FUNCTIONAL NEUROANATOMY OF SPINAL CORD LEARNING
... Like the lateral tract fibres enter the tip of posterior column contribute to posteriolateral tract of lissauer and synapses with cells of substantia gelatinosa → Second order neuron axon cross obliquely in anterior commissure → Joins spinal lemniscus remaining course is same as Lateral spinothalami ...
... Like the lateral tract fibres enter the tip of posterior column contribute to posteriolateral tract of lissauer and synapses with cells of substantia gelatinosa → Second order neuron axon cross obliquely in anterior commissure → Joins spinal lemniscus remaining course is same as Lateral spinothalami ...
Regulation of Stroke-Induced Neurogenesis in Adult Brain—Recent
... The data described here demonstrate that a stroke, induced by MCAO in adult rats, leads to long-term alterations in the structure and function of the SVZ ipsilateral to the ischemic damage. At least up to 1 year after the insult, the SVZ continues to produce new neuroblasts, which migrate into the s ...
... The data described here demonstrate that a stroke, induced by MCAO in adult rats, leads to long-term alterations in the structure and function of the SVZ ipsilateral to the ischemic damage. At least up to 1 year after the insult, the SVZ continues to produce new neuroblasts, which migrate into the s ...
Bill Greenough`s research career
... The knowledge arising from this work also extended beyond their applications to brain and behavioral development. In a series of studies, Greenough demonstrated that many of the synaptic changes that occurred as a consequence of experience manipulations during development also occurred in specific f ...
... The knowledge arising from this work also extended beyond their applications to brain and behavioral development. In a series of studies, Greenough demonstrated that many of the synaptic changes that occurred as a consequence of experience manipulations during development also occurred in specific f ...
Feedforward and feedback inhibition in neostriatal GABAergic spiny
... afterhyperpolarization and fired rebound spikes following the offset of a hyperpolarizing current pulse delivered when the cell was depolarized (Fig. 4B), characteristics different from those of either PV+ or LTS neurons. Depolarization from rest sometimes evoked a plateau-like potential that did no ...
... afterhyperpolarization and fired rebound spikes following the offset of a hyperpolarizing current pulse delivered when the cell was depolarized (Fig. 4B), characteristics different from those of either PV+ or LTS neurons. Depolarization from rest sometimes evoked a plateau-like potential that did no ...
FlyEM`s formal project plan
... three months and only stop when the sample imaging has been completed. This required addressing a variety of interrupt issues: ion source reheat, utility failure (water, power, air, and temperature fluctuation), and microscope failure (focus, electrical, software, vacuum). With improvements and back ...
... three months and only stop when the sample imaging has been completed. This required addressing a variety of interrupt issues: ion source reheat, utility failure (water, power, air, and temperature fluctuation), and microscope failure (focus, electrical, software, vacuum). With improvements and back ...
Stochastic dynamics as a principle of brain function
... (the reciprocal of the synaptic conductance gj) and capacitance Csyn shown in the Figure. These effects produce excitatory or inhibitory post-synaptic potentials, EPSPs or IPSPs. These potentials are integrated by the cell, and if a threshold Vthr is reached a d-pulse (spike) is fired and transmitted ...
... (the reciprocal of the synaptic conductance gj) and capacitance Csyn shown in the Figure. These effects produce excitatory or inhibitory post-synaptic potentials, EPSPs or IPSPs. These potentials are integrated by the cell, and if a threshold Vthr is reached a d-pulse (spike) is fired and transmitted ...
Biological Foundations of Behaviour
... to another. Early in the history of brain research, scientists thought that the tip of the axon made physical contact with the dendrites or cell bodies of other neurons, passing electricity directly from one neuron to the next. Others, such as famous Spanish anatomist Santiago Ramón y Cajal and Brit ...
... to another. Early in the history of brain research, scientists thought that the tip of the axon made physical contact with the dendrites or cell bodies of other neurons, passing electricity directly from one neuron to the next. Others, such as famous Spanish anatomist Santiago Ramón y Cajal and Brit ...
M&E and the Frontal Lobes
... The middle of the seizure may take several different forms. For people who have warnings, the aura may simply continue or it may turn into a complex partial seizure or a convulsion. For those who do not have a warning, the seizure may continue as a complex partial seizure or it may evolve into a c ...
... The middle of the seizure may take several different forms. For people who have warnings, the aura may simply continue or it may turn into a complex partial seizure or a convulsion. For those who do not have a warning, the seizure may continue as a complex partial seizure or it may evolve into a c ...
Applying Transcranial Alternating Current Stimulation to the Study of Spike Timing Dependent Plasticity in Neural Networks
... physiologically accurate than the similar, but more complex, Hodgkin Huxley model, the FN model’s simplicity to implement and accurate mimicking of general neural spiking behavior make it an ideal first choice for the purposes of generating a neural micro-network. The specific FN model used here was ...
... physiologically accurate than the similar, but more complex, Hodgkin Huxley model, the FN model’s simplicity to implement and accurate mimicking of general neural spiking behavior make it an ideal first choice for the purposes of generating a neural micro-network. The specific FN model used here was ...
Noise in Neurons and Other Constraints
... fluctuations and provides an effective all-or- none response signal which is therefore thought to be noise free. How can we know what constitutes noise when recording signals from the brain? For instance, neuronal membrane potential shows small variations even at rest, even if synaptic inputs are ph ...
... fluctuations and provides an effective all-or- none response signal which is therefore thought to be noise free. How can we know what constitutes noise when recording signals from the brain? For instance, neuronal membrane potential shows small variations even at rest, even if synaptic inputs are ph ...
Self Assessment Chapter 11 part 2 - CM
... • Voltage-gated sodium channels have gone back to resting state and are able to open again • Potassium channels are activated and membrane is repolarizing or hyperpolarizing; takes a much larger stimulus to trigger an action potential ...
... • Voltage-gated sodium channels have gone back to resting state and are able to open again • Potassium channels are activated and membrane is repolarizing or hyperpolarizing; takes a much larger stimulus to trigger an action potential ...
Computation by Ensemble Synchronization in Recurrent Networks
... demonstrated that selective and robust synchronization is observed in a recurrent network in which excitatory neurons are randomly interconnected with depressing synapses (Tsodyks et al., 2000). In particular, it was shown that the network could generate a ‘Population Spike’ (PS), characterized by a ...
... demonstrated that selective and robust synchronization is observed in a recurrent network in which excitatory neurons are randomly interconnected with depressing synapses (Tsodyks et al., 2000). In particular, it was shown that the network could generate a ‘Population Spike’ (PS), characterized by a ...
MECHANISMS OF VERTEBRATE SYNAPTOGENESIS
... chemical signals transmitted through connected networks of neurons. Neurons transmit these signals to one another at specialized sites of contact called synapses. In the vertebrate nervous system, most neurons communicate via chemical synapses. As the name implies, chemical synapses function by conv ...
... chemical signals transmitted through connected networks of neurons. Neurons transmit these signals to one another at specialized sites of contact called synapses. In the vertebrate nervous system, most neurons communicate via chemical synapses. As the name implies, chemical synapses function by conv ...
NEOCORTEX
... the neck varies greatly, from virtually nothing as in "stubby" spines, in which the head attaches directly to the dendritic shaft, to necks that are several micrometers long (Jones and Powell, 1969). At the high magnifrcations achieved with the electron microscope, spines can be distinguished from o ...
... the neck varies greatly, from virtually nothing as in "stubby" spines, in which the head attaches directly to the dendritic shaft, to necks that are several micrometers long (Jones and Powell, 1969). At the high magnifrcations achieved with the electron microscope, spines can be distinguished from o ...
Perception Spike Timing-Dependent Plasticity: From Synapse to
... of glutamate receptors (NMDARs) (e.g., Refs. 13, 24, 65, 67, 119) and elevation of postsynaptic Ca2" level are required, the effectiveness of postsynaptic spiking and steady depolarization in achieving the required Ca2" level is likely to be different. This may account for the higher efficiency of t ...
... of glutamate receptors (NMDARs) (e.g., Refs. 13, 24, 65, 67, 119) and elevation of postsynaptic Ca2" level are required, the effectiveness of postsynaptic spiking and steady depolarization in achieving the required Ca2" level is likely to be different. This may account for the higher efficiency of t ...
Analogues of simple and complex cells in rhesus monkey auditory
... categories of cells with distinct receptive field (RF) types (1): Simple cells have discrete subareas of a particular orientation that respond either to the onset or the offset of a small spot of light; complex cells, by contrast, respond with mixed ON and OFF responses throughout their RF. In additi ...
... categories of cells with distinct receptive field (RF) types (1): Simple cells have discrete subareas of a particular orientation that respond either to the onset or the offset of a small spot of light; complex cells, by contrast, respond with mixed ON and OFF responses throughout their RF. In additi ...
Y.I. Molkov, Baroreflex models, Encyclopedia of Computational
... network architecture, rather than on the neurons’ biophysical properties. ...
... network architecture, rather than on the neurons’ biophysical properties. ...
supplemental figures
... started being activated from trigger (neuron #157). (b) An example of neurons first inhibited at trigger, then activated after trigger (neuron #197). (c) An example of neurons started being activated before the trigger (neuron #233). The inset color bar in all panels beside x axis is thermograph of ...
... started being activated from trigger (neuron #157). (b) An example of neurons first inhibited at trigger, then activated after trigger (neuron #197). (c) An example of neurons started being activated before the trigger (neuron #233). The inset color bar in all panels beside x axis is thermograph of ...
FIAT 8 - UCLA Statistics
... Understanding the temporal pattern of the nerve fibers. Detailed understanding of how the hair cells change sound into electrical nerve impulses ...
... Understanding the temporal pattern of the nerve fibers. Detailed understanding of how the hair cells change sound into electrical nerve impulses ...
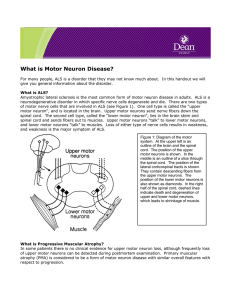
What is Motor Neuron
... food (from a grocery store of from a farm), source of drinking water (city or from a well), occupation and hobbies, etc. These studies have identified no clear factors associated with the development of ALS. A small percentage of patients, about 5%, have other members in the family with ALS. This is ...
... food (from a grocery store of from a farm), source of drinking water (city or from a well), occupation and hobbies, etc. These studies have identified no clear factors associated with the development of ALS. A small percentage of patients, about 5%, have other members in the family with ALS. This is ...
BDNF-modulated Spatial Organization of Cajal
... cortex with disorganized CR cells and aberrant cortical lamination (Ringstedt et al., 1998). During embryonic development, CR neurons express BDNF and NT4 along with their receptor TrkB (Fukumitsu et al., 1998), whereas GABAergic neurons only express TrkB (Gorba and Wahle, 1999). Both neuronal cell ...
... cortex with disorganized CR cells and aberrant cortical lamination (Ringstedt et al., 1998). During embryonic development, CR neurons express BDNF and NT4 along with their receptor TrkB (Fukumitsu et al., 1998), whereas GABAergic neurons only express TrkB (Gorba and Wahle, 1999). Both neuronal cell ...
Nerve activates contraction
... 1 Resting membrane is polarized. In the resting state, the external face of the membrane is slightly positive; its internal face is slightly negative. The chief extracellular ion is sodium (Na+), whereas the chief intracellular ion is potassium (K+). The membrane is relatively impermeable to both io ...
... 1 Resting membrane is polarized. In the resting state, the external face of the membrane is slightly positive; its internal face is slightly negative. The chief extracellular ion is sodium (Na+), whereas the chief intracellular ion is potassium (K+). The membrane is relatively impermeable to both io ...
Volitional enhancement of firing synchrony and oscillation by
... conditioned neurons (Figure 2). The authors concluded that only the operant-conditioned neurons possessing significantly increased firing rates take the lead as “master neurons”, that exhibit most prominent volitionally driven modulations in a small neural network. Such on-going progress of research ...
... conditioned neurons (Figure 2). The authors concluded that only the operant-conditioned neurons possessing significantly increased firing rates take the lead as “master neurons”, that exhibit most prominent volitionally driven modulations in a small neural network. Such on-going progress of research ...
Synaptic gating

Synaptic gating is the ability of neural circuits to gate inputs by either suppressing or facilitating specific synaptic activity. Selective inhibition of certain synapses has been studied thoroughly (see Gate theory of pain), and recent studies have supported the existence of permissively gated synaptic transmission. In general, synaptic gating involves a mechanism of central control over neuronal output. It includes a sort of gatekeeper neuron, which has the ability to influence transmission of information to selected targets independently of the parts of the synapse upon which it exerts its action (see also neuromodulation).Bistable neurons have the ability to oscillate between a hyperpolarized (down state) and a depolarized (up state) resting membrane potential without firing an action potential. These neurons can thus be referred to as up/down neurons. According to one model, this ability is linked to the presence of NMDA and AMPA glutamate receptors. External stimulation of the NMDA receptors is responsible for moving the neuron from the down state to the up state, while the stimulation of AMPA receptors allows the neuron to reach and surpass the threshold potential. Neurons that have this bistable ability have the potential to be gated because outside gatekeeper neurons can modulate the membrane potential of the gated neuron by selectively shifting them from the up state to the down state. Such mechanisms have been observed in the nucleus accumbens, with gatekeepers originating in the cortex, thalamus and basal ganglia.