the resonate-and-fire neuron: time dependent and frequency
... body corresponds to the metabollic center of a neuron, and it gives rise to two types of processes - the dendrites and the axon. The dendrites, commonly referred to as the dendritic tree, serve as the main apparatus through which a neuron receives input signals arising from other nerve cells, or pre ...
... body corresponds to the metabollic center of a neuron, and it gives rise to two types of processes - the dendrites and the axon. The dendrites, commonly referred to as the dendritic tree, serve as the main apparatus through which a neuron receives input signals arising from other nerve cells, or pre ...
Neural Coding and Auditory Perception
... that responses of a single AN fiber to a set of Huffman stimuli with varying FT resembles the responses of an array of model fibers with different characteristic frequencies (CFs) to a fixed FT stimulus, as predicted by scaling invariance. In both the model and AN fibers, changing the steepness of t ...
... that responses of a single AN fiber to a set of Huffman stimuli with varying FT resembles the responses of an array of model fibers with different characteristic frequencies (CFs) to a fixed FT stimulus, as predicted by scaling invariance. In both the model and AN fibers, changing the steepness of t ...
Using calcium imaging to understand function and learning in L2/3
... organization and functional basis of this sparse code is not well understood. I conducted two studies to characterize function and learning in the cortex. In the first study, I used population calcium i ...
... organization and functional basis of this sparse code is not well understood. I conducted two studies to characterize function and learning in the cortex. In the first study, I used population calcium i ...
Noradrenergic Modulation of Activity in a Vocal Control Nucleus In
... Extracellular recordings of the spontaneous activity of 108 isolated RA neurons (median peak-to-peak spike height was 0.52 mV) were made in the brain slices. As previously reported in vivo (Adret and Margoliash 2002; Yu and Margoliash 1996) and in vitro (Mooney 1992), RA neurons exhibited spontaneou ...
... Extracellular recordings of the spontaneous activity of 108 isolated RA neurons (median peak-to-peak spike height was 0.52 mV) were made in the brain slices. As previously reported in vivo (Adret and Margoliash 2002; Yu and Margoliash 1996) and in vitro (Mooney 1992), RA neurons exhibited spontaneou ...
Impaired odour discrimination on desynchronization of odour
... Investigation of olfactory processing in the locust antennal lobe—a functional and morphological analogue of the vertebrate olfactory bulb—has indicated that both monomolecular and complex odours are represented there combinatorially by dynamical assemblies of projection neurons5,9–11. Each neuron i ...
... Investigation of olfactory processing in the locust antennal lobe—a functional and morphological analogue of the vertebrate olfactory bulb—has indicated that both monomolecular and complex odours are represented there combinatorially by dynamical assemblies of projection neurons5,9–11. Each neuron i ...
The Anterior Cingulate Cortex - John Allman
... There is a remarkable counterpart to these monkey experiments in electroencephalographic (EEG) recordings made from scalp electrodes in humans. A large body of EEG data indicates that the anterior cingulate is the source of a 4- to 7-Hertz signal present when the subject is performing a task requiri ...
... There is a remarkable counterpart to these monkey experiments in electroencephalographic (EEG) recordings made from scalp electrodes in humans. A large body of EEG data indicates that the anterior cingulate is the source of a 4- to 7-Hertz signal present when the subject is performing a task requiri ...
2. Parkinsons diseas and Movement Disorders. 1998
... Different areas of the cerebral cortex (neocortex) may be distinguished from one another by their histological features and neuroanatomical connections. Brodmann’s numbering scheme for cortical areas has been used for many years and will be introduced in this section. Projection areas. By following ...
... Different areas of the cerebral cortex (neocortex) may be distinguished from one another by their histological features and neuroanatomical connections. Brodmann’s numbering scheme for cortical areas has been used for many years and will be introduced in this section. Projection areas. By following ...
The evolution of brains from early mammals to humans
... grasp maternal hair and nurse.29 As placental mammals could have long gestation periods for brain development, they thereby escaped this restriction. Overall, the comparative evidence indicates that early mammals had on the order of 15–20 cortical areas (see Figure 1) that were specialized for diffe ...
... grasp maternal hair and nurse.29 As placental mammals could have long gestation periods for brain development, they thereby escaped this restriction. Overall, the comparative evidence indicates that early mammals had on the order of 15–20 cortical areas (see Figure 1) that were specialized for diffe ...
Predictive Coding: A Possible Explanation of Filling
... model and the efficient coding of natural images. In such probabilistic frameworks, the job of the visual system is to infer or estimate the properties of the world from signals coming from receptors [26–28]. In HPC framework, this job is hypothesized to be completed by concurrent prediction-correct ...
... model and the efficient coding of natural images. In such probabilistic frameworks, the job of the visual system is to infer or estimate the properties of the world from signals coming from receptors [26–28]. In HPC framework, this job is hypothesized to be completed by concurrent prediction-correct ...
Anterograde or retrograde transsynaptic labeling
... efining the connections among neurons will be necessary in order to fully understand the information transformations carried out by the nervous system. Ideally, a method for this task would be rapid and straightforward in its application, could be delivered in vivo to most or all locations, and could ...
... efining the connections among neurons will be necessary in order to fully understand the information transformations carried out by the nervous system. Ideally, a method for this task would be rapid and straightforward in its application, could be delivered in vivo to most or all locations, and could ...
- Donders Institute for Brain, Cognition and Behaviour
... magnetoencephalography (Nishitani and Hari, 2000). What specific aspects of an action are encoded by the mirror system? Single-unit studies in the monkey suggest that cortical representations of an action are organized around the goal or target of that action. Many F5 neurons become active during ac ...
... magnetoencephalography (Nishitani and Hari, 2000). What specific aspects of an action are encoded by the mirror system? Single-unit studies in the monkey suggest that cortical representations of an action are organized around the goal or target of that action. Many F5 neurons become active during ac ...
Motor systems
... activation within a pool leads to activation of units producing the smallest amount of force before those producing larger amounts of force. This sequence, known as a size principle, results from passive electrical properties of motor neurons and their synaptic inputs. Alternative recruitment sequen ...
... activation within a pool leads to activation of units producing the smallest amount of force before those producing larger amounts of force. This sequence, known as a size principle, results from passive electrical properties of motor neurons and their synaptic inputs. Alternative recruitment sequen ...
Open access
... in the final behavior initiating mechanism, deep buried in the flys brain. Such mechanism or agent provide the fly with genuine spontaneity -a distinctive label of living creaturesenabling the insect to get bored about tedious situations and deciding (self decision) to take radical (and possibly life s ...
... in the final behavior initiating mechanism, deep buried in the flys brain. Such mechanism or agent provide the fly with genuine spontaneity -a distinctive label of living creaturesenabling the insect to get bored about tedious situations and deciding (self decision) to take radical (and possibly life s ...
BIOL 105 S 2011 MTX 2 QA 110512.1
... A) bipolar. B) unipolar. C) anaxonic. D) multipolar. E) tripolar. Answer: D ...
... A) bipolar. B) unipolar. C) anaxonic. D) multipolar. E) tripolar. Answer: D ...
Morphological Changes in the Hippocampus Following Nicotine and
... is administered once or repeatedly (Riljak et al. 2005). The cell loss is not specific for kainic acid administration only but also for other neurotoxic insults (e.g. alcohol) (Milotová et al. 2005). Nitric oxide (NO) is produced from L-arginine by nitric oxide synthase (NOS). There are at least thr ...
... is administered once or repeatedly (Riljak et al. 2005). The cell loss is not specific for kainic acid administration only but also for other neurotoxic insults (e.g. alcohol) (Milotová et al. 2005). Nitric oxide (NO) is produced from L-arginine by nitric oxide synthase (NOS). There are at least thr ...
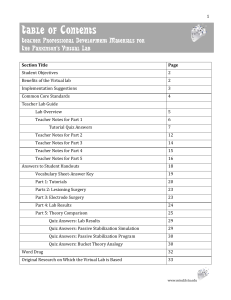
Table of Contents - The Mind Project
... In addition to role-playing and being able to collect data to interpret, this virtual lab, allows students to see how the research process works, on a bigger, grander scale. Students learn that there is a cellular phenomenon that scientists do not understand. Data show that Parkinson’s patients have ...
... In addition to role-playing and being able to collect data to interpret, this virtual lab, allows students to see how the research process works, on a bigger, grander scale. Students learn that there is a cellular phenomenon that scientists do not understand. Data show that Parkinson’s patients have ...
Synaptic Pruning in Development: A Novel Account in Neural Terms
... 1995] and the dentate gyrus [Eckenho and Rakic, 1991]. The time scale of synaptic elimination was found to vary between di erent cortical areas, coarsely following a dorsal to frontal order [Rakic et al., 1994]. Larger temporal di erences were found between species; in some species, the peak level ...
... 1995] and the dentate gyrus [Eckenho and Rakic, 1991]. The time scale of synaptic elimination was found to vary between di erent cortical areas, coarsely following a dorsal to frontal order [Rakic et al., 1994]. Larger temporal di erences were found between species; in some species, the peak level ...
Theoretical Systems Neuroscience
... representations of the world. To start with the basics, we only focus on a tiny aspect of the world, namely a single feature of a single object. This could for example be the orientation of a line segment, the spatial location of a dot, the direction of motion of a tennis ball, or ...
... representations of the world. To start with the basics, we only focus on a tiny aspect of the world, namely a single feature of a single object. This could for example be the orientation of a line segment, the spatial location of a dot, the direction of motion of a tennis ball, or ...
Logical Levels of Steroid Hormone Action in the
... evidence exists, however, for steroid actions in the MPOA to facilitate mounting, intromission, and ejaculation, since lesions of this region eliminate these male sexual behaviors in rats, electrical stimulation augments these behaviors, and androgen implants in this region in castrates reinstate th ...
... evidence exists, however, for steroid actions in the MPOA to facilitate mounting, intromission, and ejaculation, since lesions of this region eliminate these male sexual behaviors in rats, electrical stimulation augments these behaviors, and androgen implants in this region in castrates reinstate th ...
For Peer Review - diss.fu
... modulation of ascending monoamine systems in response to afferents from limbic regions and basal ganglia. The LHb is implicated in various biological functions, such as reward, sleepwake cycle, feeding, pain processing and memory formation. The modulatory role of the LHb is partly assumed by putativ ...
... modulation of ascending monoamine systems in response to afferents from limbic regions and basal ganglia. The LHb is implicated in various biological functions, such as reward, sleepwake cycle, feeding, pain processing and memory formation. The modulatory role of the LHb is partly assumed by putativ ...
Opposite Functions of Histamine H1 and H2 Receptors and H3
... the recording electrode (Zhou and Hablitz 1996). After electrophysiological recordings, brain slices were fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde in 0.1 M phosphate buffer (PB) at 4°C overnight. Without resectioning, slices were then processed for visualization of neurobiotin-filled neurons. Endogenous peroxid ...
... the recording electrode (Zhou and Hablitz 1996). After electrophysiological recordings, brain slices were fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde in 0.1 M phosphate buffer (PB) at 4°C overnight. Without resectioning, slices were then processed for visualization of neurobiotin-filled neurons. Endogenous peroxid ...
Electrophysiological and Pharmacological Evidence for the Role of
... activity in the NAS of anesthetized animals, an effect that appears to be mediated by both D, and D, dopamine receptors (White and Wang, 1986; White et al., 1987). Moreover, it has been suggested that the synergistic action of these two dopamine receptor subtypes may be necessary for the full expres ...
... activity in the NAS of anesthetized animals, an effect that appears to be mediated by both D, and D, dopamine receptors (White and Wang, 1986; White et al., 1987). Moreover, it has been suggested that the synergistic action of these two dopamine receptor subtypes may be necessary for the full expres ...
Lactate Receptor Sites Link Neurotransmission
... receptor in the brain has not been reported, nor its ultrastructural localization in brain or adipose tissue. Here, we show for the first time the subcellular localization and the function of the lactate receptor GPR81 protein in brain cells. L-Lactate caused a dose-dependent reduction of cAMP in hip ...
... receptor in the brain has not been reported, nor its ultrastructural localization in brain or adipose tissue. Here, we show for the first time the subcellular localization and the function of the lactate receptor GPR81 protein in brain cells. L-Lactate caused a dose-dependent reduction of cAMP in hip ...
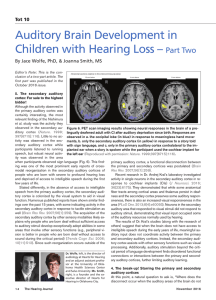
Auditory Brain Development in Children with Hearing Loss – Part Two
... area (PLoS One. 2013;8[4]:e60093). Neurons in the secondary secondary auditory cortex in response to tactile stimulation as auditory area that responded to visual stimuli did not respond to well (Brain Res Rev. 2007;56[1]:259). The acquisition of the auditory stimuli, demonstrating that visual input ...
... area (PLoS One. 2013;8[4]:e60093). Neurons in the secondary secondary auditory cortex in response to tactile stimulation as auditory area that responded to visual stimuli did not respond to well (Brain Res Rev. 2007;56[1]:259). The acquisition of the auditory stimuli, demonstrating that visual input ...
PRINCIPLES OF NEUROBIOLOGY CHAPTER 6
... between a PN and its corresponding ORN would thus reduce the linear correlation between ORN and PN responses. As Bhandawat et al. note, errors in the estimation of average responses could produce large errors in the rank order of odor preferences: an error in the estimate of a neuron’s response to ...
... between a PN and its corresponding ORN would thus reduce the linear correlation between ORN and PN responses. As Bhandawat et al. note, errors in the estimation of average responses could produce large errors in the rank order of odor preferences: an error in the estimate of a neuron’s response to ...
Synaptic gating

Synaptic gating is the ability of neural circuits to gate inputs by either suppressing or facilitating specific synaptic activity. Selective inhibition of certain synapses has been studied thoroughly (see Gate theory of pain), and recent studies have supported the existence of permissively gated synaptic transmission. In general, synaptic gating involves a mechanism of central control over neuronal output. It includes a sort of gatekeeper neuron, which has the ability to influence transmission of information to selected targets independently of the parts of the synapse upon which it exerts its action (see also neuromodulation).Bistable neurons have the ability to oscillate between a hyperpolarized (down state) and a depolarized (up state) resting membrane potential without firing an action potential. These neurons can thus be referred to as up/down neurons. According to one model, this ability is linked to the presence of NMDA and AMPA glutamate receptors. External stimulation of the NMDA receptors is responsible for moving the neuron from the down state to the up state, while the stimulation of AMPA receptors allows the neuron to reach and surpass the threshold potential. Neurons that have this bistable ability have the potential to be gated because outside gatekeeper neurons can modulate the membrane potential of the gated neuron by selectively shifting them from the up state to the down state. Such mechanisms have been observed in the nucleus accumbens, with gatekeepers originating in the cortex, thalamus and basal ganglia.