Conditioning models of addiction: Part 1
... Over millions of years, the brains of animals have evolved a motivational system that helps animals survive and reproduce. Behavioural responses that lead to positive consequences, such as the reduction of hunger, are likely to be repeated. Moreover, animals learn to escape from or avoid painful or ...
... Over millions of years, the brains of animals have evolved a motivational system that helps animals survive and reproduce. Behavioural responses that lead to positive consequences, such as the reduction of hunger, are likely to be repeated. Moreover, animals learn to escape from or avoid painful or ...
Here
... Conditioning, in physiology, a behavioral process whereby a response becomes more frequent or more predictable in a given environment as a result of reinforcement, with reinforcement typically being a stimulus or reward for a desired response. Early in the 20th century, through the study of reflexes ...
... Conditioning, in physiology, a behavioral process whereby a response becomes more frequent or more predictable in a given environment as a result of reinforcement, with reinforcement typically being a stimulus or reward for a desired response. Early in the 20th century, through the study of reflexes ...
Classical Conditioning
... • Laid the foundation for the mental processes & that John B. Watson ideas classical conditioning is a – To study how organisms respond to stimuli in their environments ...
... • Laid the foundation for the mental processes & that John B. Watson ideas classical conditioning is a – To study how organisms respond to stimuli in their environments ...
Learning
... fairly high rate of response because many responses need to be made to get the reinforcer, but there is typically a pause after each reinforcer is obtained. B-Variable ratio: the reinforcer is obtained only after a varying number of responses have been made. These schedules produce very high rates o ...
... fairly high rate of response because many responses need to be made to get the reinforcer, but there is typically a pause after each reinforcer is obtained. B-Variable ratio: the reinforcer is obtained only after a varying number of responses have been made. These schedules produce very high rates o ...
AP Psychology
... reinforcement. (see Why Reinforcers Work) 20. Define punishment and describe its role in operant conditioning. Discuss the disadvantages of and guidelines for using punishment. (see Punishment) 21. Discuss how operant conditioning can be used to treat problematic behavior. (see Some Applications of ...
... reinforcement. (see Why Reinforcers Work) 20. Define punishment and describe its role in operant conditioning. Discuss the disadvantages of and guidelines for using punishment. (see Punishment) 21. Discuss how operant conditioning can be used to treat problematic behavior. (see Some Applications of ...
Thank you for helping the effort to translate PsychologyTools
... the CS and the US becomes weaker. This process is known as extinction. With time the CS stops leading to the CR and the CR is said to be extinguished. Why is classical conditioning important to therapists? Often neutral stimuli become associated with fearful situations and cause difficulties in peop ...
... the CS and the US becomes weaker. This process is known as extinction. With time the CS stops leading to the CR and the CR is said to be extinguished. Why is classical conditioning important to therapists? Often neutral stimuli become associated with fearful situations and cause difficulties in peop ...
MS-PowerPoint
... organism’s response to stimulus once that stimulus becomes familiar; simply getting used to... • However, organism does not learn anything new from that event ...
... organism’s response to stimulus once that stimulus becomes familiar; simply getting used to... • However, organism does not learn anything new from that event ...
CS - s3.amazonaws.com
... Associative Learning Learning that certain events occur together two stimuli a response and its consequences For example, you could associate Token Economy tickets with the Ziploc container at the front of the room, since I keep them there. Conditioning is the process of learning associations ...
... Associative Learning Learning that certain events occur together two stimuli a response and its consequences For example, you could associate Token Economy tickets with the Ziploc container at the front of the room, since I keep them there. Conditioning is the process of learning associations ...
Memory - K-Dub
... consistent responding, even if reinforcement stops (resists extinction) If the slot machine sometimes pays, I’ll pull the lever as many times as possible because it may pay this time! ...
... consistent responding, even if reinforcement stops (resists extinction) If the slot machine sometimes pays, I’ll pull the lever as many times as possible because it may pay this time! ...
Classical Conditioning
... Conditioning The process of learning associations between environmental events and behavioral responses. Two basic forms of conditioning are: • Classical conditioning (often involves involuntary responses) • Operant conditioning (often involves voluntary responses) Classical Conditioning A process o ...
... Conditioning The process of learning associations between environmental events and behavioral responses. Two basic forms of conditioning are: • Classical conditioning (often involves involuntary responses) • Operant conditioning (often involves voluntary responses) Classical Conditioning A process o ...
Chapter 5: Learning
... responses has been shown by research to be effective in influencing attitudes toward products or brands. III. Contemporary Views of Classical Conditioning Contemporary learning researchers acknowledge the importance of both mental factors and evolutionary influences in classical conditioning. A. Cog ...
... responses has been shown by research to be effective in influencing attitudes toward products or brands. III. Contemporary Views of Classical Conditioning Contemporary learning researchers acknowledge the importance of both mental factors and evolutionary influences in classical conditioning. A. Cog ...
Edward L. Thorndike
... • Operant conditioning investigates the influence of consequences on subsequent behavior. • Classical conditioning looks at conditioned involuntary responses such as eyeblinks or salivation, whereas Operant conditioning investigates the learning of voluntary responses such as pecking at a target or ...
... • Operant conditioning investigates the influence of consequences on subsequent behavior. • Classical conditioning looks at conditioned involuntary responses such as eyeblinks or salivation, whereas Operant conditioning investigates the learning of voluntary responses such as pecking at a target or ...
Thank you for helping the effort to translate Psychology Tools
... the CS and the US becomes weaker. This process is known as extinction. With time the CS stops leading to the CR and the CR is said to be extinguished. Why is classical conditioning important to therapists? Often neutral stimuli become associated with fearful situations and cause difficulties in peop ...
... the CS and the US becomes weaker. This process is known as extinction. With time the CS stops leading to the CR and the CR is said to be extinguished. Why is classical conditioning important to therapists? Often neutral stimuli become associated with fearful situations and cause difficulties in peop ...
Unconditioned Response, UR
... stimuli (CS and US). Operant conditioning, on the other hand, forms an association between behaviors and the resulting events, i.e. punishments and rewards ...
... stimuli (CS and US). Operant conditioning, on the other hand, forms an association between behaviors and the resulting events, i.e. punishments and rewards ...
Learning a - landman
... Strength of the original learning Pattern of reinforcement Variety of settings in which original learning took place Complexity of the behavior Learning through punishment ...
... Strength of the original learning Pattern of reinforcement Variety of settings in which original learning took place Complexity of the behavior Learning through punishment ...
practiceassessment-teacher-website-ch8
... bell he then gave the dog food. After several of these parings, Pavlov noticed that the dog would now salivate each time he solely heard the bell. Before conditioning had taken place the bell was called: A) Neutral stimulus (NS) D) Conditioned stimulus (CS) B) Unconditioned stimulus (UCS) E) Conditi ...
... bell he then gave the dog food. After several of these parings, Pavlov noticed that the dog would now salivate each time he solely heard the bell. Before conditioning had taken place the bell was called: A) Neutral stimulus (NS) D) Conditioned stimulus (CS) B) Unconditioned stimulus (UCS) E) Conditi ...
Module 2
... Studied with a procedure called Introspection Patients were asked about stimuli Focused on the fundamental mental states of: ...
... Studied with a procedure called Introspection Patients were asked about stimuli Focused on the fundamental mental states of: ...
Learning file RG 2
... Cognitive Map: a mental representation of the layout of one's environment. Latent Learning: learning that occurs, but is not apparent, until there is an incentive to demonstrate it Overjustification Effect: the effect of promising a reward for doing what one already likes to do. The person may now s ...
... Cognitive Map: a mental representation of the layout of one's environment. Latent Learning: learning that occurs, but is not apparent, until there is an incentive to demonstrate it Overjustification Effect: the effect of promising a reward for doing what one already likes to do. The person may now s ...
Document
... – each of these schedules will produce different response patterns in subjects; the variable ratio schedule best for most resistant to extinction ...
... – each of these schedules will produce different response patterns in subjects; the variable ratio schedule best for most resistant to extinction ...
Worksheet - Ms. Paras
... (Unconditioned stimulus), UCR (Unconditioned response), CS (Conditioned stimulus), and CR (conditioned response). If you decide the situation seems to be an example of operant conditioning, you should decide which of the following principles best fits: A. Positive reinforcement B. Negative reinforce ...
... (Unconditioned stimulus), UCR (Unconditioned response), CS (Conditioned stimulus), and CR (conditioned response). If you decide the situation seems to be an example of operant conditioning, you should decide which of the following principles best fits: A. Positive reinforcement B. Negative reinforce ...
Ch. 6: William James
... made discoveries – Applied the principles of his psychology to his own creativity ...
... made discoveries – Applied the principles of his psychology to his own creativity ...
Nervous System
... and stop in a humid area. Hydra that may bring the tentacles in contact with a food source, and ...
... and stop in a humid area. Hydra that may bring the tentacles in contact with a food source, and ...
Unit 5 Notes
... Superstitions: conditioned beliefs/behaviors with no statistical correlations to support them. So are superstitions the result of classic, operant, or observational conditioning?? Basically, yes. If you walk under a ladder and then trip and break your arm and that causes you to avoid walking under ...
... Superstitions: conditioned beliefs/behaviors with no statistical correlations to support them. So are superstitions the result of classic, operant, or observational conditioning?? Basically, yes. If you walk under a ladder and then trip and break your arm and that causes you to avoid walking under ...
Learning Chapter 7 PowerPoint
... 1. In classical conditioning, which is an originally irrelevant stimulus that becomes associated and triggers a learned response? ANSWER ...
... 1. In classical conditioning, which is an originally irrelevant stimulus that becomes associated and triggers a learned response? ANSWER ...
Research Paper: Individual investigation of a learning theory
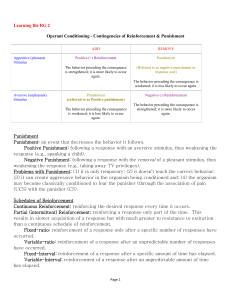
... In the above diagram, it illustrates that a response results in positive reinforcement. After repetition; (over time) the original response becomes known as a conditioned response; which results in a conditioned stimulus, also known as the reward/food. The pigeon learns that if it presses the button ...
... In the above diagram, it illustrates that a response results in positive reinforcement. After repetition; (over time) the original response becomes known as a conditioned response; which results in a conditioned stimulus, also known as the reward/food. The pigeon learns that if it presses the button ...
Operant conditioning

Operant conditioning (also, “instrumental conditioning”) is a learning process in which behavior is sensitive to, or controlled by its consequences. For example, a child may learn to open a box to get the candy inside, or learn to avoid touching a hot stove. In contrast, classical conditioning causes a stimulus to signal a positive or negative consequence; the resulting behavior does not produce the consequence. For example, the sight of a colorful wrapper comes to signal ""candy"", causing a child to salivate, or the sound of a door slam comes to signal an angry parent, causing a child to tremble. The study of animal learning in the 20th century was dominated by the analysis of these two sorts of learning, and they are still at the core of behavior analysis.