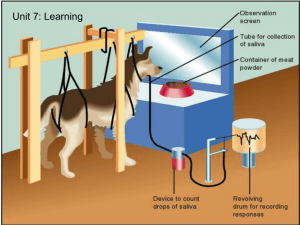
Classical Conditioning
... Stimulus: causes an organism to react or respond Response: The reaction to a stimulus ...
... Stimulus: causes an organism to react or respond Response: The reaction to a stimulus ...
Notes Part 1 (10 pts)
... o associate a neutral stimulus (bell) with an unconditioned stimulus (food) So this neutral stimulus (bell) comes to elicit a conditioned response (salivate) Extinction o diminishing of a CR (salivation) o in classical conditioning, when a UCS (food) does not follow a CS(bell) Spontaneous Recovery ...
... o associate a neutral stimulus (bell) with an unconditioned stimulus (food) So this neutral stimulus (bell) comes to elicit a conditioned response (salivate) Extinction o diminishing of a CR (salivation) o in classical conditioning, when a UCS (food) does not follow a CS(bell) Spontaneous Recovery ...
13 Learning Guided Notes - Appoquinimink High School
... ___________________________ (to the bell) For example: For Pavlov, the previously _____________________________ was the ________________. During conditioning, the tone was paired with the food (__________). After conditioning, the tone, when presented alone, produced ___________________________ ...
... ___________________________ (to the bell) For example: For Pavlov, the previously _____________________________ was the ________________. During conditioning, the tone was paired with the food (__________). After conditioning, the tone, when presented alone, produced ___________________________ ...
HERE
... “To predict, given the stimulus, what reaction will take place; or, given the reaction, state what the situation or stimulus is that has caused the reaction” (1930, p. 11). ...
... “To predict, given the stimulus, what reaction will take place; or, given the reaction, state what the situation or stimulus is that has caused the reaction” (1930, p. 11). ...
chp 1
... • Cognitive theories focus on consumers as problem solvers who learn when they observe relationships ...
... • Cognitive theories focus on consumers as problem solvers who learn when they observe relationships ...
Chapter 7 Objectives 1. List three key ideas in the definition of
... 2. Define classical conditioning. Identify the unconditioned stimulus (UCS), unconditioned response (UCR), conditioned stimulus (CS), and conditioned response (CR) in Pavlov’s experiments and other examples. 3. Compare the acquisition, extinction, and spontaneous recovery of a classically conditione ...
... 2. Define classical conditioning. Identify the unconditioned stimulus (UCS), unconditioned response (UCR), conditioned stimulus (CS), and conditioned response (CR) in Pavlov’s experiments and other examples. 3. Compare the acquisition, extinction, and spontaneous recovery of a classically conditione ...
Classical Conditioning
... CS is presented and terminated BEFORE presentation of the UCS/US Conditioning often effective when the interval BETWEEN presentation of the CS the UCS/US is about a half second Fear studies; dependent on usage of hippocampus ...
... CS is presented and terminated BEFORE presentation of the UCS/US Conditioning often effective when the interval BETWEEN presentation of the CS the UCS/US is about a half second Fear studies; dependent on usage of hippocampus ...
Jeopardy Learning
... Learning that occurs rapidly as a result of understanding all the elements of a problem ...
... Learning that occurs rapidly as a result of understanding all the elements of a problem ...
Module 20: Classical Conditioning
... Acquisition: The initial stage in classical conditioning when the neutral stimulus is associated with an unconditioned stimulus. This kind of conditioning occurs faster when there is a small amount of time between when the conditioned stimulus is presented and when the UCS is presented. Extinctio ...
... Acquisition: The initial stage in classical conditioning when the neutral stimulus is associated with an unconditioned stimulus. This kind of conditioning occurs faster when there is a small amount of time between when the conditioned stimulus is presented and when the UCS is presented. Extinctio ...
WORKSHEET 8.1 Classical vs. Instrumental Conditioning
... John B. Watson was attempting to teach Albert, an infant, to fear a white rat. Watson presented the rat to Albert and then smacked a metal pipe on concrete, creating a huge and terrible noise. Albert responded with fear. This process was repeated many times until Albert began to show fearful behavio ...
... John B. Watson was attempting to teach Albert, an infant, to fear a white rat. Watson presented the rat to Albert and then smacked a metal pipe on concrete, creating a huge and terrible noise. Albert responded with fear. This process was repeated many times until Albert began to show fearful behavio ...
File - Mr. Kittek
... d. A classically conditioned response, like any other behavior, is subject to change. - Pavlov discovered that if he stopped presenting food after the sound of the tuning fork, the sound gradually lost its effect on the dog. - He called this _________________________________ because the CR had gradu ...
... d. A classically conditioned response, like any other behavior, is subject to change. - Pavlov discovered that if he stopped presenting food after the sound of the tuning fork, the sound gradually lost its effect on the dog. - He called this _________________________________ because the CR had gradu ...
Page 1 ! ! ! ! ! ! ) ) ) ) ) ) ) ) ) ) ) ) ) ) ) ) ) ) ) Page 2 Learning)and
... is!presented!without!the!US.!The!condition!will!gradually!disappear.!! Implication:!You!can!change!behavior!by!ceasing!the!pairing!of!the!conditioned!stimulus!&!the! unconditioned!stimulus! Spontaneous/recovery:!a!CR!(salivation!in!response!to!the!light!or!bell)!will!reappear!after!a!rest!period,! ...
... is!presented!without!the!US.!The!condition!will!gradually!disappear.!! Implication:!You!can!change!behavior!by!ceasing!the!pairing!of!the!conditioned!stimulus!&!the! unconditioned!stimulus! Spontaneous/recovery:!a!CR!(salivation!in!response!to!the!light!or!bell)!will!reappear!after!a!rest!period,! ...
CLASSICAL CONDITIONING I. IVAN PAVLOV (1844
... Most advanced mode of thinking (if developed & maintained) ...
... Most advanced mode of thinking (if developed & maintained) ...
Behavioral Learning Theory
... illogical fears and concerns like fear of failure, fear of public speaking and general school obsession. Behavioral or operant conditioning occurs when a response to a stimulus is reinforced. Basically, operant conditioning is a simple feedback system. If a reward or reinforcement follows the respon ...
... illogical fears and concerns like fear of failure, fear of public speaking and general school obsession. Behavioral or operant conditioning occurs when a response to a stimulus is reinforced. Basically, operant conditioning is a simple feedback system. If a reward or reinforcement follows the respon ...
3D Classical Conditioning
... Conditioned Stimulus (CS) • Previously neutral stimulus that, through learning, gains the power to cause a response • The CS must be a neutral stimulus before conditioning occurs. ...
... Conditioned Stimulus (CS) • Previously neutral stimulus that, through learning, gains the power to cause a response • The CS must be a neutral stimulus before conditioning occurs. ...
Julie, Nattalie, Lisa Pavlov`s_Theory_of_Learning 2
... Nattallie Masso BSN, RN Wilmington University, MSN6501 ...
... Nattallie Masso BSN, RN Wilmington University, MSN6501 ...
L8learning
... Unconditioned stimulus Unconditioned response Conditioned stimulus Conditioned response ...
... Unconditioned stimulus Unconditioned response Conditioned stimulus Conditioned response ...
Can you answer these questions about classical and operant
... A. Learning is a relatively permanent change in behavior B. Learning only occurs through conditioning C. Learning is a passive process D. All of the above 4. In classical conditioning, the natural and unlearned reaction to an unconditioned stimulus (UCS) is known as the: A. Unconditioned stimulus B. ...
... A. Learning is a relatively permanent change in behavior B. Learning only occurs through conditioning C. Learning is a passive process D. All of the above 4. In classical conditioning, the natural and unlearned reaction to an unconditioned stimulus (UCS) is known as the: A. Unconditioned stimulus B. ...
Classical conditioning

Classical conditioning (also known as Pavlovian or respondent conditioning) is a learning process in which an innate response to a potent stimulus comes to be elicited in response to a previously neutral stimulus; this is achieved by repeated pairings of the neutral stimulus with the potent stimulus. The basic facts about classical conditioning were discovered by Ivan Pavlov through his famous experiments with dogs. Together with operant conditioning, classical conditioning became the foundation of Behaviorism, a school of psychology that dominated psychology in the mid-20th century and is still an important influence on the practice of psychological therapy and the study of animal behaviour (ethology). Classical conditioning is now the best understood of the basic learning processes, and its neural substrates are beginning to be understood.