File
... Study Guide Chapters 9 – Learning: Principles & Applications Study the following and be prepared with your notebook: Chapter 9, Section 1: Classical Conditioning Vocabulary o Classical conditioning o Conditioned response (CR) o Neutral stimulus o Generalization o Unconditioned stimulus (US) o Disc ...
... Study Guide Chapters 9 – Learning: Principles & Applications Study the following and be prepared with your notebook: Chapter 9, Section 1: Classical Conditioning Vocabulary o Classical conditioning o Conditioned response (CR) o Neutral stimulus o Generalization o Unconditioned stimulus (US) o Disc ...
Classical Conditioning
... CS, such as the sound of a bell, classical conditioning had taken place because salivation would not be a usual response to the sound of a bell. ...
... CS, such as the sound of a bell, classical conditioning had taken place because salivation would not be a usual response to the sound of a bell. ...
Describe and evaluate either classical or operant
... and fear the unconditioned response (UCR). The other stimuli were neutral because they did not produce fear. When Albert was just over eleven months old, the rat and the UCS were presented together: as Albert reached out to stroke the animal, Watson struck the bar behind his head. This occurred seve ...
... and fear the unconditioned response (UCR). The other stimuli were neutral because they did not produce fear. When Albert was just over eleven months old, the rat and the UCS were presented together: as Albert reached out to stroke the animal, Watson struck the bar behind his head. This occurred seve ...
Review Answers- Learning ch7
... b. Unconscious meaning that is attributed to new response patterns c. Response patterns that become extinguished gradually over time d. Delayed responses that occur when new stimuli are paired with familiar ones e. Learning that occurs is in the absence of rewards. * 12. That rats were more likely t ...
... b. Unconscious meaning that is attributed to new response patterns c. Response patterns that become extinguished gradually over time d. Delayed responses that occur when new stimuli are paired with familiar ones e. Learning that occurs is in the absence of rewards. * 12. That rats were more likely t ...
Edexcel AS learning approach classical conditioning
... Q: Give an example of how a more serious sexual fetish might be acquired by classical conditioning. ...
... Q: Give an example of how a more serious sexual fetish might be acquired by classical conditioning. ...
Classical Conditioning
... of time between presentations of the UCS/US – Combined with trace conditioning based on a period of time • i.e. dog starts to salivate at 7:59am because s/he is fed at 8am everyday ...
... of time between presentations of the UCS/US – Combined with trace conditioning based on a period of time • i.e. dog starts to salivate at 7:59am because s/he is fed at 8am everyday ...
A.P. Psychology 6 (A) - Classical Conditioning
... The originally irrelevant stimulus that, after association with an unconditioned stimulus (US), elicits a learned response ...
... The originally irrelevant stimulus that, after association with an unconditioned stimulus (US), elicits a learned response ...
File
... If you are bitten by a big dog and instead of generalizing and being scared of all dogs, you are only scared of big dogs ...
... If you are bitten by a big dog and instead of generalizing and being scared of all dogs, you are only scared of big dogs ...
Chapter Five Practice Quiz 2 Name: Schedule of reinforcement in
... 4. The reinforcement of each and every correct response. Continuous reinforcement 5. Development of nausea or aversive response to a particular taste because that taste was followed by a nausea reaction, occurring after only one association. Conditioned taste aversion 6. Modern theory in which class ...
... 4. The reinforcement of each and every correct response. Continuous reinforcement 5. Development of nausea or aversive response to a particular taste because that taste was followed by a nausea reaction, occurring after only one association. Conditioned taste aversion 6. Modern theory in which class ...
learning - baileyda
... • The initial stage of learning. • The phase where the neutral stimulus is associated with the UCS so that the neutral stimulus comes to elicit the CR (thus becoming the CS). • Higher order conditioning- a new neutral stimulus can become a new conditioned stimulus example if a tone signals salivatio ...
... • The initial stage of learning. • The phase where the neutral stimulus is associated with the UCS so that the neutral stimulus comes to elicit the CR (thus becoming the CS). • Higher order conditioning- a new neutral stimulus can become a new conditioned stimulus example if a tone signals salivatio ...
Classical Conditioning
... Acquisition Acquisition is the first stage in classical conditioning – where a NS is linked with a US that the NS begins triggering the CS Why are our bodies set up to be conditioned? Classical conditioning helps us prepare for good and bad events. This is why the neutral stimulus must happen f ...
... Acquisition Acquisition is the first stage in classical conditioning – where a NS is linked with a US that the NS begins triggering the CS Why are our bodies set up to be conditioned? Classical conditioning helps us prepare for good and bad events. This is why the neutral stimulus must happen f ...
Classical Conditioning PPT
... conditioning, a stimulus that unconditionally naturally and automatically - triggers a response Unconditioned Response (UCR): in classical conditioning, the unlearned, naturally occuring response to the UCS ...
... conditioning, a stimulus that unconditionally naturally and automatically - triggers a response Unconditioned Response (UCR): in classical conditioning, the unlearned, naturally occuring response to the UCS ...
Classical Conditioning
... • Laid the foundation for the mental processes & that John B. Watson ideas classical conditioning is a – To study how organisms respond to stimuli in their environments ...
... • Laid the foundation for the mental processes & that John B. Watson ideas classical conditioning is a – To study how organisms respond to stimuli in their environments ...
Learning Learning
... • Learning to link two stimuli in a way that helps us anticipate an event to which we have a reaction ...
... • Learning to link two stimuli in a way that helps us anticipate an event to which we have a reaction ...
Notes: Classical Conditioning
... Learning- A relatively permanent change in behavior that occurs because of experience. ...
... Learning- A relatively permanent change in behavior that occurs because of experience. ...
Types of learning
... Sensitization is an example of non-associative learning in which the progressive amplification of a response follows repeated administrations of a stimulus (Bell et al., 1995). An everyday example of this mechanism is the repeated tonic stimulation of peripheral nerves that will occur if a person ru ...
... Sensitization is an example of non-associative learning in which the progressive amplification of a response follows repeated administrations of a stimulus (Bell et al., 1995). An everyday example of this mechanism is the repeated tonic stimulation of peripheral nerves that will occur if a person ru ...
Chapter 1
... • The stimulus that was originally neutral becomes conditioned after it has been paired with the unconditioned stimulus • Will eventually elicit the unconditioned response by itself ...
... • The stimulus that was originally neutral becomes conditioned after it has been paired with the unconditioned stimulus • Will eventually elicit the unconditioned response by itself ...
Agenda: 1. Daily Sheet 2. Classical Conditioning Notes 3. Real
... Stimulus- what causes the response Response- the reaction to the stimulus Classical Conditioning- learning to associate two stimuli with each other and respond the same to both (ex: food & bell in Pavlov’s experiment) ...
... Stimulus- what causes the response Response- the reaction to the stimulus Classical Conditioning- learning to associate two stimuli with each other and respond the same to both (ex: food & bell in Pavlov’s experiment) ...
Learning – Classical Conditioning
... recommended study of behavior without reference to unobservable mental processes not universally accepted by all schools of thought today ...
... recommended study of behavior without reference to unobservable mental processes not universally accepted by all schools of thought today ...
Assumptions of Behaviorism
... A prompt of cue that comes before a behavior that results in the correct behavior being elicited. ...
... A prompt of cue that comes before a behavior that results in the correct behavior being elicited. ...
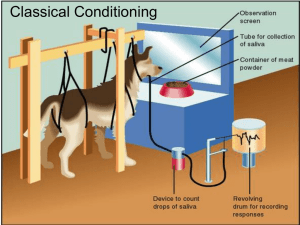
Classical conditioning

Classical conditioning (also known as Pavlovian or respondent conditioning) is a learning process in which an innate response to a potent stimulus comes to be elicited in response to a previously neutral stimulus; this is achieved by repeated pairings of the neutral stimulus with the potent stimulus. The basic facts about classical conditioning were discovered by Ivan Pavlov through his famous experiments with dogs. Together with operant conditioning, classical conditioning became the foundation of Behaviorism, a school of psychology that dominated psychology in the mid-20th century and is still an important influence on the practice of psychological therapy and the study of animal behaviour (ethology). Classical conditioning is now the best understood of the basic learning processes, and its neural substrates are beginning to be understood.