Learning Notes I think this is a fun lesson! Anyone with
... Learning is more than taking classes! It changes your behavior and how you react in certain situations. A fixed action pattern is determined by genetics, specific to each species. For example, a bee does not learn to become aggressive at the sight of blue, her genes simply turn on. Some people beli ...
... Learning is more than taking classes! It changes your behavior and how you react in certain situations. A fixed action pattern is determined by genetics, specific to each species. For example, a bee does not learn to become aggressive at the sight of blue, her genes simply turn on. Some people beli ...
Chapter 8 Practice Tes2
... C. suppress but not eliminate D. have unpredictable effects on 53. A fixed-interval schedule of reinforcement is one in which a response is reinforced only after a(n): A. specified time period has elapsed B. unpredictable time period has elapsed C. specified number of responses has been made D. unpr ...
... C. suppress but not eliminate D. have unpredictable effects on 53. A fixed-interval schedule of reinforcement is one in which a response is reinforced only after a(n): A. specified time period has elapsed B. unpredictable time period has elapsed C. specified number of responses has been made D. unpr ...
Basic Statistics for the Behavioral Sciences
... • Variable Interval Schedule (VI) – Reinforcement is given for the first correct response made after a varied (average) amount of time • Slow, steady response rates • Extremely resistant to extinction ...
... • Variable Interval Schedule (VI) – Reinforcement is given for the first correct response made after a varied (average) amount of time • Slow, steady response rates • Extremely resistant to extinction ...
Module 10: Operant & Cognitive Approaches
... ▪ During conditioning: Neutral Stimulus/NS (bell) + Unconditioned Stimulus/UCS (food) = Unconditioned Response/UCR (salivating dog) ...
... ▪ During conditioning: Neutral Stimulus/NS (bell) + Unconditioned Stimulus/UCS (food) = Unconditioned Response/UCR (salivating dog) ...
chapter 8 notes
... • 6. Negative reinforcement is another term for punishment. • 7. Psychologists agree that punishment, regardless of its form, has little effect on behavior. • 8. Animals learn only when rewards (AKA reinforcers) are given. • 9. Animals can learn to make virtually any response if consistently rewarde ...
... • 6. Negative reinforcement is another term for punishment. • 7. Psychologists agree that punishment, regardless of its form, has little effect on behavior. • 8. Animals learn only when rewards (AKA reinforcers) are given. • 9. Animals can learn to make virtually any response if consistently rewarde ...
Chapter 6 Outline Click Here!
... b. Classical Conditioning – Type of Learning in which a Stimulus acquires the Capacity to Evoke a Response that was originally evoked by another Stimulus. c. Ivan Pavlov i. Pavlovian Conditioning ii. Pavlov’s Dogs – Prior to Dogs being Fed Meat, a Clicking Noise Occurred. 1. Dogs started Salivating ...
... b. Classical Conditioning – Type of Learning in which a Stimulus acquires the Capacity to Evoke a Response that was originally evoked by another Stimulus. c. Ivan Pavlov i. Pavlovian Conditioning ii. Pavlov’s Dogs – Prior to Dogs being Fed Meat, a Clicking Noise Occurred. 1. Dogs started Salivating ...
Psychoanalytic Theory
... crisis. His first five stages build on Freud’s theory; but he also described three adult stages. Behaviorism A theory of human development that studies observable behavior. Also called learning theory as it describes the laws and processes by which behavior is learned. Conditioning - the processes b ...
... crisis. His first five stages build on Freud’s theory; but he also described three adult stages. Behaviorism A theory of human development that studies observable behavior. Also called learning theory as it describes the laws and processes by which behavior is learned. Conditioning - the processes b ...
Learning and Memory
... Hippocampus has a three synaptic pathway Stimulate one area (mossy fibers) and record the action potentials in another (CA1) Stimulate multiple times to get a baseline response Once a stable baseline is established give a brief high frequency stimulating pulse Use the same stimulating pulse as in ba ...
... Hippocampus has a three synaptic pathway Stimulate one area (mossy fibers) and record the action potentials in another (CA1) Stimulate multiple times to get a baseline response Once a stable baseline is established give a brief high frequency stimulating pulse Use the same stimulating pulse as in ba ...
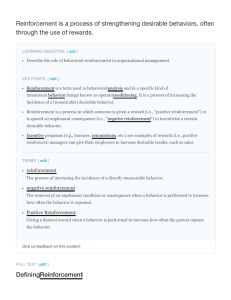
Reinforcement is a process of strengthening desirable
... Reinforcement is a term used in behavioral analysis and in a specific kind of intentional behavior change known as operantconditioning. It is a process of increasing the incidence of a (measurable) desirable behavior. Reinforcement is a process in which someone is given a reward (i.e., "positive rei ...
... Reinforcement is a term used in behavioral analysis and in a specific kind of intentional behavior change known as operantconditioning. It is a process of increasing the incidence of a (measurable) desirable behavior. Reinforcement is a process in which someone is given a reward (i.e., "positive rei ...
CHAPTER 8 CONDITIONING AND LEARNING
... 2. conditioned emotional response – an emotional response that has been linked to a previously non-emotional stimulus by classical conditioning. 3. vicarious classical conditioning – classical conditioning brought about by observing another person react to a particular stimulus. V. Operant Condition ...
... 2. conditioned emotional response – an emotional response that has been linked to a previously non-emotional stimulus by classical conditioning. 3. vicarious classical conditioning – classical conditioning brought about by observing another person react to a particular stimulus. V. Operant Condition ...
Classical Conditioning
... Negative Reinforcement The removal of a punishment or an aversive stimulus It STRENGTHENS behavior ...
... Negative Reinforcement The removal of a punishment or an aversive stimulus It STRENGTHENS behavior ...
Lecture Materials
... stimulus which is ‘rewarding’ to the animal. Negative reinforcement strengthens behavior because it stops or removes an unpleasant experience. For example, if you do not complete your homework you give your teacher 5.00 you will complete your homework to avoid paying 5.00, thus strengthening the beh ...
... stimulus which is ‘rewarding’ to the animal. Negative reinforcement strengthens behavior because it stops or removes an unpleasant experience. For example, if you do not complete your homework you give your teacher 5.00 you will complete your homework to avoid paying 5.00, thus strengthening the beh ...
1. An event that decreases the behavior that precedes it
... A) consistently used reinforcement in combination with punishment to shape their children's moral behavior. B) modeled a strong moral or humanitarian concern. C) consistently used psychological punishment rather than physical punishment in shaping their children's behavior. D) consistently used perm ...
... A) consistently used reinforcement in combination with punishment to shape their children's moral behavior. B) modeled a strong moral or humanitarian concern. C) consistently used psychological punishment rather than physical punishment in shaping their children's behavior. D) consistently used perm ...
Behavior Analysis and Strategy Application after Brain Injury
... Establishing Operation: Any change in the environment that alters the effectiveness of some stimulus or event as a reinforcer. Discriminative Stimulus: An event or stimulus that precedes a response and sets the occasion for the behavior to occur. Response/Behavior: "If a dead man can do it, it ain't ...
... Establishing Operation: Any change in the environment that alters the effectiveness of some stimulus or event as a reinforcer. Discriminative Stimulus: An event or stimulus that precedes a response and sets the occasion for the behavior to occur. Response/Behavior: "If a dead man can do it, it ain't ...
Pavlov spent the rest of his life outlining his ideas. He - JMB
... rang the bell, your dog could learn to salivate to the light without food ever being directly associated with it. ...
... rang the bell, your dog could learn to salivate to the light without food ever being directly associated with it. ...
Chapter 5 - Cengage Learning
... 2. Pavlov’s experiment demonstrated classical conditioning, in which a neutral stimulus is repeatedly paired with a stimulus that already triggers a reflexive response until the previously neutral stimulus alone provokes a similar response. a) The stimulus that naturally elicits a response without l ...
... 2. Pavlov’s experiment demonstrated classical conditioning, in which a neutral stimulus is repeatedly paired with a stimulus that already triggers a reflexive response until the previously neutral stimulus alone provokes a similar response. a) The stimulus that naturally elicits a response without l ...
Learning - Cloudfront.net
... Placed rabbit in corner of room while Peter munched on cookies. Gradually, the animal was brought closer. Peter ate treats and touched the rabbit at the same time ...
... Placed rabbit in corner of room while Peter munched on cookies. Gradually, the animal was brought closer. Peter ate treats and touched the rabbit at the same time ...
Learning - Mr. Hunsaker`s Classes
... • Although classical conditioning happens quite easily, there are a few basic principles that researchers have discovered: – The UR (unconditioned response) and CR (conditioned response) are essentially the same – salivation. – The CS (conditioned stimulus) must precede the US (unconditioned stimulu ...
... • Although classical conditioning happens quite easily, there are a few basic principles that researchers have discovered: – The UR (unconditioned response) and CR (conditioned response) are essentially the same – salivation. – The CS (conditioned stimulus) must precede the US (unconditioned stimulu ...
Chapter 6 – Perception
... a. If you associate a sound with a frightening consequence, then your fear may be aroused by the sound itself b. If sea snail repeatedly receives an electric shock just after being squirted, its withdrawal response to being squirted becomes stronger : associates squirt with shock c. Seals repeat beh ...
... a. If you associate a sound with a frightening consequence, then your fear may be aroused by the sound itself b. If sea snail repeatedly receives an electric shock just after being squirted, its withdrawal response to being squirted becomes stronger : associates squirt with shock c. Seals repeat beh ...
chapter 5 learning lecture notes
... nausea from that same taste. Taste aversions demonstrate that classical conditioning can occur even when there is a considerable delay between the CS (taste) and UCS (nauseous sensations). 7. Higher order conditioning occurs when a CS acts like a UCS, creating additional conditioned stimuli out of e ...
... nausea from that same taste. Taste aversions demonstrate that classical conditioning can occur even when there is a considerable delay between the CS (taste) and UCS (nauseous sensations). 7. Higher order conditioning occurs when a CS acts like a UCS, creating additional conditioned stimuli out of e ...
Convert
... Repetitive behaviors Reduce anxiety Acquired & maintained by… Negative reinforcement ~ ...
... Repetitive behaviors Reduce anxiety Acquired & maintained by… Negative reinforcement ~ ...
Unit 6 Power Point
... distinctive noise. After a while, Lulu starts to salivate whenever she hears the can opener. UCS? food ...
... distinctive noise. After a while, Lulu starts to salivate whenever she hears the can opener. UCS? food ...
Operant conditioning

Operant conditioning (also, “instrumental conditioning”) is a learning process in which behavior is sensitive to, or controlled by its consequences. For example, a child may learn to open a box to get the candy inside, or learn to avoid touching a hot stove. In contrast, classical conditioning causes a stimulus to signal a positive or negative consequence; the resulting behavior does not produce the consequence. For example, the sight of a colorful wrapper comes to signal ""candy"", causing a child to salivate, or the sound of a door slam comes to signal an angry parent, causing a child to tremble. The study of animal learning in the 20th century was dominated by the analysis of these two sorts of learning, and they are still at the core of behavior analysis.