neural representation and the cortical code
... perceptual discrimination of visual motion, these might be two neurons in the middle temporal cortical area (MT), an area believed to be involved in the representation of visual motion. The response properties of these two neurons to stimuli are identical by construction, yet neuron B2 has no axon a ...
... perceptual discrimination of visual motion, these might be two neurons in the middle temporal cortical area (MT), an area believed to be involved in the representation of visual motion. The response properties of these two neurons to stimuli are identical by construction, yet neuron B2 has no axon a ...
Attractor concretion as a mechanism for the formation of context
... defined by the elevated probability of the transitions between CS APunishment and CS B-Reward. The animal observes rarely that CS AReward is followed by CS B-Reward or CS A-Punishment. In other words, if we look at the matrix of transitions between these sequences, we can clearly identify two cluster ...
... defined by the elevated probability of the transitions between CS APunishment and CS B-Reward. The animal observes rarely that CS AReward is followed by CS B-Reward or CS A-Punishment. In other words, if we look at the matrix of transitions between these sequences, we can clearly identify two cluster ...
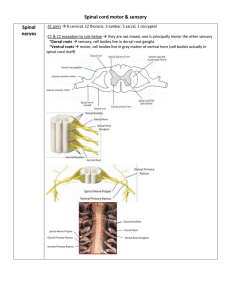
Changes in spinal cord
... *tectum is associated with visual movements also- coordination of muscle with visual input? ...
... *tectum is associated with visual movements also- coordination of muscle with visual input? ...
Document
... • Synaptic transmission and neural coding – All-or-none law – a neuron is either firing action potential, or not, so how can the nervous system code for/represent complexity of experience? – Power of nervous system lies in the complexity of the connections between neurons – Lock-and-key action – the ...
... • Synaptic transmission and neural coding – All-or-none law – a neuron is either firing action potential, or not, so how can the nervous system code for/represent complexity of experience? – Power of nervous system lies in the complexity of the connections between neurons – Lock-and-key action – the ...
The organization of the cortical motor system: new concepts
... cortical convexity, F5c). Functional data confirm this morphological subdivision. Each of the 3 subdivisions of inferior area 6 is part of a different parieto-frontal circuit. The properties of the 3 circuits will be dealt with separately in the sections below. 6.1. The VIP-F4 circuit Area VIP occup ...
... cortical convexity, F5c). Functional data confirm this morphological subdivision. Each of the 3 subdivisions of inferior area 6 is part of a different parieto-frontal circuit. The properties of the 3 circuits will be dealt with separately in the sections below. 6.1. The VIP-F4 circuit Area VIP occup ...
Multilayer neural networks
... network simultaneously throughout the whole network, rather than at specific locations. In other words, in neural networks, both data and its processing are global rather than local. Learning is a fundamental and essential characteristic of biological neural networks. The ease with which they can ...
... network simultaneously throughout the whole network, rather than at specific locations. In other words, in neural networks, both data and its processing are global rather than local. Learning is a fundamental and essential characteristic of biological neural networks. The ease with which they can ...
Lecture CH18 chem131pikul partA
... transmits nerve impulses from one neuron to another. •The space between the two neurons is called a synapse. •The presynaptic neuron releases the neurotransmitter. ...
... transmits nerve impulses from one neuron to another. •The space between the two neurons is called a synapse. •The presynaptic neuron releases the neurotransmitter. ...
PDF
... inconsistencies between successive estimates of these values along sample trajectories. These values, sometimes called cached values because of the way they store experience, encompass all future probabilistic transitions and rewards in a single scalar number that denotes the overall future worth of ...
... inconsistencies between successive estimates of these values along sample trajectories. These values, sometimes called cached values because of the way they store experience, encompass all future probabilistic transitions and rewards in a single scalar number that denotes the overall future worth of ...
Autonomic Nervous System
... parasympathetic ganglia for the heart ,lungs, intestines, and bladder? What is the parasympathetic role in cutaneous functions? How do sympathetic axons get to the heart & lungs? ...
... parasympathetic ganglia for the heart ,lungs, intestines, and bladder? What is the parasympathetic role in cutaneous functions? How do sympathetic axons get to the heart & lungs? ...
ImageSurfer: Visualization of Dendritic Spines
... Neurons transmit information using electrochemical reactions. When a neuron fires, it sends an electrical impulse down a long arm-like structure called an axon. At the end of the axon the impulse sets off a chemical transfer. The chemicals diffuse across a gap to dendrites, on neighboring receiver n ...
... Neurons transmit information using electrochemical reactions. When a neuron fires, it sends an electrical impulse down a long arm-like structure called an axon. At the end of the axon the impulse sets off a chemical transfer. The chemicals diffuse across a gap to dendrites, on neighboring receiver n ...
Introduction to Psychology, 7th Edition, Rod
... – axon membrane has chemical gates that can open to allow electrically charged particles to enter or can close to keep out these particles – ions are chemical particles that have electrical charges – opposite charges attract and like charges repel ...
... – axon membrane has chemical gates that can open to allow electrically charged particles to enter or can close to keep out these particles – ions are chemical particles that have electrical charges – opposite charges attract and like charges repel ...
The neural basis of the speed–accuracy tradeoff - Eric
... fast and stimulus onset. Under the assumption that the observed BOLD signal in these areas is produced by the activity of integrator neurons, the data from these three fMRI studies suggest that speed instructions increase the baseline activity of these neurons. We are not aware of any neurophysiolog ...
... fast and stimulus onset. Under the assumption that the observed BOLD signal in these areas is produced by the activity of integrator neurons, the data from these three fMRI studies suggest that speed instructions increase the baseline activity of these neurons. We are not aware of any neurophysiolog ...
On the Role of the Pontine Brainstem in Vocal Pattern Generation: A
... firing was related to call patterns (Hage and Jürgens, 2006). The question of how VOC controls cranial motoneuron pools involved in FM vocalizations was left open in that study. In the present study, we compared neuronal activities of vocalization-correlated neurons (VM neurons) from VOC with those ...
... firing was related to call patterns (Hage and Jürgens, 2006). The question of how VOC controls cranial motoneuron pools involved in FM vocalizations was left open in that study. In the present study, we compared neuronal activities of vocalization-correlated neurons (VM neurons) from VOC with those ...
PDF
... have a variety of shapes and sizes. Ocular dominance columns, one of the textbook examples of columnar organization, are actually slab-like domains; and column width is variable as a function of the visual field; that is, larger in the foveal representation. In the peripheral visual field representa ...
... have a variety of shapes and sizes. Ocular dominance columns, one of the textbook examples of columnar organization, are actually slab-like domains; and column width is variable as a function of the visual field; that is, larger in the foveal representation. In the peripheral visual field representa ...
Chapter 13
... Motor neuron- impulses triggered by integration center propagate out of CNS motor neuron body part that responds: Effector- if skeletal muscle= somatic reflex, if smooth, cardiac muscle or gland=autonomic ...
... Motor neuron- impulses triggered by integration center propagate out of CNS motor neuron body part that responds: Effector- if skeletal muscle= somatic reflex, if smooth, cardiac muscle or gland=autonomic ...
Chapter 1
... Winter effect? • More schizophrenics are born during the winter and spring than during any other time of the year. • Infants born between January and May – Experienced second trimester of prenatal development in the fall or ...
... Winter effect? • More schizophrenics are born during the winter and spring than during any other time of the year. • Infants born between January and May – Experienced second trimester of prenatal development in the fall or ...
Electrophysiological evidence that noradrenergic neurons of the rat
... (plateau). The firing rate of the neurons during the effect was measured during the plateau phase. The onset of the plateau (latency, s) was defined as the time interval between the onset of the bicuculline application and the moment at which mean discharge value exceeded mean baseline activity by t ...
... (plateau). The firing rate of the neurons during the effect was measured during the plateau phase. The onset of the plateau (latency, s) was defined as the time interval between the onset of the bicuculline application and the moment at which mean discharge value exceeded mean baseline activity by t ...
Definition of Neuronal Circuitry Controlling the Activity of Phrenic
... though a few labeled neurons were present in the raphe nuclei, medial reticular formation, and parabrachial nucleus. Nevertheless, differences in the organization of neurons presynaptic to phrenic motoneurons were recently demonstrated in an emetic species, the ferret. In contrast to the rat, the ve ...
... though a few labeled neurons were present in the raphe nuclei, medial reticular formation, and parabrachial nucleus. Nevertheless, differences in the organization of neurons presynaptic to phrenic motoneurons were recently demonstrated in an emetic species, the ferret. In contrast to the rat, the ve ...
Principles of Neural Science
... In the brain, electrical synaptic transmission is rapid and rather stereotyped. Electrical synapses are used primarily to send simple depolarizing signals; they do not lend themselves to producing inhibitory actions or making long-lasting changes in the electrical properties of postsynaptic cells. I ...
... In the brain, electrical synaptic transmission is rapid and rather stereotyped. Electrical synapses are used primarily to send simple depolarizing signals; they do not lend themselves to producing inhibitory actions or making long-lasting changes in the electrical properties of postsynaptic cells. I ...
The fate of Nissl-stained dark neurons following
... N-DNs increased their pERK immunoreactivity. On the other hand, in the hippocampus the number of dead neurons was approximately the same number as that of the N-DNs, and most N-DNs showed an increased pERK immunoreactivity. These data suggest that not all N-DNs inevitably die especially in the neoco ...
... N-DNs increased their pERK immunoreactivity. On the other hand, in the hippocampus the number of dead neurons was approximately the same number as that of the N-DNs, and most N-DNs showed an increased pERK immunoreactivity. These data suggest that not all N-DNs inevitably die especially in the neoco ...
Respiratory Centers
... • more frequently they fire, more deeply you inhale • longer duration they fire, breath is prolonged, slow rate Expiratory center (ventral respiratory group, VRG) •involved in forced expiration ...
... • more frequently they fire, more deeply you inhale • longer duration they fire, breath is prolonged, slow rate Expiratory center (ventral respiratory group, VRG) •involved in forced expiration ...
The Motor Cortex and Descending Control of Movement
... terminate within multiple segments of the spinal cord. These features collectively show that outputs from the PMRF have the potential to influence multiple motoneuron pools and subsequently numerous different muscles. The traditional view is that the RST is largely concerned with control of proximal ...
... terminate within multiple segments of the spinal cord. These features collectively show that outputs from the PMRF have the potential to influence multiple motoneuron pools and subsequently numerous different muscles. The traditional view is that the RST is largely concerned with control of proximal ...
Forward Processing of Long-Term Associative Memory in Monkey
... Figure 2. Stimulus-selective responses to both paired associates of two representative A36 neurons (A and B for one neuron; C and D for the other neuron). A, C, Raster displays and PSTHs in the optimal (optimal, thick black line) and pair ( pair, thick gray line) trials. The trials were aligned at t ...
... Figure 2. Stimulus-selective responses to both paired associates of two representative A36 neurons (A and B for one neuron; C and D for the other neuron). A, C, Raster displays and PSTHs in the optimal (optimal, thick black line) and pair ( pair, thick gray line) trials. The trials were aligned at t ...
Chapter 15: Neural Integration I: Sensory Pathways and the Somatic
... The simplest receptors are the dendrites of sensory neurons. ...
... The simplest receptors are the dendrites of sensory neurons. ...
Neuroanatomical Background to Understanding the Brain of the
... simply that these areas are grossly damaged, but that the circuitry connecting these areas with each other and with several key regions, are either interrupted by mechanical or toxic damage, or dysregulated by several endogenous factors. These factors may include abnormal neurotransmitter systems, s ...
... simply that these areas are grossly damaged, but that the circuitry connecting these areas with each other and with several key regions, are either interrupted by mechanical or toxic damage, or dysregulated by several endogenous factors. These factors may include abnormal neurotransmitter systems, s ...
Synaptic gating

Synaptic gating is the ability of neural circuits to gate inputs by either suppressing or facilitating specific synaptic activity. Selective inhibition of certain synapses has been studied thoroughly (see Gate theory of pain), and recent studies have supported the existence of permissively gated synaptic transmission. In general, synaptic gating involves a mechanism of central control over neuronal output. It includes a sort of gatekeeper neuron, which has the ability to influence transmission of information to selected targets independently of the parts of the synapse upon which it exerts its action (see also neuromodulation).Bistable neurons have the ability to oscillate between a hyperpolarized (down state) and a depolarized (up state) resting membrane potential without firing an action potential. These neurons can thus be referred to as up/down neurons. According to one model, this ability is linked to the presence of NMDA and AMPA glutamate receptors. External stimulation of the NMDA receptors is responsible for moving the neuron from the down state to the up state, while the stimulation of AMPA receptors allows the neuron to reach and surpass the threshold potential. Neurons that have this bistable ability have the potential to be gated because outside gatekeeper neurons can modulate the membrane potential of the gated neuron by selectively shifting them from the up state to the down state. Such mechanisms have been observed in the nucleus accumbens, with gatekeepers originating in the cortex, thalamus and basal ganglia.