Trends in Cognitive Sciences 2007 Bogacz
... equation that describes an optimal test, and (ii) behaviour in terms of speed–accuracy trade-offs. Neurobiology of decision The neural bases of decision making are typically studied in experiments by presenting a subject with a stimulus that comprises moving dots [8]. A fraction of these dots move c ...
... equation that describes an optimal test, and (ii) behaviour in terms of speed–accuracy trade-offs. Neurobiology of decision The neural bases of decision making are typically studied in experiments by presenting a subject with a stimulus that comprises moving dots [8]. A fraction of these dots move c ...
Neurotransmitters: Acetylcholine and Dopamine
... – It is still not fully understood how memory formation occurs – However, research has shown that when a shortterm memory is converted into long-term storage in the hippocampus, neurons in the brain help to synthesize protein molecules and new connections between neurons are formed ...
... – It is still not fully understood how memory formation occurs – However, research has shown that when a shortterm memory is converted into long-term storage in the hippocampus, neurons in the brain help to synthesize protein molecules and new connections between neurons are formed ...
Words in the Brain - Rice University -
... The node as a cortical column • The properties of the cortical column are approximately those described by Vernon Mountcastle – Mountcastle, Perceptual Neuroscience, 1998 • Additional properties of columns and functional webs can be derived from Mountcastle’s treatment together with neurolinguistic ...
... The node as a cortical column • The properties of the cortical column are approximately those described by Vernon Mountcastle – Mountcastle, Perceptual Neuroscience, 1998 • Additional properties of columns and functional webs can be derived from Mountcastle’s treatment together with neurolinguistic ...
Autonomic nervous system
... ventral root and enter spinal nerve Exit spinal nerve via communicating ramus Enter sympathetic trunk/chain where postganglionic neurons :Has three options… ...
... ventral root and enter spinal nerve Exit spinal nerve via communicating ramus Enter sympathetic trunk/chain where postganglionic neurons :Has three options… ...
Slide 1
... Recorded from MT neurons Quantify attentional effect by comparing the responses of individual MT neurons to identical visual display conditions when the monkey was instructed to attend to one or the other aperture Neuronal responses were measured as the number of spikes that the cell fired dur ...
... Recorded from MT neurons Quantify attentional effect by comparing the responses of individual MT neurons to identical visual display conditions when the monkey was instructed to attend to one or the other aperture Neuronal responses were measured as the number of spikes that the cell fired dur ...
Cough, Expiration and Aspiration Reflexes following
... Shannon et al. (1998, 2000). According to this model neuronal circuitries of the Respiratory Central Pattern Generator can also produce the cough motor pattern. However, the possibility that other brainstem circuits overlapping the main respiratory networks may also participate has not been excluded ...
... Shannon et al. (1998, 2000). According to this model neuronal circuitries of the Respiratory Central Pattern Generator can also produce the cough motor pattern. However, the possibility that other brainstem circuits overlapping the main respiratory networks may also participate has not been excluded ...
The Motor System of the Cortex and the Brain Stem
... direction, discharge was minimal. Therefore, the discharge during the delay period appeared to be related in some way to the target’s position. Importantly, after the go signal was given, the discharge remained the same as it was during the delay period. This second observation suggests that the in ...
... direction, discharge was minimal. Therefore, the discharge during the delay period appeared to be related in some way to the target’s position. Importantly, after the go signal was given, the discharge remained the same as it was during the delay period. This second observation suggests that the in ...
Spike Train - CMU Statistics
... Spike Train Definition A spike train is a sequence of recorded times at which a neuron fires an action potential. When the voltage drop across a neural soma or axon membrane is recorded, intermittent pulses of roughly 100 millivolts over 1-2 milliseconds are observed—these are action potentials or “ ...
... Spike Train Definition A spike train is a sequence of recorded times at which a neuron fires an action potential. When the voltage drop across a neural soma or axon membrane is recorded, intermittent pulses of roughly 100 millivolts over 1-2 milliseconds are observed—these are action potentials or “ ...
Document
... Allow you to understand the unusual use of the words (eg.if I say bank you can understand it by wernick’s area , while if I say river bank _side of river _ it’s unusal term processed by wernick’s homologue ). ❹Taste and olfaction: Primary gustatory cortex:you trace the post central gyrus until you ...
... Allow you to understand the unusual use of the words (eg.if I say bank you can understand it by wernick’s area , while if I say river bank _side of river _ it’s unusal term processed by wernick’s homologue ). ❹Taste and olfaction: Primary gustatory cortex:you trace the post central gyrus until you ...
video slide - Plattsburgh State Faculty and Research Web Sites
... • The net flow of K+ ions will continue and the negative charge will increase until the difference in charge between the inside and outside of the cell (which attracts K+ ions back into the cell) balances the effect of the concentration gradient for K+, which is causing K+ ions to flow out. • If it ...
... • The net flow of K+ ions will continue and the negative charge will increase until the difference in charge between the inside and outside of the cell (which attracts K+ ions back into the cell) balances the effect of the concentration gradient for K+, which is causing K+ ions to flow out. • If it ...
In VivoCalcium Imaging Reveals Functional Rewiring of Single
... Functional mapping and microstimulation studies suggest that recovery after stroke damage can be attributed to surviving brain regions taking on the functional roles of lost tissues. Although this model is well supported by data, it is not clear how activity in single neurons is altered in relation ...
... Functional mapping and microstimulation studies suggest that recovery after stroke damage can be attributed to surviving brain regions taking on the functional roles of lost tissues. Although this model is well supported by data, it is not clear how activity in single neurons is altered in relation ...
The Role of Dopamine and Its Dysfunction as a Consequence of
... to the nucleus accumbens through the amygdala and the hippocampus. The nigrostriatal pathway joins the substantia nigra with the neostriatum. The neuronal somata are located in the substantia nigra, and the axons of these neurons are ramified into the caudate nucleus and putamen. This pathway is als ...
... to the nucleus accumbens through the amygdala and the hippocampus. The nigrostriatal pathway joins the substantia nigra with the neostriatum. The neuronal somata are located in the substantia nigra, and the axons of these neurons are ramified into the caudate nucleus and putamen. This pathway is als ...
Mirror Neurons: Findings and Functions
... One of the hypothesized functions of animal MNs is to aid understanding the intention of an observed motor action, as already hypothesized by Di Pellegrino et al. (1992). They found the firing of MNs did not depend on a specific object involved in the motor action or on a specific motor gesture, but ...
... One of the hypothesized functions of animal MNs is to aid understanding the intention of an observed motor action, as already hypothesized by Di Pellegrino et al. (1992). They found the firing of MNs did not depend on a specific object involved in the motor action or on a specific motor gesture, but ...
Chapter 13: The Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves, and Spinal
... Withdrawal reflex When pain receptors are activated it causes automatic withdrawal of the threatened body part. ...
... Withdrawal reflex When pain receptors are activated it causes automatic withdrawal of the threatened body part. ...
Neuron/Glia Relationships Observed Over Intervals
... (Purves et al., 1987), we also noted that vesicle-filled preganglionic nerve terminals appeared to be more prevalent in the vicinity of the glial nuclei than in regions removed from this site. The preganglionic nerve terminals tended to establish synaptic contacts in a complex of short finger-like e ...
... (Purves et al., 1987), we also noted that vesicle-filled preganglionic nerve terminals appeared to be more prevalent in the vicinity of the glial nuclei than in regions removed from this site. The preganglionic nerve terminals tended to establish synaptic contacts in a complex of short finger-like e ...
Two-photon imaging and analysis of neural network dynamics
... down to nearly 1 mm. Two-photon microscopy has proven particularly powerful in combination with fluorescent reporters of neuronal activity. Such indicators (either small organic molecules or proteins) change their fluorescence properties as a function of either membrane potential or intracellular ca ...
... down to nearly 1 mm. Two-photon microscopy has proven particularly powerful in combination with fluorescent reporters of neuronal activity. Such indicators (either small organic molecules or proteins) change their fluorescence properties as a function of either membrane potential or intracellular ca ...
Visuomotor Functions in the Frontal Lobe
... the same level as V3 and V4, whereas the medial FEF (8m), which produces longer saccades, is at the same level as TE, LIP, V3A, and FST. Anatomically, the FEF is feedforward to several occipital, parietal, and temporal areas. Panel adapted with permission from Markov et al. (2014). (c) Hierarchy of ...
... the same level as V3 and V4, whereas the medial FEF (8m), which produces longer saccades, is at the same level as TE, LIP, V3A, and FST. Anatomically, the FEF is feedforward to several occipital, parietal, and temporal areas. Panel adapted with permission from Markov et al. (2014). (c) Hierarchy of ...
Computational themes of peripheral processing
... an intensity-invariant representation of the amplitude modulation of the perceived signal and to increase the signalto-noise ratio. Next, the representation of the amplitude modulation of a signal by the auditory receptor neurons (Machens et al. 2001) needs to be processed in a way that higher level ...
... an intensity-invariant representation of the amplitude modulation of the perceived signal and to increase the signalto-noise ratio. Next, the representation of the amplitude modulation of a signal by the auditory receptor neurons (Machens et al. 2001) needs to be processed in a way that higher level ...
Soghomonian J.J., Sethares C., and Peters, A
... Much of the cognitive decline shown by aging primates can be attributed to dysfunction of prefrontal cortex and, as shown previously, about 30% of asymmetric (excitatory) and symmetric (inhibitory) axodendritic synapses are lost from the neuropil of layer 2/3 in prefrontal area 46 with age (Peters e ...
... Much of the cognitive decline shown by aging primates can be attributed to dysfunction of prefrontal cortex and, as shown previously, about 30% of asymmetric (excitatory) and symmetric (inhibitory) axodendritic synapses are lost from the neuropil of layer 2/3 in prefrontal area 46 with age (Peters e ...
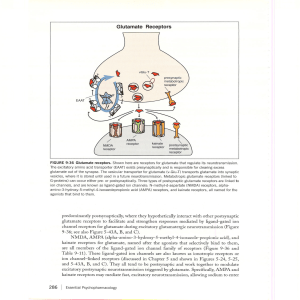
Glutamate Receptors
... dopamine hyperactivity reduces the thalamic filter and permits the escape of excessive sensory information coming into the thalamus, thus allowing it to get into the cortex by means of ascending thalamocortical neurons. If this were not bad enough, there is hypothetical NMDA receptor hypofunction in ...
... dopamine hyperactivity reduces the thalamic filter and permits the escape of excessive sensory information coming into the thalamus, thus allowing it to get into the cortex by means of ascending thalamocortical neurons. If this were not bad enough, there is hypothetical NMDA receptor hypofunction in ...
cerebellar projections to the superior colliculus in the cat1
... nucleus. These findings point to the lateral nucleus and, to a lesser extent, to the anterior interpositus as the origin of the degenerated fibers described by Lago (1975) as ending in the stratum griseum intermedium of the superior colliculus after lesions of the brachium conjunctivum in the cat. I ...
... nucleus. These findings point to the lateral nucleus and, to a lesser extent, to the anterior interpositus as the origin of the degenerated fibers described by Lago (1975) as ending in the stratum griseum intermedium of the superior colliculus after lesions of the brachium conjunctivum in the cat. I ...
FREE Sample Here
... A. all neurons produce an action potential at the same time or none at all. B. all of the extracellular sodium enters the axon, or none at all. C. once an axon reaches threshold, the amplitude and velocity of an action potential are nearly equal each time. D. neurons are either active all the time o ...
... A. all neurons produce an action potential at the same time or none at all. B. all of the extracellular sodium enters the axon, or none at all. C. once an axon reaches threshold, the amplitude and velocity of an action potential are nearly equal each time. D. neurons are either active all the time o ...
Orexinergic Input to Dopaminergic Neurons of the Human Ventral
... hypocretin 1 and hypocretin 2) have been implicated in a variety of behavioral states including feeding [1], sleep and arousal [2], reward processing and drug abuse [3]. As reviewed recently, orexinergic signaling modulates many responses to drugs of abuse and food, such as hyperlocomotor activity a ...
... hypocretin 1 and hypocretin 2) have been implicated in a variety of behavioral states including feeding [1], sleep and arousal [2], reward processing and drug abuse [3]. As reviewed recently, orexinergic signaling modulates many responses to drugs of abuse and food, such as hyperlocomotor activity a ...
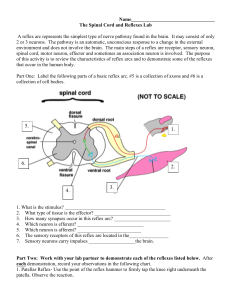
Name__________________________________ The Spinal Cord
... The Spinal Cord and Reflexes Lab A reflex arc represents the simplest type of nerve pathway found in the brain. It may consist of only 2 or 3 neurons. The pathway is an automatic, unconscious response to a change in the external environment and does not involve the brain. The main steps of a reflex ...
... The Spinal Cord and Reflexes Lab A reflex arc represents the simplest type of nerve pathway found in the brain. It may consist of only 2 or 3 neurons. The pathway is an automatic, unconscious response to a change in the external environment and does not involve the brain. The main steps of a reflex ...
Synaptic gating

Synaptic gating is the ability of neural circuits to gate inputs by either suppressing or facilitating specific synaptic activity. Selective inhibition of certain synapses has been studied thoroughly (see Gate theory of pain), and recent studies have supported the existence of permissively gated synaptic transmission. In general, synaptic gating involves a mechanism of central control over neuronal output. It includes a sort of gatekeeper neuron, which has the ability to influence transmission of information to selected targets independently of the parts of the synapse upon which it exerts its action (see also neuromodulation).Bistable neurons have the ability to oscillate between a hyperpolarized (down state) and a depolarized (up state) resting membrane potential without firing an action potential. These neurons can thus be referred to as up/down neurons. According to one model, this ability is linked to the presence of NMDA and AMPA glutamate receptors. External stimulation of the NMDA receptors is responsible for moving the neuron from the down state to the up state, while the stimulation of AMPA receptors allows the neuron to reach and surpass the threshold potential. Neurons that have this bistable ability have the potential to be gated because outside gatekeeper neurons can modulate the membrane potential of the gated neuron by selectively shifting them from the up state to the down state. Such mechanisms have been observed in the nucleus accumbens, with gatekeepers originating in the cortex, thalamus and basal ganglia.