Metabolic engineering of bacteria
... • Shuttle vectors: hybrid plasmids with more than one type of replicon to increase host range • Recombination is an important tool for maintaining recombinant DNA and for manipulating the genome ...
... • Shuttle vectors: hybrid plasmids with more than one type of replicon to increase host range • Recombination is an important tool for maintaining recombinant DNA and for manipulating the genome ...
Electrophoresis literally means “the condition of
... tightly wound into 46 chromosomes. Each chromosome has many sections that are called genes. Each gene codes for a protein and the proteins that they code for determine an individual’s ...
... tightly wound into 46 chromosomes. Each chromosome has many sections that are called genes. Each gene codes for a protein and the proteins that they code for determine an individual’s ...
File - MRS. WILSON Science
... Every cell needs its own complete set of DNA, and the discovery of the threedimensional structure of DNA immediately suggested a mechanism by which the copying of DNA, or DNA replication, could occur. Because the DNA bases pair in only one way, both strands of DNA act as templates that direct the pr ...
... Every cell needs its own complete set of DNA, and the discovery of the threedimensional structure of DNA immediately suggested a mechanism by which the copying of DNA, or DNA replication, could occur. Because the DNA bases pair in only one way, both strands of DNA act as templates that direct the pr ...
What holds chromosomes together: Researchers
... Credit: Max Planck Society collaboration with colleagues from South Korea, have now elucidated the structure of a precursor of human SMC-kleisin complexes of the bacterium Bacillus subtilis. The researchers showed that the To ensure that the genetic material is equally and bacterial SMC-kleisin comp ...
... Credit: Max Planck Society collaboration with colleagues from South Korea, have now elucidated the structure of a precursor of human SMC-kleisin complexes of the bacterium Bacillus subtilis. The researchers showed that the To ensure that the genetic material is equally and bacterial SMC-kleisin comp ...
Title of Assignment:
... 3. A multicellular organism develops from a single zygote, and its phenotype depends on its genotype, which is established at fertilization. 4. Genes are a set of instructions encoded in the DNA sequence of each organism that specify the sequence of amino acids in proteins characteristic of that org ...
... 3. A multicellular organism develops from a single zygote, and its phenotype depends on its genotype, which is established at fertilization. 4. Genes are a set of instructions encoded in the DNA sequence of each organism that specify the sequence of amino acids in proteins characteristic of that org ...
No Slide Title
... Nutritional value can be enhanced, for example, by introduction of genes that increase seed protein content. ...
... Nutritional value can be enhanced, for example, by introduction of genes that increase seed protein content. ...
1. A nucleotide is a ______. 2. DNA consists of two antiparallel
... following choices pairs with adenine in RNA? If the DNA sequence is ATCGCTCC, the corresponding bases in mRNA are Vertebrate cells apparently possess a protein that by binding to clusters of 5-methylcytosine ensures that the bound gene will stay in the "off' position. This control on the role of ge ...
... following choices pairs with adenine in RNA? If the DNA sequence is ATCGCTCC, the corresponding bases in mRNA are Vertebrate cells apparently possess a protein that by binding to clusters of 5-methylcytosine ensures that the bound gene will stay in the "off' position. This control on the role of ge ...
MBLG2x71 Course Information for mmb web site
... central focus is on the control of replication, transcription and translation and how these processes can be studied and manipulated in the laboratory. Experiments in model organisms are provided to illustrate how the field has advanced, together with discussion of work carried out in human systems ...
... central focus is on the control of replication, transcription and translation and how these processes can be studied and manipulated in the laboratory. Experiments in model organisms are provided to illustrate how the field has advanced, together with discussion of work carried out in human systems ...
Know your molecules organizer
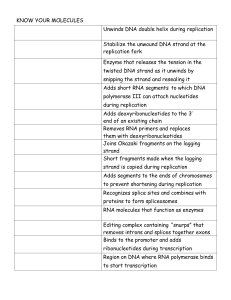
... Unwinds DNA double helix during replication Stabilize the unwound DNA strand at the replication fork Enzyme that releases the tension in the twisted DNA strand as it unwinds by snipping the strand and resealing it Adds short RNA segments to which DNA polymerase III can attach nucleotides during repl ...
... Unwinds DNA double helix during replication Stabilize the unwound DNA strand at the replication fork Enzyme that releases the tension in the twisted DNA strand as it unwinds by snipping the strand and resealing it Adds short RNA segments to which DNA polymerase III can attach nucleotides during repl ...
10 DNA Vocabulary - Petal School District
... 3. nucleotide—the monomer for nucleic acids; made of a phosphate, sugar, and nitrogen base 4. hydrogen bonds—hold nitrogen base pairs together 5. genetic code—the sequence of the nitrogen bases (nucleotides) on DNA 6. DNA replication—process that copies the DNA 7. template strands—the original stran ...
... 3. nucleotide—the monomer for nucleic acids; made of a phosphate, sugar, and nitrogen base 4. hydrogen bonds—hold nitrogen base pairs together 5. genetic code—the sequence of the nitrogen bases (nucleotides) on DNA 6. DNA replication—process that copies the DNA 7. template strands—the original stran ...
DNA, RNA, PROTEINS STARTS WITH
... _C_ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ . 2. The group of 3 nitrogen bases in the mRNA message that is read together is called a _C_ __ __ __ __. 3. In dividing cells, the DNA is scrunched into _C_ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ so it can be moved. 4. The mRNA message tells the ribosomes which _A_ __ __ __ __ _A ...
... _C_ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ . 2. The group of 3 nitrogen bases in the mRNA message that is read together is called a _C_ __ __ __ __. 3. In dividing cells, the DNA is scrunched into _C_ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ so it can be moved. 4. The mRNA message tells the ribosomes which _A_ __ __ __ __ _A ...
DNA - eduBuzz.org
... called DNA. DNA All the genetic information of an organism is contained within it’s DNA DNA is a code that determines the sequence of amino acids in a protein DNA stands for DeoxyriboNucleic Acid DNA consists of two strands which are arranged in a twisted coil structure known as a double helix. Each ...
... called DNA. DNA All the genetic information of an organism is contained within it’s DNA DNA is a code that determines the sequence of amino acids in a protein DNA stands for DeoxyriboNucleic Acid DNA consists of two strands which are arranged in a twisted coil structure known as a double helix. Each ...
Molecular Genetics Review - Biology 12U Chapter 7: Nucleic Acids
... transfer of genetic information genetic code- continuity, redundancy, universality From DNA to RNA – transcription initiation, elongation, termination terms- messenger RNA, sense strand, anti-sense strand, promoter sequence,RNA polymerase, precursor RNA, 5'cap, poly-A tail, spliceosome, smal ...
... transfer of genetic information genetic code- continuity, redundancy, universality From DNA to RNA – transcription initiation, elongation, termination terms- messenger RNA, sense strand, anti-sense strand, promoter sequence,RNA polymerase, precursor RNA, 5'cap, poly-A tail, spliceosome, smal ...
This is to serve as a general overview of important topics. I highly
... Where does DNA replication occur? DNA is copied via a ____________________________ model. Other proposed models include conservative and dispersive models. The two complementary strands are held together ______________________ bonds. Within the DNA there bonds are __________________ ...
... Where does DNA replication occur? DNA is copied via a ____________________________ model. Other proposed models include conservative and dispersive models. The two complementary strands are held together ______________________ bonds. Within the DNA there bonds are __________________ ...
Frontiers of Genetics
... • Restriction enzymes are proteins that cut genes at specific DNA sequences. • Over 75 different kinds of restriction enzymes are known; each one “recognizes” and cut DNA at a particular sequence • Restriction enzymes allow DNA to be cut into fragments that can be isolated, separated, and analyzed. ...
... • Restriction enzymes are proteins that cut genes at specific DNA sequences. • Over 75 different kinds of restriction enzymes are known; each one “recognizes” and cut DNA at a particular sequence • Restriction enzymes allow DNA to be cut into fragments that can be isolated, separated, and analyzed. ...
Assessment Builder - Printer Friendly Version Name: Date: 1 The
... This technique used to analyze DNA directly results in (1) synthesizing large fragments of DNA (2) separating DNA fragments on the basis of size (3) producing genetically engineered DNA molecules (4) removing the larger DNA fragments from the samples ...
... This technique used to analyze DNA directly results in (1) synthesizing large fragments of DNA (2) separating DNA fragments on the basis of size (3) producing genetically engineered DNA molecules (4) removing the larger DNA fragments from the samples ...
DNA People - Biology Junction
... Grow E. coli bacteria with radioactive 15N (its heavier than 14N) so bacteria incorporate heavy N into their DNA Then grow in media with only 14N Centrifuge DNA at different times to separate by size. (The more 15N it has the heavier it is) Pattern shows which model is correct ...
... Grow E. coli bacteria with radioactive 15N (its heavier than 14N) so bacteria incorporate heavy N into their DNA Then grow in media with only 14N Centrifuge DNA at different times to separate by size. (The more 15N it has the heavier it is) Pattern shows which model is correct ...
Cre-Lox recombination

In the field of genetics, Cre-Lox recombination is known as a site-specific recombinase technology, and is widely used to carry out deletions, insertions, translocations and inversions at specific sites in the DNA of cells. It allows the DNA modification to be targeted to a specific cell type or be triggered by a specific external stimulus. It is implemented both in eukaryotic and prokaryotic systems.The system consists of a single enzyme, Cre recombinase, that recombines a pair of short target sequences called the Lox sequences. This system can be implemented without inserting any extra supporting proteins or sequences. The Cre enzyme and the original Lox site called the LoxP sequence are derived from bacteriophage P1.Placing Lox sequences appropriately allows genes to be activated, repressed, or exchanged for other genes. At a DNA level many types of manipulations can be carried out. The activity of the Cre enzyme can be controlled so that it is expressed in a particular cell type or triggered by an external stimulus like a chemical signal or a heat shock. These targeted DNA changes are useful in cell lineage tracing and when mutants are lethal if expressed globally.The Cre-Lox system is very similar in action and in usage to the FLP-FRT recombination system.