The lion roared in response to a query regarding the bossÕs mood would involve comparing the bossÕs display of anger to a lionÕs roaring. Some theories involve the transfer or cancellation of incompatible ...
... 2. Comparison. A metaphor is a condensed statement of a similarity or analogy. The utterance of The lion roared in response to a query regarding the bossÕs mood would involve comparing the bossÕs display of anger to a lionÕs roaring. Some theories involve the transfer or cancellation of incompatible ...
Proposal - people.vcu.edu
... and in vangl mutant zebrafish, suggesting the two are involved in the same signaling pathway, PCP (Lu et al 2004). PTK-7 is a single polypeptide chain with one transmembrane domain. The extracellular domain is composed of several immunoglobulin like domains. The transmembrane domain is a combinatio ...
... and in vangl mutant zebrafish, suggesting the two are involved in the same signaling pathway, PCP (Lu et al 2004). PTK-7 is a single polypeptide chain with one transmembrane domain. The extracellular domain is composed of several immunoglobulin like domains. The transmembrane domain is a combinatio ...
Athletic Injuries ATC 222
... direct pressure on nostril cotton/gauze plug refrain from nose blowing for 2 hours ...
... direct pressure on nostril cotton/gauze plug refrain from nose blowing for 2 hours ...
Chapter 11 PowerPoint - Hillsborough Community College
... – Each cell can wrap up to 60 axons at once – Myelin sheath gap is present – No outer collar of perinuclear cytoplasm – Thinnest fibers are unmyelinated, but covered by long extensions of adjacent neuroglia ...
... – Each cell can wrap up to 60 axons at once – Myelin sheath gap is present – No outer collar of perinuclear cytoplasm – Thinnest fibers are unmyelinated, but covered by long extensions of adjacent neuroglia ...
Document
... Ex: Sensory neurons: When I touch boiling water my sense of touch will transmit a signal to my brain. My interneurons receive the signal and process that the water is hot. My motor neurons allow me to move my hand away from the water. ...
... Ex: Sensory neurons: When I touch boiling water my sense of touch will transmit a signal to my brain. My interneurons receive the signal and process that the water is hot. My motor neurons allow me to move my hand away from the water. ...
INTERNEURONS OF THE NEOCORTICAL INHIBITORY SYSTEM
... axon commonly emerges from one of the primary dendrites and forms a narrow (<50 µm) band that crosses all layers (see online supplementary information S1 (table)). Bipolar neurons can be excitatory by releasing only VIP, or inhibitory by releasing mainly GABA (inhibitory BPCs also express VIP). Thei ...
... axon commonly emerges from one of the primary dendrites and forms a narrow (<50 µm) band that crosses all layers (see online supplementary information S1 (table)). Bipolar neurons can be excitatory by releasing only VIP, or inhibitory by releasing mainly GABA (inhibitory BPCs also express VIP). Thei ...
chapt14_HumanBiology14e_lecture
... Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. ...
... Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. ...
Cerebral Cortex
... mainly on different levels of the soma-dendritic membranes of other cells. The collaterals of pyramidal cell axons tend to be preferentially distributed to certain layers depending on the target of the principal axon of the pyramidal cell. Most output cells, seem to be affected monosynaptically by s ...
... mainly on different levels of the soma-dendritic membranes of other cells. The collaterals of pyramidal cell axons tend to be preferentially distributed to certain layers depending on the target of the principal axon of the pyramidal cell. Most output cells, seem to be affected monosynaptically by s ...
Ramayya, A. G., Zaghloul, K. A., Weidemann, C. T., Baltuch, G. H.
... activity using the WaveClus software package (Quiroga et al., 2005). We band-pass filtered each voltage recording from 400 to 5000 Hz and manually removed periods of motion artifact. We identified spike events as positive or negative deflections in the voltage trace that crossed a threshold that was ...
... activity using the WaveClus software package (Quiroga et al., 2005). We band-pass filtered each voltage recording from 400 to 5000 Hz and manually removed periods of motion artifact. We identified spike events as positive or negative deflections in the voltage trace that crossed a threshold that was ...
Progress Report – Glover
... Søviknes has also carried out a systematic assessment of neurogenesis in the entire central nervous system using timed applications of the thymidine analog BrdU. Through this work, we now know when neurons are born in the different parts of the nervous system, important information for future experi ...
... Søviknes has also carried out a systematic assessment of neurogenesis in the entire central nervous system using timed applications of the thymidine analog BrdU. Through this work, we now know when neurons are born in the different parts of the nervous system, important information for future experi ...
Insights from models of rhythmic motor systems
... Not intrinsically bursting neurons: Neurons that do not generate bursts of action potentials when isolated from synaptic inputs. Open-loop system: In an open-loop system, the flow of information is unidirectional, that is, from component A to component B without feedback from B to A. In an open-loop ...
... Not intrinsically bursting neurons: Neurons that do not generate bursts of action potentials when isolated from synaptic inputs. Open-loop system: In an open-loop system, the flow of information is unidirectional, that is, from component A to component B without feedback from B to A. In an open-loop ...
Short-Term Synaptic Plasticity Orchestrates the Response of Pyramidal
... provide a feature upon which the relative timing of activity between cell classes can be examined. The neurons examined in Silberberg et al. (2004) were classified by the dynamics of the synapse received from the bursting layer V pyramidal population and comprised: layer V pyramidal cells receiving ...
... provide a feature upon which the relative timing of activity between cell classes can be examined. The neurons examined in Silberberg et al. (2004) were classified by the dynamics of the synapse received from the bursting layer V pyramidal population and comprised: layer V pyramidal cells receiving ...
Study materials CNS
... 1. ASCENDING (ACTIVATING) SYSTEM OF RF (RAS) is activated by collaterals of the specific long sensory pathways. Input to the RF network without somatotopic localization produces loss of modality specificity => nonspecific system. So RAS bypasses the specific thalamic nuclei to project diffusely into ...
... 1. ASCENDING (ACTIVATING) SYSTEM OF RF (RAS) is activated by collaterals of the specific long sensory pathways. Input to the RF network without somatotopic localization produces loss of modality specificity => nonspecific system. So RAS bypasses the specific thalamic nuclei to project diffusely into ...
Newsletter CSN Info April `16
... The paper present a multi-scale spiking network model of all vision-related areas of macaque cortex that represents each area by a full-scale microcircuit with area-specific architecture. The layer- and population-resolved network connectivity integrates axonal tracing data from the CoCoMac database ...
... The paper present a multi-scale spiking network model of all vision-related areas of macaque cortex that represents each area by a full-scale microcircuit with area-specific architecture. The layer- and population-resolved network connectivity integrates axonal tracing data from the CoCoMac database ...
From view cells and place cells to cognitive map learning
... from the frontal or hippocampal de®cits in that there is no additional memory de®cit after PPC lesions. From the anatomical data, it is not possible to say that complex object recognition cannot be used for navigation, but the ablation of the Te2 region does not perturbate navigation tasks like thos ...
... from the frontal or hippocampal de®cits in that there is no additional memory de®cit after PPC lesions. From the anatomical data, it is not possible to say that complex object recognition cannot be used for navigation, but the ablation of the Te2 region does not perturbate navigation tasks like thos ...
Tourette - neuro - neuropsych
... motor association cortex) Mesolimbic: deals with the ventral striatum, olfactory tubercle and parts of the limbic system Tuberinfundibular: involved in parts of the brain that deal with stress ...
... motor association cortex) Mesolimbic: deals with the ventral striatum, olfactory tubercle and parts of the limbic system Tuberinfundibular: involved in parts of the brain that deal with stress ...
Reading Part 5: The Nervous System
... causes a ligand or mechanically gated channel to open or close. Depending on the type of ion channel opened, the membrane can become more negative (hyperpolarized) or more positive (depolarized). ...
... causes a ligand or mechanically gated channel to open or close. Depending on the type of ion channel opened, the membrane can become more negative (hyperpolarized) or more positive (depolarized). ...
Chapter 2
... (−70 mV) with respect to the outside when the neuron is not conducting a signal. This resting membrane potential opposes the outward diffusion of K⫹ and the inward diffusion of Cl⫺ because unlike charges attract and like charges repel one another. The membrane is much less permeable to Na⫹ because t ...
... (−70 mV) with respect to the outside when the neuron is not conducting a signal. This resting membrane potential opposes the outward diffusion of K⫹ and the inward diffusion of Cl⫺ because unlike charges attract and like charges repel one another. The membrane is much less permeable to Na⫹ because t ...
What is brain dynamics - Brain Dynamics Laboratory
... with nonlinear coupling interactions between neuronal populations. • Nonlinear deterministic systems may show a sensitive dependence on initial conditions, implying that different states of a system, being arbitrarily close initially, can become exponentially separated in sufficiently long times. Th ...
... with nonlinear coupling interactions between neuronal populations. • Nonlinear deterministic systems may show a sensitive dependence on initial conditions, implying that different states of a system, being arbitrarily close initially, can become exponentially separated in sufficiently long times. Th ...
Synaptic gating

Synaptic gating is the ability of neural circuits to gate inputs by either suppressing or facilitating specific synaptic activity. Selective inhibition of certain synapses has been studied thoroughly (see Gate theory of pain), and recent studies have supported the existence of permissively gated synaptic transmission. In general, synaptic gating involves a mechanism of central control over neuronal output. It includes a sort of gatekeeper neuron, which has the ability to influence transmission of information to selected targets independently of the parts of the synapse upon which it exerts its action (see also neuromodulation).Bistable neurons have the ability to oscillate between a hyperpolarized (down state) and a depolarized (up state) resting membrane potential without firing an action potential. These neurons can thus be referred to as up/down neurons. According to one model, this ability is linked to the presence of NMDA and AMPA glutamate receptors. External stimulation of the NMDA receptors is responsible for moving the neuron from the down state to the up state, while the stimulation of AMPA receptors allows the neuron to reach and surpass the threshold potential. Neurons that have this bistable ability have the potential to be gated because outside gatekeeper neurons can modulate the membrane potential of the gated neuron by selectively shifting them from the up state to the down state. Such mechanisms have been observed in the nucleus accumbens, with gatekeepers originating in the cortex, thalamus and basal ganglia.