Classical Conditioning
... bell when placing food down) 3. CS- Conditioned Stimulus- bell CR- Conditioned Response- salivate when hearing bell ...
... bell when placing food down) 3. CS- Conditioned Stimulus- bell CR- Conditioned Response- salivate when hearing bell ...
syllabus
... * habituation: pp. 47-51; omit pp. 51-53 on "Physiological Mechanisms Of Habituation"; continue with pp. 53-59 on the "Opponent-Process Theory" CH.4: Basic Principles Of Classical Conditioning -- entire chapter; note highlights and exceptions: * omit "Aversive Counterconditioning" and "Treatment of ...
... * habituation: pp. 47-51; omit pp. 51-53 on "Physiological Mechanisms Of Habituation"; continue with pp. 53-59 on the "Opponent-Process Theory" CH.4: Basic Principles Of Classical Conditioning -- entire chapter; note highlights and exceptions: * omit "Aversive Counterconditioning" and "Treatment of ...
Names - appsychologykta
... avoid, were unable to act in subsequent situations where avoidance or escape was possible. Extending the ramifications of these findings to humans, Seligman and his colleagues found that human motivation to initiate responses is also undermined by a lack of control over one's surroundings. Further r ...
... avoid, were unable to act in subsequent situations where avoidance or escape was possible. Extending the ramifications of these findings to humans, Seligman and his colleagues found that human motivation to initiate responses is also undermined by a lack of control over one's surroundings. Further r ...
... Animal models in current studies on human learning.- In this paper, the current contributions of animal research to contemporary conceptions in human learning are analysed. Three areas of inquiry which are yielding important results to the progress of our ideas about human learning are examined. Fir ...
Classical Conditioning
... • Neutral Stimulus (NS): the bell- before experiment dogs might have made dogs ears perk up not have made dogs salivate because it had nothing to do with food • Conditioned Response (CR): Salivation in response to the bell was a conditioned response (before bell was neutral or did not mean anything) ...
... • Neutral Stimulus (NS): the bell- before experiment dogs might have made dogs ears perk up not have made dogs salivate because it had nothing to do with food • Conditioned Response (CR): Salivation in response to the bell was a conditioned response (before bell was neutral or did not mean anything) ...
Chapter 8 pt. 1: Learning and Classical Conditioning
... Spontaneous Recovery Spontaneous Recovery refers to the reappearance, after a rest period, of an extinguished conditioned response. ...
... Spontaneous Recovery Spontaneous Recovery refers to the reappearance, after a rest period, of an extinguished conditioned response. ...
PSYC+103+Ch
... Neutral stimulus (NS): (i.e. tone of bell) a stimulus that doesn’t bring about specified response before conditioning Unconditioned Stimulus (UCS): (i.e. meat powder) stimulus that naturally brings about specified response (UCR) Unconditioned Response (UCR): (i.e. salivation) response that is natura ...
... Neutral stimulus (NS): (i.e. tone of bell) a stimulus that doesn’t bring about specified response before conditioning Unconditioned Stimulus (UCS): (i.e. meat powder) stimulus that naturally brings about specified response (UCR) Unconditioned Response (UCR): (i.e. salivation) response that is natura ...
Learning - McMurray VMC
... Review of Classical Conditioning Terms Neutral Stimulus (NS) A stimulus that does not cause a response Unconditioned Stimulus (US) a stimulus that causes an automatic response ...
... Review of Classical Conditioning Terms Neutral Stimulus (NS) A stimulus that does not cause a response Unconditioned Stimulus (US) a stimulus that causes an automatic response ...
File
... Associative Learning: Learning that certain events occur together the events may be two stimuli (as in classical conditioning) or a response and its consequences (as in operant conditioning). Ex.) Two related events: Stimulus 1: Lightening + Stimulus 2: Thunder Result after repetition: Stimulus: We ...
... Associative Learning: Learning that certain events occur together the events may be two stimuli (as in classical conditioning) or a response and its consequences (as in operant conditioning). Ex.) Two related events: Stimulus 1: Lightening + Stimulus 2: Thunder Result after repetition: Stimulus: We ...
A.P. Psychology Modules 20-22
... Conditioned Stimulus (CS) originally irrelevant stimulus that, after association with an unconditioned stimulus, comes to trigger a conditioned response Conditioned Response (CR) learned response to a previously neutral conditioned stimulus ...
... Conditioned Stimulus (CS) originally irrelevant stimulus that, after association with an unconditioned stimulus, comes to trigger a conditioned response Conditioned Response (CR) learned response to a previously neutral conditioned stimulus ...
Chapter 8 pt. 1: Learning and Classical Conditioning
... Spontaneous Recovery Generalization Discrimination ...
... Spontaneous Recovery Generalization Discrimination ...
Slides 6
... Stimulus Generalization He also showed a fear response to a fluffy rabbit, a Santa Claus mask, Watson’s white hair, etc. Stimulus Discrimination He showed less fear response to a dog, and none to people’s hair that wasn’t white. Extinction Eventually his conditioned fear of rats and related things m ...
... Stimulus Generalization He also showed a fear response to a fluffy rabbit, a Santa Claus mask, Watson’s white hair, etc. Stimulus Discrimination He showed less fear response to a dog, and none to people’s hair that wasn’t white. Extinction Eventually his conditioned fear of rats and related things m ...
Learning - Psychological Sciences
... Classical Conditioning: Conditioned Stimuli and Responses Conditioned Stimulus (CS) – an originally neutral stimulus that, after association with an unconditioned stimulus (US), comes to trigger a conditioned response. - Example: tone, bell ringing ...
... Classical Conditioning: Conditioned Stimuli and Responses Conditioned Stimulus (CS) – an originally neutral stimulus that, after association with an unconditioned stimulus (US), comes to trigger a conditioned response. - Example: tone, bell ringing ...
Classical Conditioning
... Pavlov (early 20th century) influenced Watson • Watson is the father of behaviorism – Little Albert experiment ...
... Pavlov (early 20th century) influenced Watson • Watson is the father of behaviorism – Little Albert experiment ...
File
... it is time to write up your experience. First you need to explain how the experiment went, why it did or did not work, and what could have made it more or less successful in about 150-250 words. You must also apply the 9 terms to your experiment. The grade for this assignment is not based on the suc ...
... it is time to write up your experience. First you need to explain how the experiment went, why it did or did not work, and what could have made it more or less successful in about 150-250 words. You must also apply the 9 terms to your experiment. The grade for this assignment is not based on the suc ...
here
... neutral stimulus needs to come before the unconditioned stimulus. 2. The time in between the two stimuli should be about half a second. ...
... neutral stimulus needs to come before the unconditioned stimulus. 2. The time in between the two stimuli should be about half a second. ...
Mr. Walter Names: Psychology II Classical conditioning in the media
... http://teachers.sduhsd.k12.ca.us/jetheridge/Psychology/Classical%20Conditioni ...
... http://teachers.sduhsd.k12.ca.us/jetheridge/Psychology/Classical%20Conditioni ...
Classical conditioning

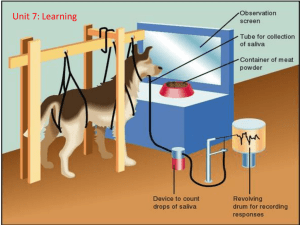
Classical conditioning (also known as Pavlovian or respondent conditioning) is a learning process in which an innate response to a potent stimulus comes to be elicited in response to a previously neutral stimulus; this is achieved by repeated pairings of the neutral stimulus with the potent stimulus. The basic facts about classical conditioning were discovered by Ivan Pavlov through his famous experiments with dogs. Together with operant conditioning, classical conditioning became the foundation of Behaviorism, a school of psychology that dominated psychology in the mid-20th century and is still an important influence on the practice of psychological therapy and the study of animal behaviour (ethology). Classical conditioning is now the best understood of the basic learning processes, and its neural substrates are beginning to be understood.