Biology Chapter 12 Review 5-6
... 5. Identify the 4 different types of nitrogenous bases? 6. Nitrogenous bases can be sorted into two groups. Name the groups and explain how they are classified. 7. What units make up the backbone of DNA? 8. Explain how the information Watson and Crick acquired from Rosalind Franklin and Chargaff was ...
... 5. Identify the 4 different types of nitrogenous bases? 6. Nitrogenous bases can be sorted into two groups. Name the groups and explain how they are classified. 7. What units make up the backbone of DNA? 8. Explain how the information Watson and Crick acquired from Rosalind Franklin and Chargaff was ...
DNA,RNA & Protein synthesis game
... the debate regarding hereditary material over these two molecules ...
... the debate regarding hereditary material over these two molecules ...
Unit Study Guide
... The study guide is to help you stay on top of studying throughout each section of the unit. I will assign specified groups of questions for homework following corresponding lectures. These sections will not be checked the following day to ensure that you have done the assignment; however, all questi ...
... The study guide is to help you stay on top of studying throughout each section of the unit. I will assign specified groups of questions for homework following corresponding lectures. These sections will not be checked the following day to ensure that you have done the assignment; however, all questi ...
Ch9outline
... Tying Concepts Together: The base sequence of DNA determines the amino acid sequence of a protein The Genetic Message Expressed I: Protein Form 9.12: Proteins are polyamides 9.13: Polypeptides are short chains of amino acids 9.14: Protein shapes are determined by interactions *9.15: Your hair curls ...
... Tying Concepts Together: The base sequence of DNA determines the amino acid sequence of a protein The Genetic Message Expressed I: Protein Form 9.12: Proteins are polyamides 9.13: Polypeptides are short chains of amino acids 9.14: Protein shapes are determined by interactions *9.15: Your hair curls ...
Summary: Activity 3
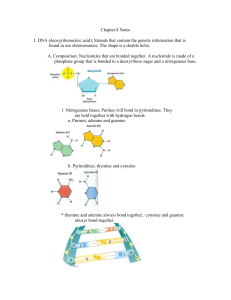
... __________ groups of the two strands. The rungs of the ladder are made of four bases. They are designed by the letters ___,___,___, and ____. The four combine in only two ways. A and ___ always go together, and G and ___ always go together. Each pair, A-T and G-C, represents a _________ of the genet ...
... __________ groups of the two strands. The rungs of the ladder are made of four bases. They are designed by the letters ___,___,___, and ____. The four combine in only two ways. A and ___ always go together, and G and ___ always go together. Each pair, A-T and G-C, represents a _________ of the genet ...
Messenger RNA
... So, now, we know the nucleus controls the cell's activities through the chemical DNA, but how? It is the sequence of bases that determine which protein is to be made. The sequence is like a code that we can now interpret. The sequence determines which proteins are made and the proteins determine whi ...
... So, now, we know the nucleus controls the cell's activities through the chemical DNA, but how? It is the sequence of bases that determine which protein is to be made. The sequence is like a code that we can now interpret. The sequence determines which proteins are made and the proteins determine whi ...
Inquiry into Life Twelfth Edition
... DSB End Resection • Resection occurs on both strands using prior nicks • Recombinases load asymmetrically onto the newly created singlestranded regions • One protein tags coated free 3’-end for invasion into homologous duplex • This leads to initiating Holliday complex formation ...
... DSB End Resection • Resection occurs on both strands using prior nicks • Recombinases load asymmetrically onto the newly created singlestranded regions • One protein tags coated free 3’-end for invasion into homologous duplex • This leads to initiating Holliday complex formation ...
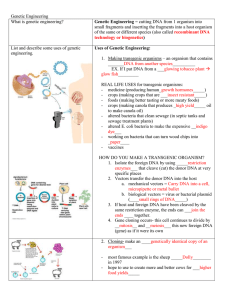
Genetic Engineering
... 1. Isolate the foreign DNA by using _____restriction enzymes___ that cleave (cut) the donor DNA at very specific places 2. Vectors transfer the donor DNA into the host a. mechanical vectors = Carry DNA into a cell, micropipette or metal bullet b. biological vectors = virus or bacterial plasmid (____ ...
... 1. Isolate the foreign DNA by using _____restriction enzymes___ that cleave (cut) the donor DNA at very specific places 2. Vectors transfer the donor DNA into the host a. mechanical vectors = Carry DNA into a cell, micropipette or metal bullet b. biological vectors = virus or bacterial plasmid (____ ...
Homologous recombination
... Retrotransposition mechanisms using DNA targets. The COXI gene of strain 1+t20 (top) contains both the donor aI1 intron (hatched) and the 5 848 ectopic site in intron 5 (open rectangle) The mechanism on the left begins with reverse splicing into the ectopic site in double-stranded DNA. Inefficient n ...
... Retrotransposition mechanisms using DNA targets. The COXI gene of strain 1+t20 (top) contains both the donor aI1 intron (hatched) and the 5 848 ectopic site in intron 5 (open rectangle) The mechanism on the left begins with reverse splicing into the ectopic site in double-stranded DNA. Inefficient n ...
Biotechnology Free Response Questions part II
... (b) Cells regulate both protein synthesis and protein activity. Discuss TWO specific mechanisms of protein regulation in eukaryotic cells. (c) The central dogma does not apply to some viruses. Select a specific virus or type of virus and explain how it deviates from the central dogma. ...
... (b) Cells regulate both protein synthesis and protein activity. Discuss TWO specific mechanisms of protein regulation in eukaryotic cells. (c) The central dogma does not apply to some viruses. Select a specific virus or type of virus and explain how it deviates from the central dogma. ...
Fast Facts about Human Genetics • DNA stands for Deoxy
... The nucleus, or control centre, of a cell, is where the DNA is coiled up into chromosomes. With the exception of reproductive cells, every cell has 46 chromosomes. Twenty-two pairs of the chromosomes are similar in terms of size, shape and genetic content. The twenty-third pair determines the sex of ...
... The nucleus, or control centre, of a cell, is where the DNA is coiled up into chromosomes. With the exception of reproductive cells, every cell has 46 chromosomes. Twenty-two pairs of the chromosomes are similar in terms of size, shape and genetic content. The twenty-third pair determines the sex of ...
F4-6 Gene Regulation and Mutation Ch12,13
... c. Regulatory gene – makes repressor proteins to prevent or allow transcription d. Genes coding for proteins B. Lac Operon (Example of gene regulation) 1. When E-coli bacteria is exposed to lactose (milk sugar) it makes enzymes to break down lactose for an energy source 2. Lac (tose) Operon – contai ...
... c. Regulatory gene – makes repressor proteins to prevent or allow transcription d. Genes coding for proteins B. Lac Operon (Example of gene regulation) 1. When E-coli bacteria is exposed to lactose (milk sugar) it makes enzymes to break down lactose for an energy source 2. Lac (tose) Operon – contai ...
Study_Guide
... and guanine (G). State that ribonucleic acid (RNA) is a polynucleotide, usually single-stranded, made up of nucleotides containing the bases adenine (A), uracil (U), cytosine (C) and guanine (G). Describe, with the aid of diagrams, how hydrogen bonding between complementary base pairs (A to T, G ...
... and guanine (G). State that ribonucleic acid (RNA) is a polynucleotide, usually single-stranded, made up of nucleotides containing the bases adenine (A), uracil (U), cytosine (C) and guanine (G). Describe, with the aid of diagrams, how hydrogen bonding between complementary base pairs (A to T, G ...
Ch.6.2Review - Cobb Learning
... temporary copy of a DNA sequence. 15. The “factory” that assembles proteins is known as a(n) ______________________. 16. A mirror-like copy of DNA called ______________________ moves from the nucleus to the ribosome. ...
... temporary copy of a DNA sequence. 15. The “factory” that assembles proteins is known as a(n) ______________________. 16. A mirror-like copy of DNA called ______________________ moves from the nucleus to the ribosome. ...
B5 5 a day - Science Revision
... You are provided with several plant shoots and a sample of auxin. Describe an experiment that you could carry out to show that auxin causes a shoot to bend. ...
... You are provided with several plant shoots and a sample of auxin. Describe an experiment that you could carry out to show that auxin causes a shoot to bend. ...
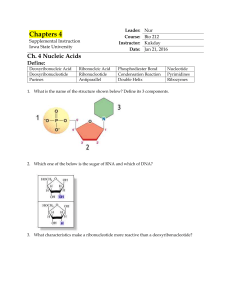
Ch. 4 Nucleic Acids Define
... 1. What is the name of the structure shown below? Define its 3 components. ...
... 1. What is the name of the structure shown below? Define its 3 components. ...
Transcription/Translation
... isolate genes and DNA sequence, study them directly and store it in a convenient manner that facilitates future applications • Cloning the DNA sequence accomplishes all of these ...
... isolate genes and DNA sequence, study them directly and store it in a convenient manner that facilitates future applications • Cloning the DNA sequence accomplishes all of these ...
Chapter 11 Notes
... 4. The amino acids on the t-RNA molecules join by peptide bonds, and the t-RNA molecule is released. 5. A chain of amino acids is formed until a stop codon is reached on the m-RNA strand. ...
... 4. The amino acids on the t-RNA molecules join by peptide bonds, and the t-RNA molecule is released. 5. A chain of amino acids is formed until a stop codon is reached on the m-RNA strand. ...
DNA Glossary - FutureLearn
... A homozygote has identical alleles for a specified gene A heterozygote has different alleles for a specified gene on each chromosome The human genome consists of the total DNA structure, consisting of over 3 billion base pairs Twenty-two of the 23 pairs of chromosomes look the same and carry the sam ...
... A homozygote has identical alleles for a specified gene A heterozygote has different alleles for a specified gene on each chromosome The human genome consists of the total DNA structure, consisting of over 3 billion base pairs Twenty-two of the 23 pairs of chromosomes look the same and carry the sam ...
Cre-Lox recombination

In the field of genetics, Cre-Lox recombination is known as a site-specific recombinase technology, and is widely used to carry out deletions, insertions, translocations and inversions at specific sites in the DNA of cells. It allows the DNA modification to be targeted to a specific cell type or be triggered by a specific external stimulus. It is implemented both in eukaryotic and prokaryotic systems.The system consists of a single enzyme, Cre recombinase, that recombines a pair of short target sequences called the Lox sequences. This system can be implemented without inserting any extra supporting proteins or sequences. The Cre enzyme and the original Lox site called the LoxP sequence are derived from bacteriophage P1.Placing Lox sequences appropriately allows genes to be activated, repressed, or exchanged for other genes. At a DNA level many types of manipulations can be carried out. The activity of the Cre enzyme can be controlled so that it is expressed in a particular cell type or triggered by an external stimulus like a chemical signal or a heat shock. These targeted DNA changes are useful in cell lineage tracing and when mutants are lethal if expressed globally.The Cre-Lox system is very similar in action and in usage to the FLP-FRT recombination system.