Chapter Outline
... 3. Learning occurs when a neutral stimulus is regularly paired with a US and the neutral stimulus becomes a CS that elicits a CR that is similar to the original, unlearned one 4. Classical conditioning is also called Pavlovian or respondent conditioning B. Principles of classical conditioning 1. Ext ...
... 3. Learning occurs when a neutral stimulus is regularly paired with a US and the neutral stimulus becomes a CS that elicits a CR that is similar to the original, unlearned one 4. Classical conditioning is also called Pavlovian or respondent conditioning B. Principles of classical conditioning 1. Ext ...
File - It does not do to dwell on dreams and forget to live
... unconditioned stimulus and unconditioned response, respectively. The original and most famous example of classical conditioning involved the salivary conditioning of Pavlov's dogs. During his research on the physiology of digestion in dogs, Pavlov noticed that, rather than simply salivating in the p ...
... unconditioned stimulus and unconditioned response, respectively. The original and most famous example of classical conditioning involved the salivary conditioning of Pavlov's dogs. During his research on the physiology of digestion in dogs, Pavlov noticed that, rather than simply salivating in the p ...
half a second before
... The initial stage in classical conditioning. during which association between a neutral stimulus and a US takes place. ...
... The initial stage in classical conditioning. during which association between a neutral stimulus and a US takes place. ...
Behavioural Psychology worksheet
... 1. What can you assume that John Watson believed about human behaviour? ________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________ ...
... 1. What can you assume that John Watson believed about human behaviour? ________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________ ...
Observational Learning - Social Studies with Mrs. Gabehart
... • Insight Learning: This is an extension of the term, insight which was identified by Wolfgang Kohler while studying the behavior of chimpanzees. He said that insight learning is a type of learning or problem solving that happens all-of-a-sudden through understanding the relationships of various pa ...
... • Insight Learning: This is an extension of the term, insight which was identified by Wolfgang Kohler while studying the behavior of chimpanzees. He said that insight learning is a type of learning or problem solving that happens all-of-a-sudden through understanding the relationships of various pa ...
syllabus
... * habituation: pp. 47-51; omit pp. 51-53 on "Physiological Mechanisms Of Habituation"; continue with pp. 53-59 on the "Opponent-Process Theory" CH.4: Basic Principles Of Classical Conditioning -- entire chapter; note highlights and exceptions: * omit "Aversive Counterconditioning" and "Treatment of ...
... * habituation: pp. 47-51; omit pp. 51-53 on "Physiological Mechanisms Of Habituation"; continue with pp. 53-59 on the "Opponent-Process Theory" CH.4: Basic Principles Of Classical Conditioning -- entire chapter; note highlights and exceptions: * omit "Aversive Counterconditioning" and "Treatment of ...
Powerpoint
... experience” (Wade & Tavris, 2005, p. 285) “… any relatively permanent change in behavior that occurs because of experience” (Wade & Tavris, 2005, p. 285) But…what about new information? Ideas? Memories? ...
... experience” (Wade & Tavris, 2005, p. 285) “… any relatively permanent change in behavior that occurs because of experience” (Wade & Tavris, 2005, p. 285) But…what about new information? Ideas? Memories? ...
Lecture 26
... Pavlov was studying the digestive system of dogs and became intrigued with his observation that dogs deprived of food began to salivate when one of his assistants walked into the room. He began to investigate this phenomena and established the laws of classical conditioning. Classical Conditioning: ...
... Pavlov was studying the digestive system of dogs and became intrigued with his observation that dogs deprived of food began to salivate when one of his assistants walked into the room. He began to investigate this phenomena and established the laws of classical conditioning. Classical Conditioning: ...
File - Lindsay Social Studies
... An unconditioned response is the unlearned response that occurs naturally in response to the unconditioned stimulus. How you feel about something is your unconditioned response Can be different each time we see it ...
... An unconditioned response is the unlearned response that occurs naturally in response to the unconditioned stimulus. How you feel about something is your unconditioned response Can be different each time we see it ...
File - Ms.Carey`s Webpage!
... put food in a dog’s mouth the animal would invariably salivate. He also noticed that when he worked with the same dog repeatedly, the dog began to salivating to stimuli associated with food- to the mere sight of food, to the food dish, to the presence of the person who regularly brought the food. At ...
... put food in a dog’s mouth the animal would invariably salivate. He also noticed that when he worked with the same dog repeatedly, the dog began to salivating to stimuli associated with food- to the mere sight of food, to the food dish, to the presence of the person who regularly brought the food. At ...
File
... put food in a dog’s mouth the animal would invariably salivate. He also noticed that when he worked with the same dog repeatedly, the dog began to salivating to stimuli associated with food- to the mere sight of food, to the food dish, to the presence of the person who regularly brought the food. At ...
... put food in a dog’s mouth the animal would invariably salivate. He also noticed that when he worked with the same dog repeatedly, the dog began to salivating to stimuli associated with food- to the mere sight of food, to the food dish, to the presence of the person who regularly brought the food. At ...
File
... b. Operant; suppressing d. respondent; suppressing 17. In Pavlov’s studies of classical conditioning of a dog’s salivary responses, spontaneous recovery occurred: a. During acquisition, when the CS was first paired with the US b. During extinction, when the CS was first presented by itself c. When t ...
... b. Operant; suppressing d. respondent; suppressing 17. In Pavlov’s studies of classical conditioning of a dog’s salivary responses, spontaneous recovery occurred: a. During acquisition, when the CS was first paired with the US b. During extinction, when the CS was first presented by itself c. When t ...
Study Guide 7 Learning
... 8. Conditioned Stimulus (CS): CS in Pavlov’s dogs: 9. Conditioned Response (CR): CR in Pavlov’s dogs: 10. Acquisition: 11. What is the biological reason that humans and animals can be conditioned? 12. Define higher-order conditioning (second-order conditioning): Example: 13. Extinction: Example: 14. ...
... 8. Conditioned Stimulus (CS): CS in Pavlov’s dogs: 9. Conditioned Response (CR): CR in Pavlov’s dogs: 10. Acquisition: 11. What is the biological reason that humans and animals can be conditioned? 12. Define higher-order conditioning (second-order conditioning): Example: 13. Extinction: Example: 14. ...
Intro to Learning
... • Acquisition: the stage when the CS and US are paired together. • Generalization: when the CR occurs even if the CS is slightly different • Discrimination: the capacity to distinguish between similar but distinct stimuli. • Extinction: the gradual elimination of a learned response that occurs when ...
... • Acquisition: the stage when the CS and US are paired together. • Generalization: when the CR occurs even if the CS is slightly different • Discrimination: the capacity to distinguish between similar but distinct stimuli. • Extinction: the gradual elimination of a learned response that occurs when ...
Classical Conditioning
... principles of classical conditioning? • Learning of an association does not require repeated pairings of the stimulus and response. • The time delay is in hours and not seconds. ...
... principles of classical conditioning? • Learning of an association does not require repeated pairings of the stimulus and response. • The time delay is in hours and not seconds. ...
Module 10: Operant & Cognitive Approaches
... ▪ During conditioning: Neutral Stimulus/NS (bell) + Unconditioned Stimulus/UCS (food) = Unconditioned Response/UCR (salivating dog) ...
... ▪ During conditioning: Neutral Stimulus/NS (bell) + Unconditioned Stimulus/UCS (food) = Unconditioned Response/UCR (salivating dog) ...
Day 16 (Nov 15th, chapter 6).
... and neutral stimuli - a neutral stimulus is consistently followed by a UCS as it becomes a CS ...
... and neutral stimuli - a neutral stimulus is consistently followed by a UCS as it becomes a CS ...
Chapter 8 Vocabulary
... experience. (p.287) In ____________________ ____________________, organisms learn that certain events occur together. Two variations of associative learning are classical conditioning and operant conditioning. (p. 288) ______________________ is the school of thought maintaining that psychology shoul ...
... experience. (p.287) In ____________________ ____________________, organisms learn that certain events occur together. Two variations of associative learning are classical conditioning and operant conditioning. (p. 288) ______________________ is the school of thought maintaining that psychology shoul ...
Ch. 5 Practice
... a. it is also known as second-order conditioning b. it involves a second conditioned stimulus c. it occurs even though the new CS has never been paired with the UCS d. it occurs in dogs but not in people ...
... a. it is also known as second-order conditioning b. it involves a second conditioned stimulus c. it occurs even though the new CS has never been paired with the UCS d. it occurs in dogs but not in people ...
Learning
... Review of Classical Conditioning Terms Neutral Stimulus (NS) A stimulus that does not cause a response Unconditioned Stimulus (US) a stimulus that causes an automatic response ...
... Review of Classical Conditioning Terms Neutral Stimulus (NS) A stimulus that does not cause a response Unconditioned Stimulus (US) a stimulus that causes an automatic response ...
Chapter 8
... Unconditioned Stimulus (UCS) stimulus that unconditionally--automatically and naturally--triggers a response ...
... Unconditioned Stimulus (UCS) stimulus that unconditionally--automatically and naturally--triggers a response ...
Pearson_AP_Quizzes_files/ch 5 CC quiz practice
... MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Conditioned taste aversions are found ________. A) only in nonhuman animals B) only in humans C) in virtually all animals D) in humans and other animals with a well-developed sense of taste ...
... MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Conditioned taste aversions are found ________. A) only in nonhuman animals B) only in humans C) in virtually all animals D) in humans and other animals with a well-developed sense of taste ...
CHAPTER 7—LEARNING I. Introduction A. Learning – involves the
... Conditioned stimulus (CS) – a stimulus that is initially neutral and produces no reliable response in an organism ...
... Conditioned stimulus (CS) – a stimulus that is initially neutral and produces no reliable response in an organism ...
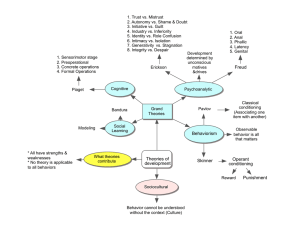
02Theories of development
... 1. Trust vs. Mistrust 2. Autonomy vs. Shame & Doubt 3. Initiative vs. Guilt 4. Industry vs. Inferiority 5. Identity vs. Role Confusion 6. Intimacy vs. Isolation 7. Generativity vs. Stagnation 8. Integrity vs. Despair 1. Sensorimotor stage 2. Preoperational 3. Concrete operations 4. Formal Operations ...
... 1. Trust vs. Mistrust 2. Autonomy vs. Shame & Doubt 3. Initiative vs. Guilt 4. Industry vs. Inferiority 5. Identity vs. Role Confusion 6. Intimacy vs. Isolation 7. Generativity vs. Stagnation 8. Integrity vs. Despair 1. Sensorimotor stage 2. Preoperational 3. Concrete operations 4. Formal Operations ...
Classical conditioning

Classical conditioning (also known as Pavlovian or respondent conditioning) is a learning process in which an innate response to a potent stimulus comes to be elicited in response to a previously neutral stimulus; this is achieved by repeated pairings of the neutral stimulus with the potent stimulus. The basic facts about classical conditioning were discovered by Ivan Pavlov through his famous experiments with dogs. Together with operant conditioning, classical conditioning became the foundation of Behaviorism, a school of psychology that dominated psychology in the mid-20th century and is still an important influence on the practice of psychological therapy and the study of animal behaviour (ethology). Classical conditioning is now the best understood of the basic learning processes, and its neural substrates are beginning to be understood.