Von Economo Neurons in the Elephant Brain
... As has been observed in humans, great apes, and cetaceans, the VENs of the elephant are primarily found in layer 5 of the cortical regions that contain them, along with populations of other large pyramidal neurons with distinctive morphologies such as the compass cells, which were also described by ...
... As has been observed in humans, great apes, and cetaceans, the VENs of the elephant are primarily found in layer 5 of the cortical regions that contain them, along with populations of other large pyramidal neurons with distinctive morphologies such as the compass cells, which were also described by ...
Involvement of the Caudal Medulla in Negative Feedback
... neurons. These inhibitory effects induced by spatial summation of nociceptive inputs have been shown to involve a supraspinally mediated negative feedback loop. The aim of the present study was to determine the anatomic level of integration of these controls and hence to ascertain what relationships ...
... neurons. These inhibitory effects induced by spatial summation of nociceptive inputs have been shown to involve a supraspinally mediated negative feedback loop. The aim of the present study was to determine the anatomic level of integration of these controls and hence to ascertain what relationships ...
... Pyramidal neurons and interneurons of the cerebral cortex were immunostained by EXTL3 antibody. Immunoreactivity was more abundant in temporo-occipital, frontotemporal and medial occipital area than in medial parietal area (Fig.3A-B, D, G, H). Olfactory areas as olfactory bulb, olfactory anterior nu ...
Discussion and future directions
... 2000) have shown that in order to hold memory activity for a saccades, the neural population develops excitatory connections between units with similar preferred saccade directions and inhibitory connections between units with dissimilar directions. Previous modeling results similar with ours have b ...
... 2000) have shown that in order to hold memory activity for a saccades, the neural population develops excitatory connections between units with similar preferred saccade directions and inhibitory connections between units with dissimilar directions. Previous modeling results similar with ours have b ...
Document
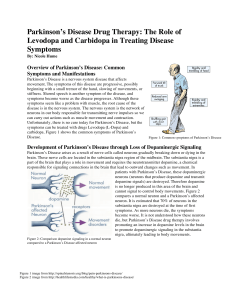
... part of the brain that plays a role in movement and requires the neurotransmitter dopamine, a chemical responsible for signaling connections in the brain that lead to outward changes such as movement. In patients with Parkinson’s Disease, these dopaminergic neurons (neurons that produce dopamine and ...
... part of the brain that plays a role in movement and requires the neurotransmitter dopamine, a chemical responsible for signaling connections in the brain that lead to outward changes such as movement. In patients with Parkinson’s Disease, these dopaminergic neurons (neurons that produce dopamine and ...
The Nervous System
... consists of a pair of oval masses on each side of 3rd ventricle in diencephalon mostly gray matter made up of many nuclei Functions include: - language, memory, emotion, integration and relay of sensory impulses to the cerebral cortex ...
... consists of a pair of oval masses on each side of 3rd ventricle in diencephalon mostly gray matter made up of many nuclei Functions include: - language, memory, emotion, integration and relay of sensory impulses to the cerebral cortex ...
InterimSummary The Nature of Learning
... Let’s consider the process of reinforcement. Briefly stated, reinforcement causes changes in an animal’s nervous system that increase the likelihood that a particular stimulus will elicit a particular response. For example, when a hungry rat is first put in an operant chamber (a “Skinner box”), it i ...
... Let’s consider the process of reinforcement. Briefly stated, reinforcement causes changes in an animal’s nervous system that increase the likelihood that a particular stimulus will elicit a particular response. For example, when a hungry rat is first put in an operant chamber (a “Skinner box”), it i ...
On the computational architecture of the neocortex
... and the remaining neurons all project directly to the cortex with no collaterals (with one exception: see discussion of R E thalamus below). Thus, except for the R E nucleus, the nuclei in the thalamus are not directly connected to each other. Where does the thalamus get its input? Some nuclei in th ...
... and the remaining neurons all project directly to the cortex with no collaterals (with one exception: see discussion of R E thalamus below). Thus, except for the R E nucleus, the nuclei in the thalamus are not directly connected to each other. Where does the thalamus get its input? Some nuclei in th ...
Brain Abnormalities in Murderers
... right hemisphere when killing mice. Severing the corpus callosum in rats leads to an increase in mice-killing, indicating that the left hemisphere acts to inhibit the right hemisphere-mediated killing via an intact corpus callosum. It has been observed that split-brain patients experience poor emoti ...
... right hemisphere when killing mice. Severing the corpus callosum in rats leads to an increase in mice-killing, indicating that the left hemisphere acts to inhibit the right hemisphere-mediated killing via an intact corpus callosum. It has been observed that split-brain patients experience poor emoti ...
Dynamic Computation in a Recurrent Network of Heterogeneous
... cluster dynamics; the chosen settings are indicated in Fig. 2. Our real-time GUI facilitated this search since we were able to monitor relevant network properties (e.g., network stability) while tuning the parameters. Having found a suitable operating point, we now constrain our analysis to the post ...
... cluster dynamics; the chosen settings are indicated in Fig. 2. Our real-time GUI facilitated this search since we were able to monitor relevant network properties (e.g., network stability) while tuning the parameters. Having found a suitable operating point, we now constrain our analysis to the post ...
Brain Development Article and Questions
... child’s earliest years can have effects that last a lifetime. Thanks to recent advances in technology, we have a clearer understanding of how these effects are related to early brain development. Neuroscientists can now identify patterns in brain activity that appear to be associated with some types ...
... child’s earliest years can have effects that last a lifetime. Thanks to recent advances in technology, we have a clearer understanding of how these effects are related to early brain development. Neuroscientists can now identify patterns in brain activity that appear to be associated with some types ...
07. Pons Internal Features 0102010-10-01 05:141.9
... • Fibers from the cdorsal and ventral cochlear nuclei ascend in the pons • Most of the fibers cross in the midline. The decussating fibers constitute the trapezoid body which intersects the medial lemnisci and then turn rostrally in the lateral part of the tegmentum to form the lateral lemniscus • S ...
... • Fibers from the cdorsal and ventral cochlear nuclei ascend in the pons • Most of the fibers cross in the midline. The decussating fibers constitute the trapezoid body which intersects the medial lemnisci and then turn rostrally in the lateral part of the tegmentum to form the lateral lemniscus • S ...
THE MACHINE OF PEACE tirar as letras da foto. MICROCODE
... The thalamus is a center of brain organization, as a crossroads of different neuronal pathways that may influence each other before being redistributed. His connections are more abundant, by far, with the cortex. The main function of the thalamus is to serve as station reorganization of stimuli fro ...
... The thalamus is a center of brain organization, as a crossroads of different neuronal pathways that may influence each other before being redistributed. His connections are more abundant, by far, with the cortex. The main function of the thalamus is to serve as station reorganization of stimuli fro ...
How the brain uses time to represent and process visual information
... of values for q, since neural coincidence-detectors with precisions ranging from milliseconds to seconds have been identified [10], and the range of timescales for which firing rates influence synaptic efficacy is also large. Fortunately, there are highly efficient algorithms [68] to calculate these ...
... of values for q, since neural coincidence-detectors with precisions ranging from milliseconds to seconds have been identified [10], and the range of timescales for which firing rates influence synaptic efficacy is also large. Fortunately, there are highly efficient algorithms [68] to calculate these ...
Chapter 11 PowerPoint - Hillsborough Community College
... • Ca2+ concentration increases in presynaptic terminal and ostsynaptic neuron • Brief high-frequency stimulation partially depolarizes the postsynaptic neuron • Chemically gated channels (NMDA receptors) allow Ca2+ entry • Ca2+ activates kinase enzymes that promote more effective responses to subseq ...
... • Ca2+ concentration increases in presynaptic terminal and ostsynaptic neuron • Brief high-frequency stimulation partially depolarizes the postsynaptic neuron • Chemically gated channels (NMDA receptors) allow Ca2+ entry • Ca2+ activates kinase enzymes that promote more effective responses to subseq ...
A Physiologically Plausible Model of Action Selection
... (1) The striatum is considered the princi- pathway). Glutamatergic cells of the STN send excitatory projections to the GP and the SNr/EP, contributing to both the tonic activity pal input nucleus of the BG, receiving exten- of the SNr/EP cells and the activity within the control pathway. sive input ...
... (1) The striatum is considered the princi- pathway). Glutamatergic cells of the STN send excitatory projections to the GP and the SNr/EP, contributing to both the tonic activity pal input nucleus of the BG, receiving exten- of the SNr/EP cells and the activity within the control pathway. sive input ...
Self-organization and interareal networks™in™the™primate cortex
... There are a number of different approaches one can adopt to study cortical development. One is to describe the cellular events, usually in vitro, of various developmental stages. This approach is often coupled to the study of gene expression and ultimately with the modification of the expression of ...
... There are a number of different approaches one can adopt to study cortical development. One is to describe the cellular events, usually in vitro, of various developmental stages. This approach is often coupled to the study of gene expression and ultimately with the modification of the expression of ...
Role of Nitric Oxide on Dopamine Release and Morphine
... vesicles at dopaminergic terminals, leading to an increase in DA release independent of frequency of stimulations. In addition, NO may also increase the docking and fusion of cholinergic vesicles at cholinergic terminals, leading to an increase in ACh release that, as described earlier, could desens ...
... vesicles at dopaminergic terminals, leading to an increase in DA release independent of frequency of stimulations. In addition, NO may also increase the docking and fusion of cholinergic vesicles at cholinergic terminals, leading to an increase in ACh release that, as described earlier, could desens ...
Neural Correlates of Executive Control in the Avian Brain
... the NCL neurons that are performing the executive control function, or whether we are observing the effects on NCL neurons of executive functions that lie elsewhere in the brain. Given the evidence that we will review shortly that NCL may be an analogue of the mammalian PFC, and given the role of th ...
... the NCL neurons that are performing the executive control function, or whether we are observing the effects on NCL neurons of executive functions that lie elsewhere in the brain. Given the evidence that we will review shortly that NCL may be an analogue of the mammalian PFC, and given the role of th ...
Chapter 27 - Fullfrontalanatomy.com
... • To function as a nerve signal over a distance, this local event must be passed along the neuron. • Action potential propagation is like a “domino effect” along a neuron. – All-or-none events – The same no matter how strong or weak the stimulus that triggers them ...
... • To function as a nerve signal over a distance, this local event must be passed along the neuron. • Action potential propagation is like a “domino effect” along a neuron. – All-or-none events – The same no matter how strong or weak the stimulus that triggers them ...
Heart-brain communication Veen, Frederik Martin van der
... compared to responses obtained from the cingulate gyrus. The pattern of cardiovascular responses which is generated by stimulating the insular cortex is best known from the studies with rats mentioned earlier (Butcher & Cechetto, 1995). From these studies it was concluded that the insular cortex ton ...
... compared to responses obtained from the cingulate gyrus. The pattern of cardiovascular responses which is generated by stimulating the insular cortex is best known from the studies with rats mentioned earlier (Butcher & Cechetto, 1995). From these studies it was concluded that the insular cortex ton ...
Save
... Broca,Werniche,Kussmaul) , can be identified with the consciousness formation that can be interpreted as a sort of constant,continous and simultaneous low-noise effect. When the cortex receives sufficient afferent impulses, it is said to be aroused or activated. That is, a critical number of cortica ...
... Broca,Werniche,Kussmaul) , can be identified with the consciousness formation that can be interpreted as a sort of constant,continous and simultaneous low-noise effect. When the cortex receives sufficient afferent impulses, it is said to be aroused or activated. That is, a critical number of cortica ...
Chapter 2
... microscopic level nor have the local axons from IC GABAergic neurons (see Section 4.2). Although the inputs to ICC have been identified at the electron microscopic level, their synaptic role in processing auditory information remains an area of intense interest. For example, it is unclear whether th ...
... microscopic level nor have the local axons from IC GABAergic neurons (see Section 4.2). Although the inputs to ICC have been identified at the electron microscopic level, their synaptic role in processing auditory information remains an area of intense interest. For example, it is unclear whether th ...
Probing neural circuits in the zebrafish: a suite of optical techniques
... acquisition box is filled, but without cutting off the edges of the cell. This enhances the signal-to-noise ratio by maximizing the number of pixels of information per frame. We focus at the brightest focal plane just prior to each trial. Within the trial, several baseline images are collected prior t ...
... acquisition box is filled, but without cutting off the edges of the cell. This enhances the signal-to-noise ratio by maximizing the number of pixels of information per frame. We focus at the brightest focal plane just prior to each trial. Within the trial, several baseline images are collected prior t ...
Synaptic gating

Synaptic gating is the ability of neural circuits to gate inputs by either suppressing or facilitating specific synaptic activity. Selective inhibition of certain synapses has been studied thoroughly (see Gate theory of pain), and recent studies have supported the existence of permissively gated synaptic transmission. In general, synaptic gating involves a mechanism of central control over neuronal output. It includes a sort of gatekeeper neuron, which has the ability to influence transmission of information to selected targets independently of the parts of the synapse upon which it exerts its action (see also neuromodulation).Bistable neurons have the ability to oscillate between a hyperpolarized (down state) and a depolarized (up state) resting membrane potential without firing an action potential. These neurons can thus be referred to as up/down neurons. According to one model, this ability is linked to the presence of NMDA and AMPA glutamate receptors. External stimulation of the NMDA receptors is responsible for moving the neuron from the down state to the up state, while the stimulation of AMPA receptors allows the neuron to reach and surpass the threshold potential. Neurons that have this bistable ability have the potential to be gated because outside gatekeeper neurons can modulate the membrane potential of the gated neuron by selectively shifting them from the up state to the down state. Such mechanisms have been observed in the nucleus accumbens, with gatekeepers originating in the cortex, thalamus and basal ganglia.